Do you know the difference between a megabit (Mb) and a megabyte (MB)? And two they sound almost the same, are spelled almost the same, but are completely different.

Both terms are very important as they define the speed of data such as internet connection (which you pay to companies) but also the size of data on storage devices such as hard drives discs.
Below we will explain everything you need to know about megabit (MB) and megabytes (MB).
What is Megabit and what is Megabyte?
First we have to look at where everything starts, and we mean the bit. The bit is a bit, a very small unit of digital, electronic data. Eight of these bits make us a byte. A megabit (Mb) contains about 1 million of these bits, and eight (8) megabits are a single megabyte.
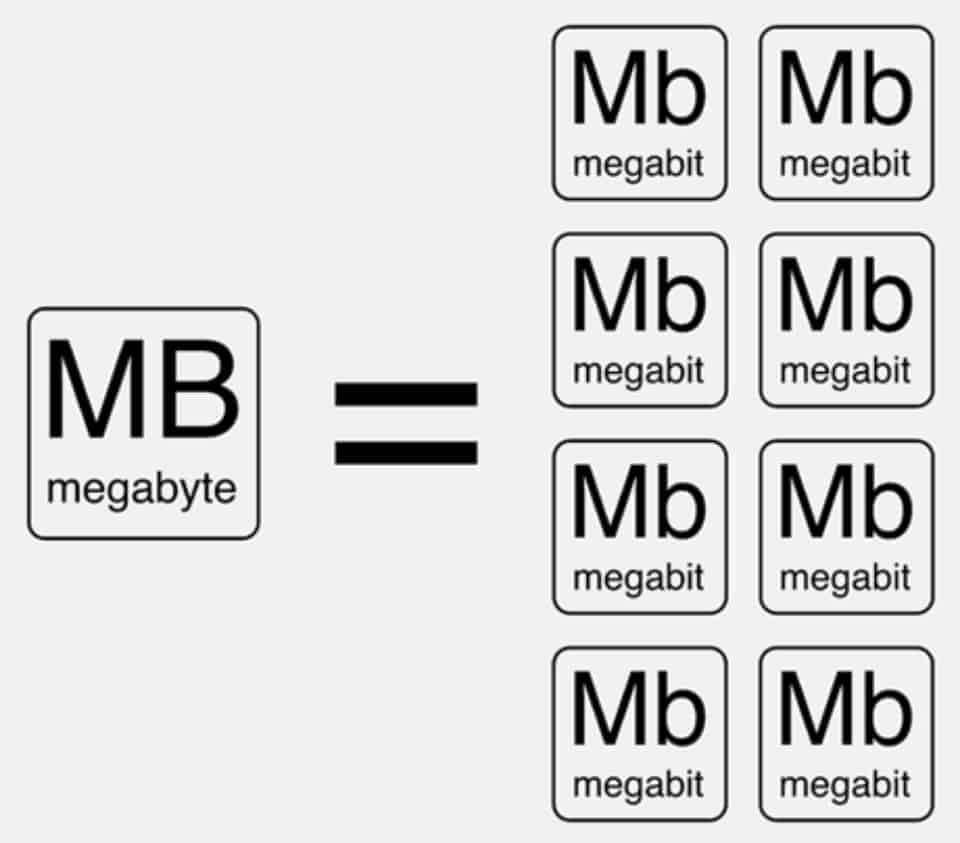
In general, the data sizes for the hard diskand files are usually measured in bytes, while bits are used to measure data in internet connections.
The gigabytes (GB) or even terabytes (TB), are more commonly used when talking about data storage. A gigabyte contains about 1000 megabytes and a terabyte is 1000 gigabytes.
What is the difference between Mb and MB?
Shortcuts are very important and you should take care of them. The megabit, which is a smaller unit than the megabyte, is written in lowercase "b", meaning "Mb". The larger unit Megabyte is written in capital "B" in "MB".
Both megabits and megabytes are commonly used to indicate speed transportof data, on hard drives or internet connections. If you are referring to internet connections only, then the abbreviations become “Mbps” and “MBps.” "ps" comes from per second, or per second.
Why you need to know about Megabit and Megabytes
We all need internet access now. So often we hear about packages offering speeds of "up to 50Mbps" or "24Mbps" and so on. So it's important to know exactly what you're paying for.
You might think that a package of 50Mbps sounds like super fast. You are not wrong, but do not expect to download files with 50MB per second.
This is because when ISPs sell a "up to 50Mbps" connection, they actually report 50 megabits per second rather than 100 megabytes per second.
An example (rounded). If you have a 100Mbps connection, this is actually 12,5MBps, which does not sound and so impressive (to those who do not know). 12,5 comes out dividing 100 with 8, since eight bits are a megabit.
So an 400Mbps connection translates to 50MBps. Again, the first number is much more impressive than the second one.
Marketing
Internet service providers use megabits as a very good marketing tactic. They can make their packages much more attractive to potential customers. Another trap is the "to", as they say you can catch these speeds, but not at rush hour.
The service SpeedTest provides you with a good test environment and displays results in Mbps. However, you can change the service setting to produce MBps results instead of Mbps.
Hard drives
If you want to buy a new hard drive for your computer, or an external hard drive, you should watch the skill. Disc sizes, usually capacity in gigabytes.
When you buy discs, you will find sizes in 256GB, 500GB, 750GB, 1TB, and so on. These numbers are translated into 256000MB, 500000MB and 750000MB, respectively.
1TB is 1000GB, so it's about 1000000MB. The formula to find out how many megabytes are contained is to multiply the gigabytes on 1000.
To convert to megabits or vice versa use your girlfriend Google.
_______________________
- FlightGear 2018.3.1 free flight simulator
- Take your photos with GoPro's Quik
- Hashcat 5.0.0: The Fastest Cracker Password
- iGuRu.gr 20's top 2018 publications






To understand better, until now I knew that 1 kilobyte = 1024 bytes because of the 2 ^ 10 relationship, so the values change for MB, GB, TB, etc.
Has something changed officially and now 1 kilobyte = 1000 byte?
Thanks in advance.
has not changed, we are talking about the difference between megabit and megabyte, or kilobit bytes