In general, we can say that the solution to many injection web attacks applications done with “Login Validation”. Input validation is the checking of any input (or data) provided by a user or application against expected criteria. Input validation prevents malicious or poorly qualified data from entering an information system. Applications should check and validate all inputs entered into a system to prevent attacks and mistakes. Input validation is also important when receiving data from external parties or sources. Incorrect input validation can allow attacks injection, memory leakage and put more systems at risk.
Some apps allow and encourage us to upload a photo, video, or avatar of ourselves (think Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, other social media, or your business or school website). What prevents attackers from simply uploading a malicious script; Usually the answer is to check and validate the input type before allowing the file to be uploaded.
Step #1: Open Kali and run Burp Suite

To get started, open Kali Linux and run BurpSuite.

Enable BurpSuite to proxy the request and responses from your browser
Step #2: Launch OWASP BWA
Now, start the OWASP Broken Web App (BWA) server and go to the DVWA application and login (admin/Password).
After logging into DVWA, go to the bottom left button and set DVWA security to “medium”. Make sure you enable it intercept on BurpSuite proxy.
Step #3: Try to upload a malicious file
Now, do it click on the upload button. Imagine it's your LinkedIn page or your Twitter profile. In both cases, you are expected to upload a photo or video.
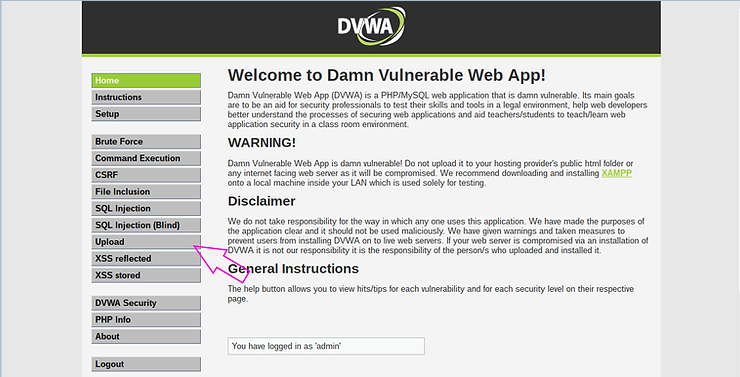
Note in the screenshot below, the app says “Choose an image to upload:".
Now, instead of uploading an image, we try to upload a malicious Python script.
I created a file and named it “malicious_python_script.py” and tried to upload it. You can create any text file, malicious or not, and attempt to upload it.
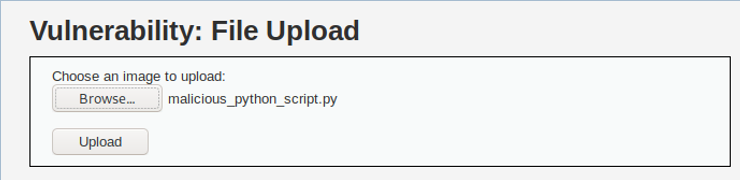
As you can see below, the application rejected our malicious script because it uses input validation to make sure the upload file is an image file.
Can we bypass this input validation?
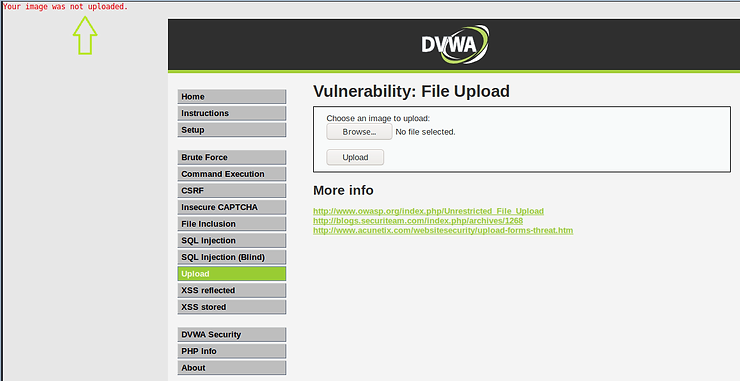
Step #4: Bypass input validation with BurpSuite
Let's go to BurpSuite and see the POST captured by the intercept. As you can see on lines 19 and 20, it recognized the file name and specified the file type as “text/x-python”. This is right. The app was designed to only allow image uploads, so it rejected our malicious file.
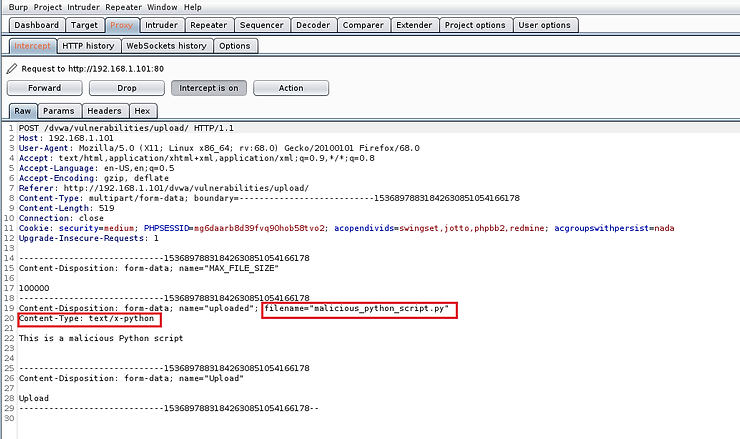
Now, let's get into intercepted POST and let's edit it slightly. Input validation was done inside the form on the client side. Now that we've intercepted it on its way to the server, we can edit the code to reflect that it's a "safe" file before sending it to the server. We can do this by changing the Content-Type on line #20 to “image/jpeg”. This way the server will accept this file, thinking that the file is a safe jpeg file.
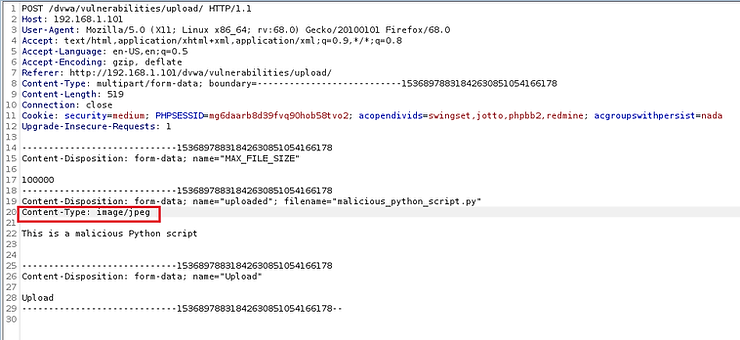
Now, in BurpSuite, forward the POST to the server.
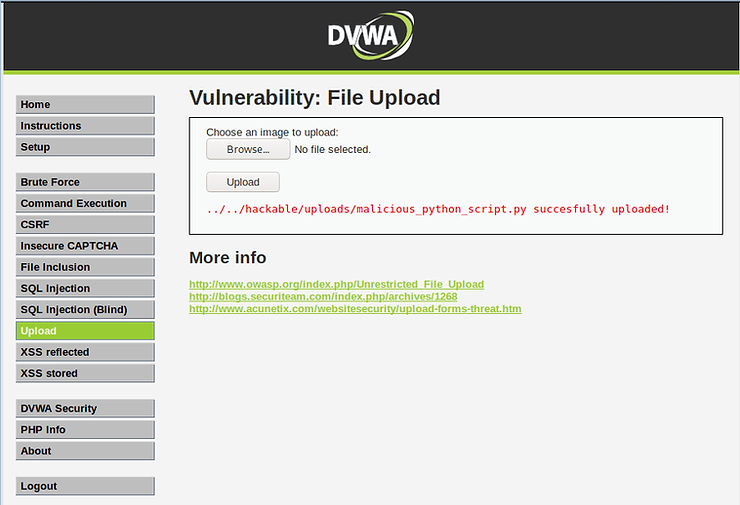
The file has been successfully uploaded and our Python script is ready to run and do its dirty work!
Epilogue
In general, input validation is the answer to the problem of input attacks in web applications. In this case, the web application only validated input on the client side, and therefore the attacker can modify the POST response to BurpSuite to edit the file type and make the server accept its malicious content!





