Two Greek researchers managed to identify a security gap in the webσελίδα of the NSA – (National Security Agency), which allowed them to use the SQL injection technique and gain access to the agency's database.
Researchers Dimitris Hatzidimitris and Anastasis Vassiliadis on 20/03/2020 identified a vulnerability in the security of the website: https://www.nsa.gov
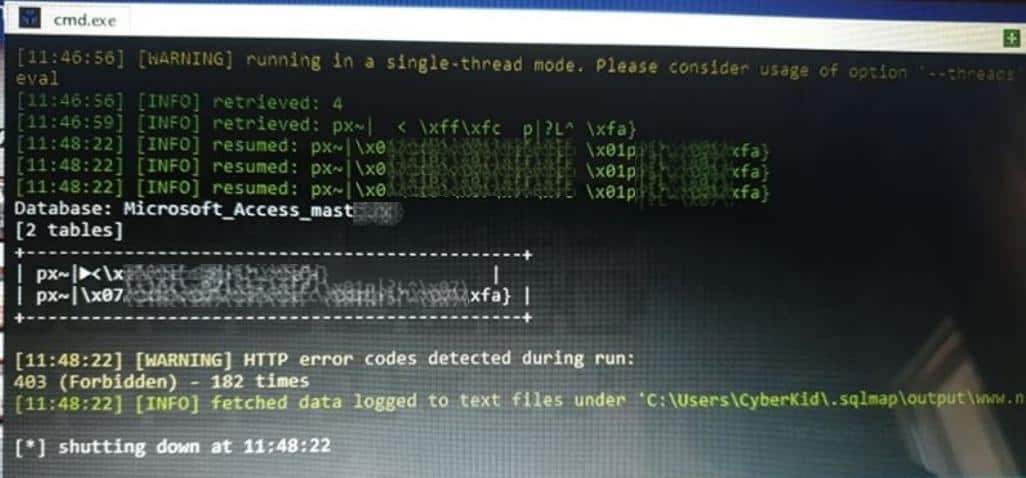
The vulnerability is of the SQL Injection type and the link for the specific weakness remains at the disposal of our editor teams.
Some of the elements of vulnerability:
Parameter: ver
Method: (GET)
Type: boolean-based blind
Title: AND boolean-based blind - WHERE or HAVING clause
Database: Microsoft_Access_mast ****
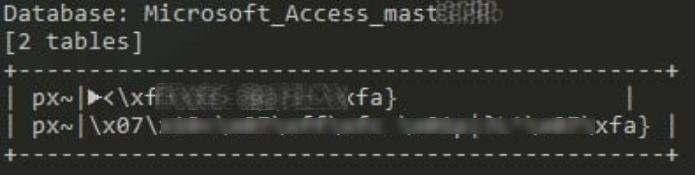
Which contains 2 tables encoded!
Researchers Dimitris Hatzidimitris and Anastasis Vassiliadis report:
After that we did not proceed to a possible access to the server beyond the base since we had already confirmed the weakness in better safety of the page.
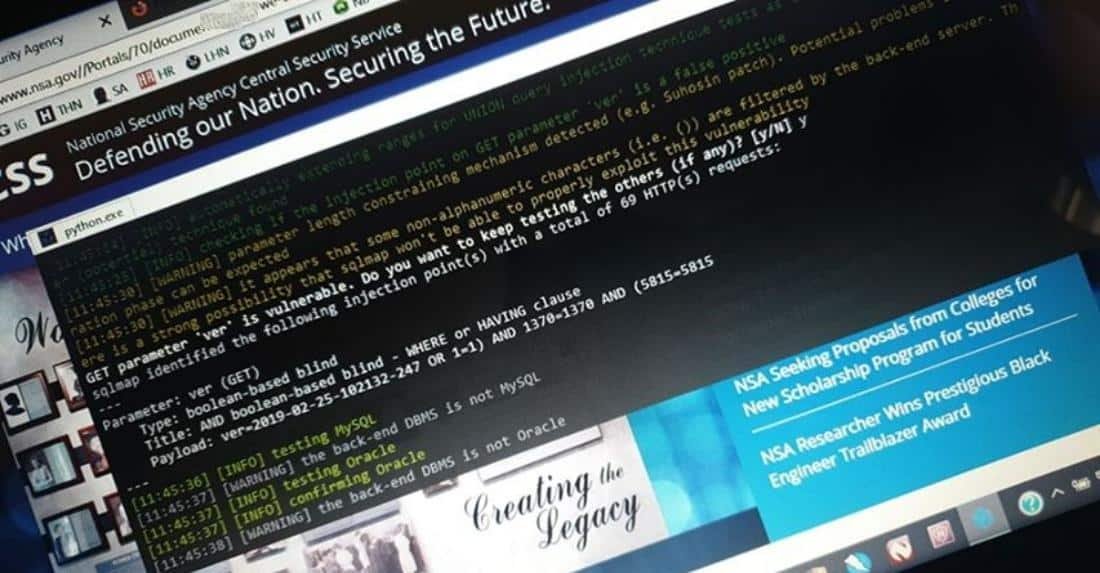
The NSA was notified in time for the security breach on 20/03/2020 and to date has not made any repairs preventing a possible leak of personal data from malicious third parties.
The information remains at the disposal of those directly interested, by the researchers themselves but also by our editorial team.
Reporting on vulnerabilities discovered in organizations is considered highly necessary (especially when they exist in websites high traffic), and for us they are an immediate priority.
We hope that in this way, i.e. the immediate exposure of each vulnerability, we contribute to a more secure one Internet.





