Can't break the front door? Then try Supply Chain Hack. See how these attacks work, with the recent example of SolarWind.

| Characteristics of a supply chain attack |
When you think of a cyber attack, it comes to mind picture ενός hacker που διερευνά ένα δίκτυο για ευπάθειες. Ή μια επίθεση ηλεκτρονικού ψαρέματος που κλέβει τα διαπιστευτήρια σύνδεσης ενός υπαλλήλου ή ένα malicious software installed on a computer.
These are all common methods of attack. But what if there was another way of penetrating a network that did not involve direct attack on the target?

An attack on the supply chain (Supply Chain Hack) does just that. It exploits target-related organizations and attacks the target supply chain. So what are supply chain attacks and how do they work?
| What is Suply Chain Hack? |
A supply chain attack seeks to harm or infiltrate an organization, identifying vulnerable parts of it. its supply network.
Here we open a parenthesis to explain what a supply chain is.
In commerce, a supply chain is a system of organizations, individuals, activities, information and resources involved in providing a product or service to a consumer. The activities of the supply chain include the conversion of natural resources, raw materials and components into a final product that is delivered to the final customer.
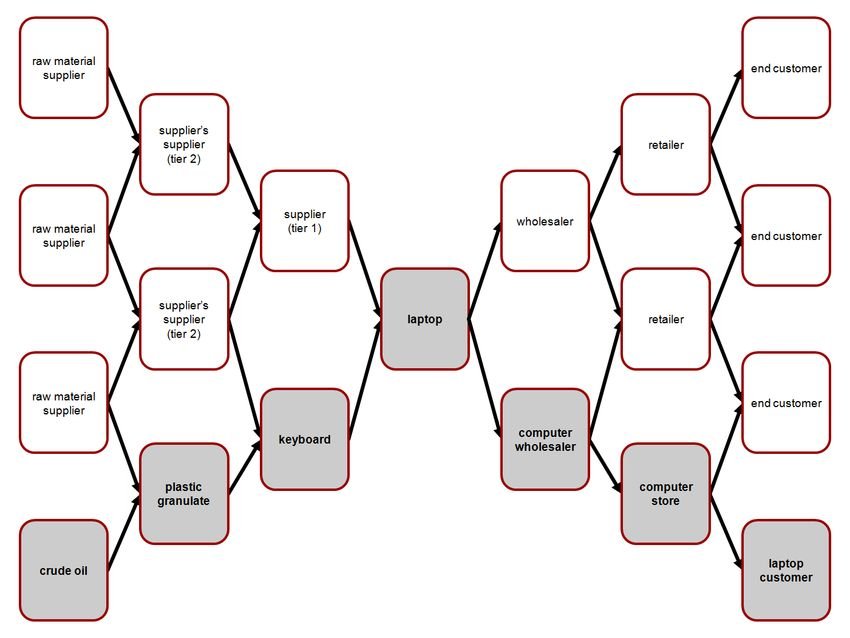
For example, to buy a laptop from the end consumer, the sales shop, the importer, the transport company, the manufacturer, the chip manufacturer, the power supply manufacturer (and in general all the manufacturers of the individual components) have mediated in order. ), the plastics industry, the silicon mining industry, etc.
A typical supply chain begins with the ecological, biological and political regulation of natural resources, followed by the extraction of raw materials by humans, and includes various production links (eg component manufacturing, assembly and merging) before proceeding to different levels of facilities. constantly shrinking in increasingly remote geographical locations, and eventually reaching the consumer.
Closes the parenthesis.
Attacking a supply chain presents many opportunities for successful penetration, even more so when attacking an organization with a complex supply chain network.
In almost all supply chain attacks, the original victim is not the sole target of the intruder. Instead, the supply chain element is a stepping stone to a larger fish. The attacker exploits the vulnerabilities to the easiest target and utilizes that he can move towards the final target.
Although supply chain attacks sound rare, a study of June 2020 by Opinion Matters for BlueVoyant [PDF, registration required] found that 80% of organizations “suffered in the last 12 months, one infringement related to third parties ”. In addition, 77% of respondents have "limited visibility around their third party suppliers".
With elements like this, you can see why supply chain attacks are not only popular, but also how they manage to move from the original target to the main organization.
Trying to figure out what's trustworthy after a supply chain attack pic.twitter.com/QSXPxOHLjm
- SwiftOnSecurity (@SwiftOnSecurity) December 17, 2020
It is extremely difficult for a company to detect an attack software supply chain by third parties. The very nature of the attack means that malicious files are hidden not only from the main target but also from the vulnerable link in the supply chain. The computer does not even need to be connected to the internet for the attack to work !!.

The target organization may realize that there is a problem only when their data starts to be sold elsewhere or something similar triggers an alarm. With such in-depth access to the internal network, it is possible to move freely within the organization, even by erasing the indicative signs of an intruder.
| Supply chain attack types |
Supply chain attacks are not one size fits all. The supply chain for a large organization can include many different parts. An attacker needs to think about what type of supply chain attack to use against a target.
Here are three notable supply chain attacks to consider as an example of an attack.
1 Target
In 2013, the American retail company Target was the object of a major attack that resulted in the loss of information about 110 million credit and debit cards used in their stores. The total amount of stolen data was only 11 GB, but the type of stolen data was very valuable.

The attackers identified Target's corporate network as the company's third-party suppliers. While the final number of exploitation efforts is unknown, the vulnerable company was ultimately Fazio Mechanical, a refrigeration contractor.
Once the contractor was in danger, the attackers waited inside his company network until escalation was possible, as Target would use the stolen credentials. Eventually, the attackers gained access to Target's servers, looking for other vulnerable systems within the company's network.
From here, attackers exploited Target's point-of-sale (POS) system, bypassing card information for millions of customers.
2. SolarWinds
A prime example of a third-party software supply chain attack is SolarWinds, whose Orion remote management software compromised in 2020. Intruders introduced a malicious door into the Orion software update process.

When the update was passed on to hundreds of thousands of SolarWinds customers, the intruder malware went with it. As the update was digitally signed as normal, everything appeared as usual.
The SolarWinds attack is one of the largest and most successful supply chain attacks ever carried out. He managed to overthrow almost the entire American system of government, with several critical services in the hands of criminals.
The case is not closed yet, and the penetration is so great that the US government accuses Russia of espionage.
3. Stuxnet
Did you know that one of the most notorious hacks of all time was a supply chain attack?
Stuxnet is a worm with a very specific purpose: systems running a specific type of software, from a specific manufacturer, located in nuclear power plants in Iran. The Stuxnet malware causes the centrifuge speed to increase dramatically, destroying the hardware in the centrifuge and the infrastructure itself in the process.

Stuxnet entered Iran's nuclear power plant supply chain using an infected module flash USB. Once installed on a computer, Stuxnet moved laterally through the network, searching for the correct control system before executing.
Because Stuxnet has a precise goal, it does not draw attention to it as it only activates when it hits a computer that meets the specifications. And in this case the hackers seem to have been government agencies of various countries.
| How to stay safe in the supply chain |
Many companies use third-party software solutions to management aspects of their business. These include remote management tools or accounting software or even platforms like Microsoft Office 365.
Companies just can't bring every aspect of their business under one roof. Nor should they. The trust of a software developer or cloud service provider should not drastically increase the chances of you or your business being attacked.
Increased security for businesses and consumers also leads hackers to solve supply chain attacks. If attackers can't find a way to get into your organization, attacking the next level is the most economical and realistic way to gain access.
In many cases, supply chain attacks are widespread, well-researched and well-funded by companies and states.
SolarWinds, for example, is the work of a nation-state hacking team that worked for months to deliver malware to the supply chain. Similarly, Stuxnet combined several 0-day attacks into a single package to strike Iran's nuclear power plants. And the Target supply chain hack took time to get started.
All of them are not accidental amateurs of malicious scenarios, who just stumbled upon a vulnerability. They are groups of hackers who work together to attack a specific target. The supply chain happens to be the path of least resistance.





