Do you suspect that your Gmail account has been compromised? Is there any strange behavior? See how you can protect your Gmail account with 6 simple steps.

Gmail is the most popular free email service used by millions of people around the world. Billions of messages are sent and received through Google's email software every day. Many of these messages contain personal or confidential information information.
Unfortunately, Gmail accounts have also become a target for hackers, as the attacks phishing and password leaks are becoming more common. To prevent your personal email from ending up in someone else's hands, you'd do well to protect your Gmail account.
Let's take a look at how to protect your Gmail account in just six easy steps.
Step 1: Open your Google Account Settings
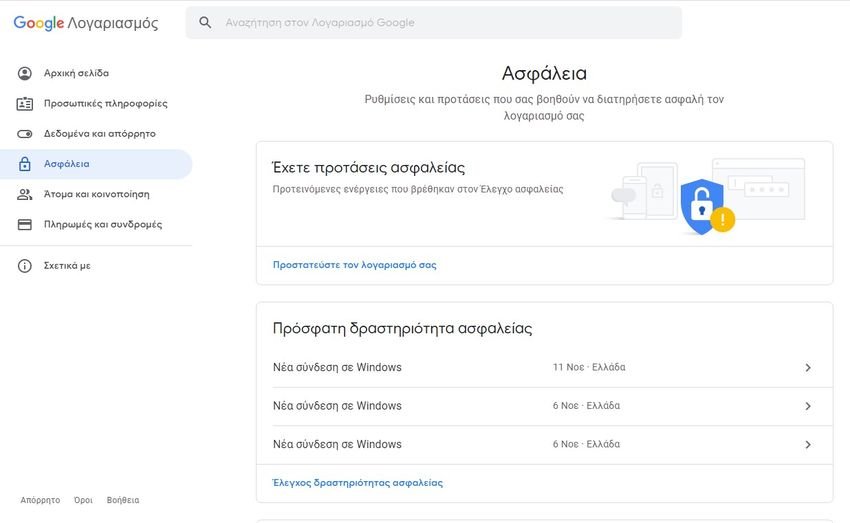
Go to Gmail and click on your profile picture at the top right of the page, which will open the Google menu. From there, select “Google Account Management“. When you signed up for Gmail, Google also created a single account to access all of its services. This is known as your Google Account.
Each service has its own settings and options, as well as critical information such as your password, two-factor authentication and other personal information managed through your Google Account. In the left menu, select “Safety".
Step 2: Resolve security issues
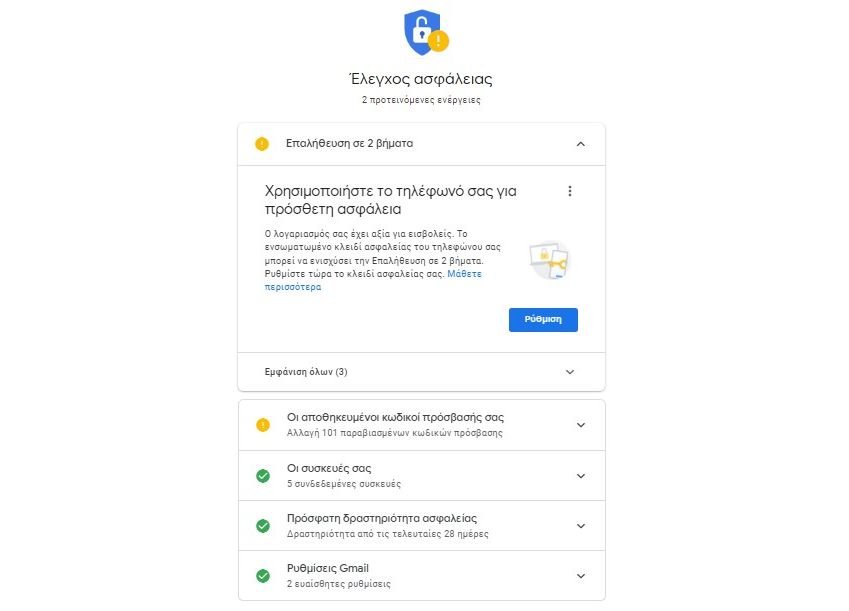
As part of an effort to better safety of your account, Google offers security recommendations. If there are outstanding issues, they will be listed at the top of your account's “Security” page. Even if there are no suggestions, click “Protect your account”At the bottom of the section“ Do you have safety suggestions ”.
This will give you an overview of the security status of your Google Account. The site uses a warning system to alert you to areas that need attention. If all six sections are green, then you can move to other areas. Otherwise, follow the instructions in each section to improve your Gmail security.
Step 3: Update your password and two-factor authentication
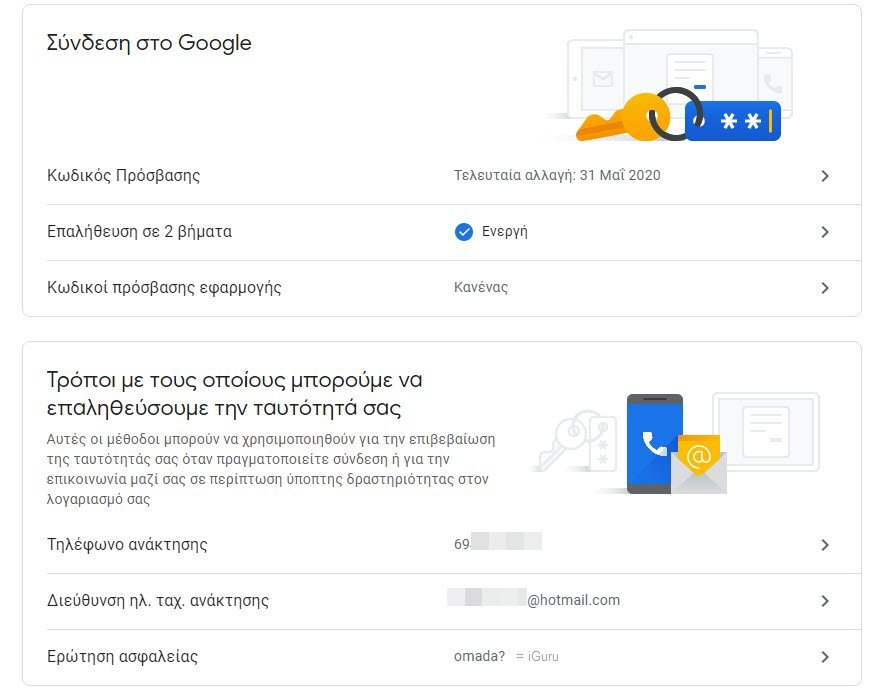
Back to the Security page of your Google Account, there is an overview titled “Sign in to Google“. Here you can see when your password was last changed and if you have enabled two-factor authentication. It is a good practice to change your password to a stronger one, especially if you use the same password on multiple services.
Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds a step to the login process. After entering your username and password, you will be prompted to enter a temporary password. This is used to ensure that you are connected and not someone with your credentials. It is definitely worth securing all your accounts with 2FA.
Google offers a few options for this service. a application ελέγχου ταυτότητας (όπως Google Authenticator ή Authy) ή έναν κωδικό SMS. Εάν χρησιμοποιείτε device Android, you may also be able to set up an authentication notification on your phone.
Step 4: Evaluate recent security activity
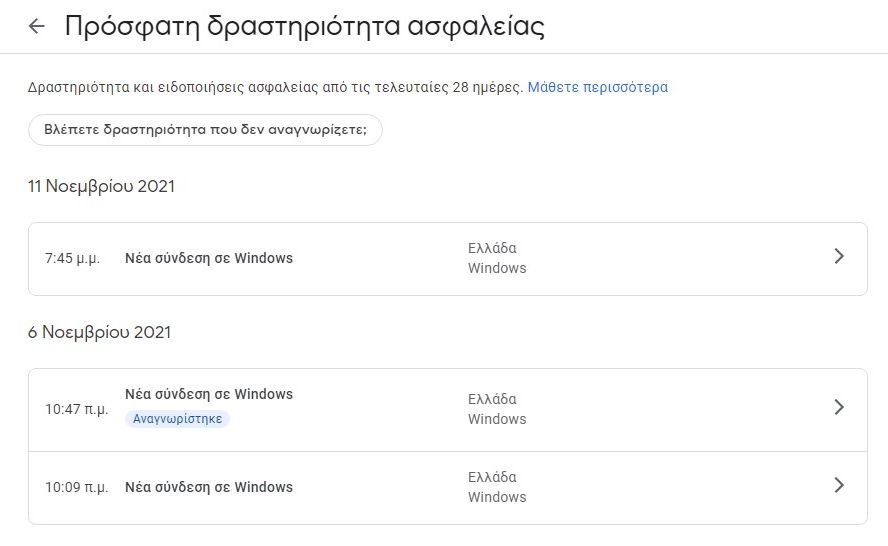
After you complete the Google security check, make sure you use a secure password, and enable two-factor authentication, you can check for previous security events in your account. On the main security settings page, scroll to “Recent security activity".
This area displays any login or access events in the last 28 days. Each item shows the device or application and the date of the event. If you open a single event, there are more details such as IP address, estimated location, and browser.
Although this is a read-only section, so you can not edit or change settings here, it should notify you if any suspicious activity has occurred on your account. Google even has a message on this page noting that if you see anything that looks suspicious, you should follow its instructions to protect your account.
Step 5. Check your devices
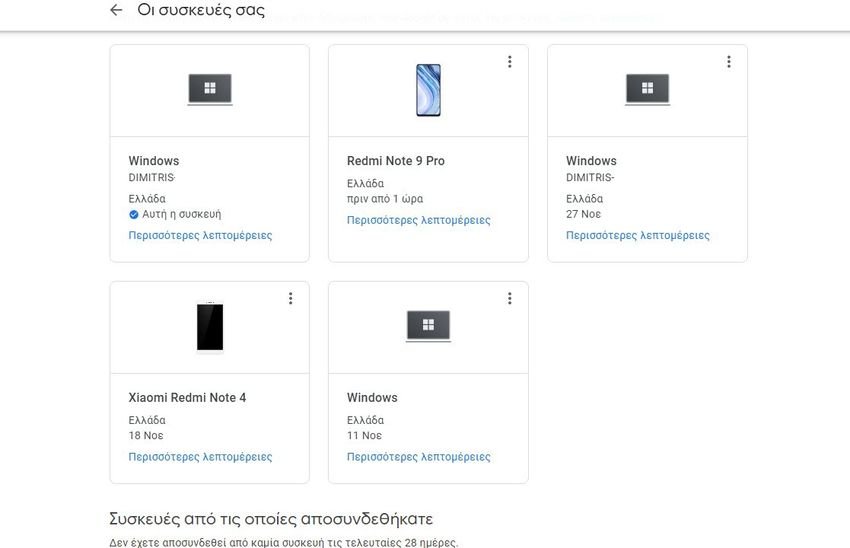
If you have checked your recent security activity and found nothing suspicious, you can check devices that have access to your Google Account. Under the heading "Your devices“, Select Device Manager. This opens a list of each device that is connected to your Gmail account.
You can choose to disconnect from unused or older devices. These will then appear in a separate collection marked “Devices from which you disconnected“. Locating devices can be a bit tricky, especially if the activity came from a Windows computer, for example, the log would only show the device name as Windows.
If you are not sure about a device, disconnect it !. The worst part is that you will need to reconnect to this device.
6. Management of third-party applications
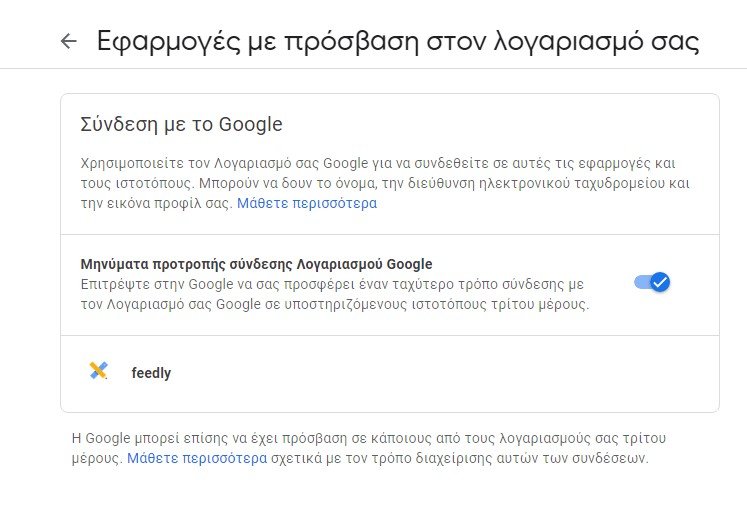
After disconnecting from devices you do not recognize, you should check them Third-party applications with access to your account, from the Security Settings> Sign in with Google page. This list details each application that you have accessed to your Google or Gmail account. As with other areas of your account, the list is an overview and you can select each item to expand the details.
You may recognize the application, but that does not necessarily mean that you should leave it untouched. The object view allows you to see the data that the application has access to. This is an important step, especially as in 2018, Google admitted that Third-party applications can read your Gmail messages.
If this is an email application, it will likely have access to your Gmail account and be able to send emails on your behalf. However, you may not have explicitly authorized access to all of your Google Drive content, for example.
Similarly, if you no longer use one of the list applications, you will need to remove it from your account. If you do not recognize an item in the list and do not believe that you have ever accessed your account, there is an option to bookmark it to Google by selecting the Report link for this application.
How to protect your Gmail account
While it is important to enable these features, you should also consider threats from which Google cannot protect you. If you use the same password everywhere or if the password is common 123456, you may endanger all your online accounts. Hackers are known to use leaked account information to carry out credential attacks.
In these attacks, a stolen email address and password are entered into multiple websites in order to gain access to your data.
To avoid the risk of this attack, be sure to use a password manager to create and save a unique link for each account.





