Windows power plans allow users to create different profile energy so that their machine consumes more or less electricity, appropriate at a given time.
When running on battery, users usually choose a lower brightness on their screen and smaller time period to find o computerς τους σε sleep mode. Το αντίθετο ακριβώς όταν το system powered by an electrical outlet.
These two power plans of the Windows they are turned on automatically when a change in the power source is detected, but to switch to a different power plan according to your own will you have to go through the "Power Options" window. Alternatively, you can create shortcuts based on the command line where you can save them wherever you want them and run them whenever you want. Here's how.
Before you create the shortcut, you need to know the GUID assigned to each power plan. Each power plan has its own GUID and you need to create a shortcut and each one of them. Open a Command Prompt window and type the following command. You will get a list of all configured power plans and their corresponding GUIDs.
powercfg / list
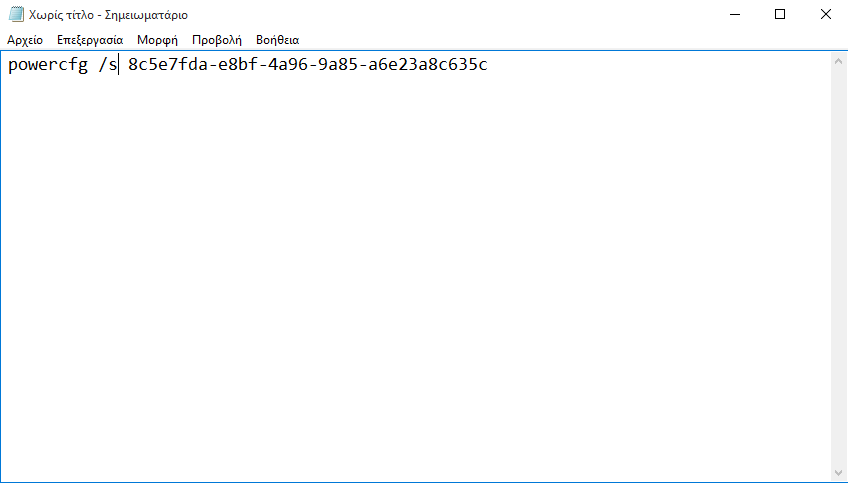
Note the GUID of the power plan for which you want to create the shortcut. Then, open a text file (use Notepad) and type the following command:
powercfg / s [GUID of the power plan]
See the corresponding example of our photo.
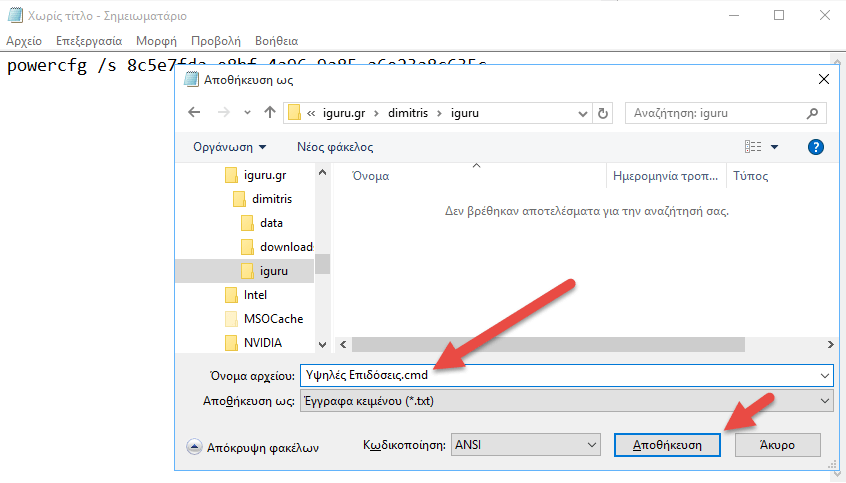
Save the file with CMD extension. Preferably, name it the same name that has the power plan so you can easily identify it.
That's it. Each time you run this file, you will go to the corresponding power plan. We tested it in Windows 7 and above and works flawlessly.