Today, Bluetooth is embedded in almost all our devices and gadgets. These include our computers, smartphones, iPods, tablets, speakers, game controllers, keyboards and many other devices.
In this series of guides, we will focus on hacking mobile devices, tablets and phones, as they are the most fertile ground for hackers. The ability to compromise Bluetooth can lead to the compromise of any information on the device (images, email, text, etc.), the control of the device, and the ability to send unwanted information to the device.

However, before we start hacking Bluetooth enabled devices, we need to understand the technology, terms and security built into Bluetooth if we want to hack it successfully. In a short article like this, I can't convey an in-depth understanding of Bluetooth, but I think I can give you a basic knowledge that you can use in future hacks.
Basically Bluetooth components: The Bluetooth is a universal protocol for low-power, near-field communication that operates at 2,4 – 2,485 GHz using a wide spectrum but also a frequency of 1.600 hops per second (this frequency transition is a security measure).
Developed in 1994 by Ericsson Corp. of Sweden and named after the 10th century Dane (Sweden and Denmark were a single country in the 10th century) King Harald Bluetooth.
The minimum specification for Bluetooth range is 10 meters, but there is no limit to the range that manufacturers can implement into their devices. Many devices have a range of up to 100 meters. With special antennas, we can extend the range even further.
When two Bluetooth devices are connected, this is referred to as pairing. Up to two Bluetooth devices can be connected to each other. Any discoverable Bluetooth device transmits the following information:
-
Name
-
Class
-
List of services
-
Technical information
When the two devices "pair", they exchange a pre-shared secret or key link. Each stores this connection key to identify the other in future pairings. Each device has a unique 48-bit identifier (a MAC-like address) and usually a name assigned by the manufacturer.
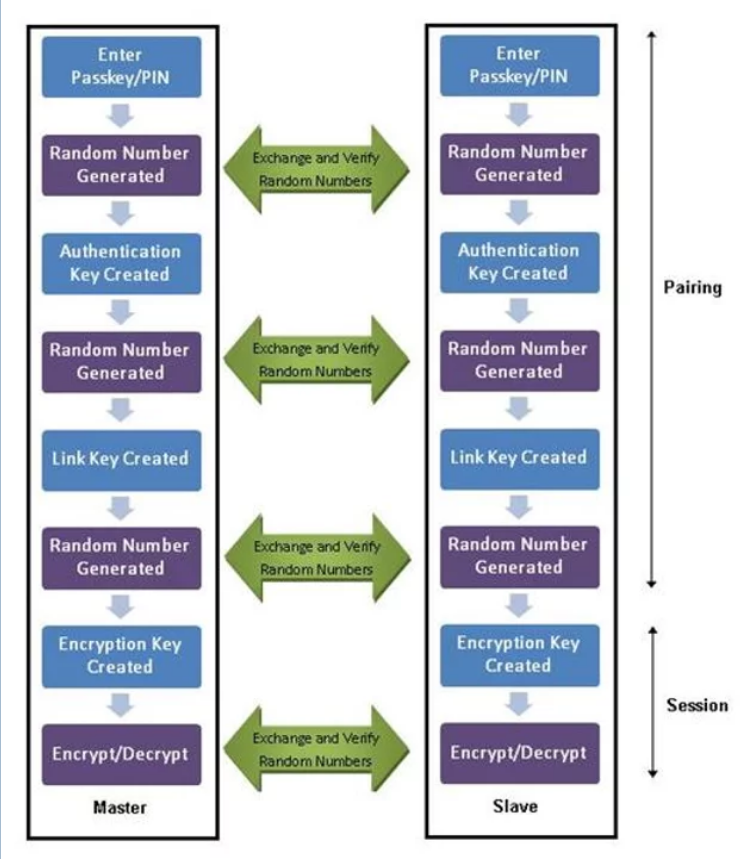
Here is a diagram of it procedureof Bluetooth pairing. Although it has become much more secure in recent years, it is still vulnerable, as we will see in future guides in this series.
Basic Bluetooth Tools for Linux
The Linux application that deals with Bluetooth protocols is BlueZ. Most Linux distributions have it installed by default, but even if they don't, you can usually find it in their repository. In the Kali Linux is installed by default.
BlueZ has a number of simple tools that we can use to manage and ultimately hack Bluetooth devices. These include the following:
-
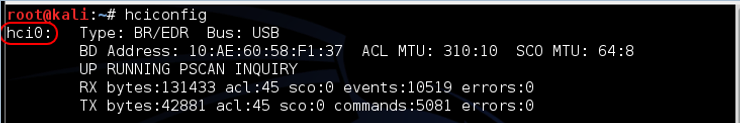
hciconfig: This tool works similar to ifconfig on Linux, except it works on Bluetooth devices. As you can see in the screenshot below, I first used it to display the Bluetooth interface (hci0) and second, I asked the device for its specifications.
-
hcitool: This is a probe tool. It can give us the device name, device ID, device category and information from the watch.
-
hcidump: This tool enables us to do packet capture, commonly known as Bluetooth sniffing.
Bluetooth Protocol Stack
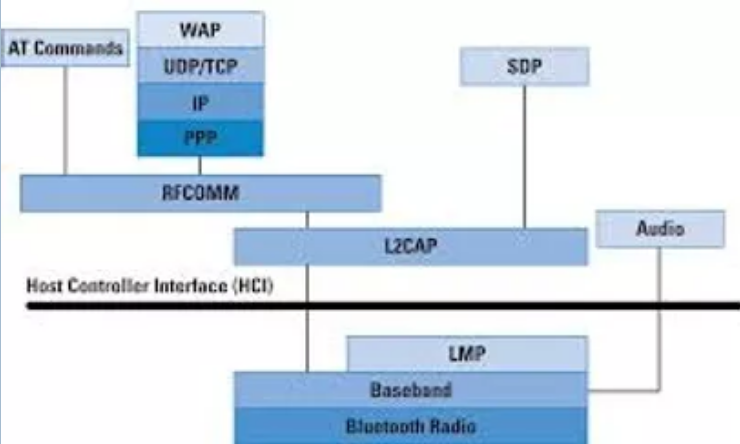
Bluetooth devices do not need to use all protocols in the stack (such as TCP/IP). Bluetooth stack has been developed to enable the use of Bluetooth by a variety of communication applications. In general, an application will uses just one piece of that stack. The Bluetooth protocol layer and their related protocols are listed below:
-
Basic Bluetooth Core protocol band: LMP, L2CAP, SDP
-
Cable replacement protocol: RFCOMM
-
Telephony control protocol: TCS Binary, AT-commands
-
Supported protocols: PPP, UDP/TCP/IP, OBEX, WAP, vCard, vCal, IrMC, WAE
In addition to protocol layers, Bluetooth also defines a central controller interface (HCI). This provides a command interface to the baseband controller, link manager and access to hardware status and control registers, hence the name of the above tools as hciconfig, hcidump and hcitool.
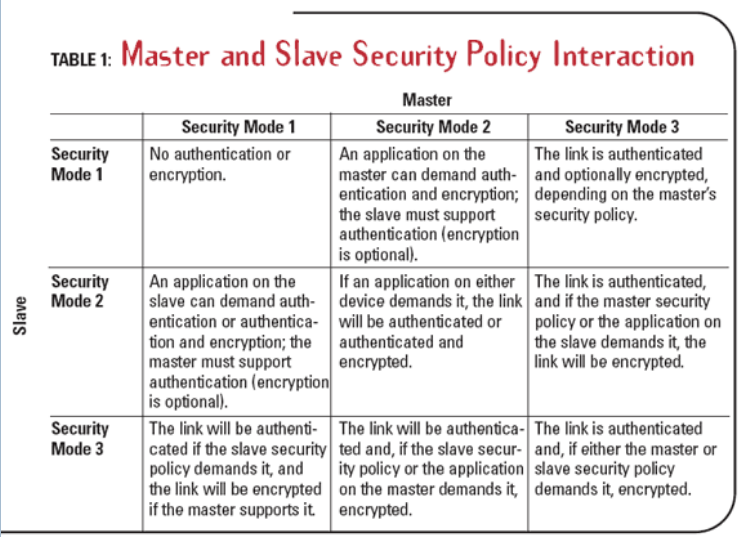
Safety Bluetooth: Bluetooth security relies on a few techniques. First, frequency hopping. Both the master transmitter and the receiver know the frequency hopping algorithm, but an outsider does not. Second, a pre-shared key exchanged during pairing that is used for authentication and encryption (128-bit). There were three functions security settings for Bluetooth. These are:
-
Safety mode 1: No safety active.
-
Security mode 2: Service level security. The central security manager handles authentication, configuration, and authorization. It may not be activated by the user. There is no device-level security.
-
Security mode 3: Device-level security. Authentication and encryption based on a secret key, where it is always visible. Enforces security for low-level connection.
Bluetooth Hacking Tools in Kali
The Kali distribution once had many Bluetooth hacking tools built into it. In Kali 2022 we have settled on only one, which works flawlessly. This does not mean that there are no other prosletterthe. There are many in the Kali repository and also on github.com that you can download. We will be using many of these in future guides.
Let let's take a brief look at some other Bluetooth hacking tools.
-
Bluelog : Scans the area to find as many devices as can be found in the area and then writes them to a file.
-
Bluemaho : A GUI-based suite of tools for auditing Bluetooth device security.
-
Blueranger : A simple Python script that uses ping i2cap to locate Bluetooth devices and determine their approximate distances.
-
Btscanner : This tool is GUI based and scans for discoverable devices within range.
-
Redfang : This tool enables us to find hidden Bluetooth devices.
-
Spooftooph : This is a Bluetooth spoofing tool.
A few Bluetooth-based attacks
-
Blueprinting : The process of footprinting.
-
Bluesnarfing : This attack receives data from the Bluetooth device. This may include SMS messages, calendar information, images, the phone book and conversations.
-
bluebugging : The attacker can take control of the target's phone. Bloover was developed as a POC tool for this purpose.
-
Bluejacking : The attacker sends a “business card” (text message) that if the user allows to be added to their contact list, allows the attacker to continue sending additional messages to them.
-
Bluesmack : A DoS attack against Bluetooth devices.
Now that we understand the basics of how Bluetooth works and Bluetooth technologies and security in general, we can start exploring ways to jailbreak and hack Bluetooth devices.
Stay tuned…





