A new ransomware attack tactic has begun to be used by hackers to blackmail their victims: They do attacks DDoS on by clicking here of the victim, until they pay the liters to decrypt their files.

A DDoS attack is when a malicious user sends a large packet data on a website or when sending a large volume of requests. Its purpose is to make a service unavailable due to workload.
It all started with a ransomware site from SunCrypt. After the negotiations were delayed, the website was attacked by DDoS.
When the victim returned to negotiations with the blackmailers, he received a message stating that SunCrypt was responsible for DDoS and would continue the attack if negotiations did not continue.
"Your site is currently down because of us. "Send us a message as soon as possible or further action will be taken," the SunCrypt ransomware operator warned.
When the victim asked why their site was down, ransomware operators said they were doing so in order to force them to negotiate.
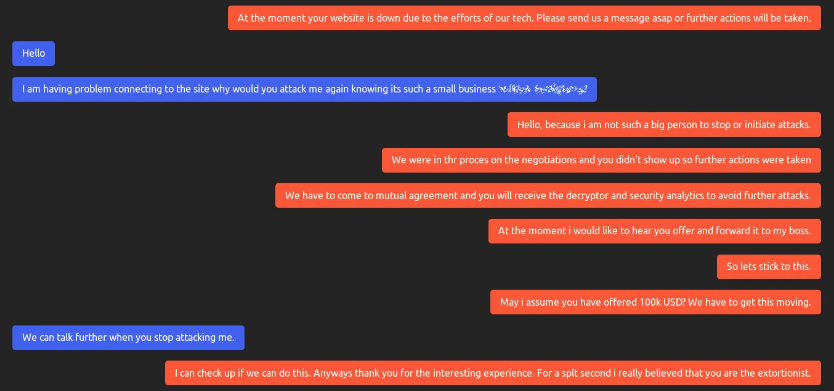
So after the victim resumed ransom negotiations, the ransomware maker agreed to stop the DDoS attacks.

Η MalwareHunterTeam said that this tactic eventually led the victim to pay the ransom.
This tactic was very effective. Combining data theft, lack of access to encrypted files and now a DDoS attack, a small business turnover victim could close his business altogether.
This is another example of ransomware groups upgrading their tactics to increase pressure on their victims to feel that there is no choice but to pay a ransom.





