Η Check Point Research, its Threat Intelligence research division Check Point Software Technologies Ltd., a cyber security company, published the Global Threat Index for December 2021.
In a month we saw her Apache Log4j vulnerability to scan the internet, the researchers reported that Trickbot is still the most widespread malware, albeit with a slightly lower rate of 4%, the impact of organizations worldwide, from 5% in November. Recently, Emotet also recovered, which quickly climbed from seventh to second place. CPR also reveals that the industry that receives the most attacks is still Education / Research.

In December, the “Apache Log4j Remote Code Execution” is the most frequently exploited vulnerability, affecting 48,3% of organizations worldwide. The vulnerability was first reported on December 9 in the Apache Log4j logging package – the most popular directorycase Java logging used in many web services and applications with over 400.000 downloads from the GitHub Project. The vulnerability caused a new plague, affecting almost half of the companies worldwide, in a very short time. Attackers are able to exploit the vulnerable applications to run cryptojackers and other malware on compromised servers. Until now, most attacks have focused on using cryptocurrency mining at the expense of victims, however, more sophisticated attackers have started to go aggressive and exploit the breach on high-value targets.
"Log4j dominated the cybersecurity news in December. "This is one of the most serious vulnerabilities we have ever seen, and because of the complexity of repairing it and its ease of use, it is likely to remain with us for many years, unless companies take immediate steps to prevent attacks," he said. Maya Horowitz, Vice President of Research at Check Point Software.
"The same month we also saw the Emotet botnet move from seventh to second place as the most common malware. Just as we suspected, Emotet did not take long to lay a solid foundation since its reappearance last November. It is misleading and spreads quickly through phishing emails with malicious attachments or links. "It's now more important than ever for everyone to have a strong email security solution and to ensure that users know how to identify a suspicious message or attachment."
CPR reports that in December Education / Research is the industry with the most attacks worldwide, followed by the Government / Armed Forces and the ISP / MSP. The "Apache Log4j Remote Code Execution" vulnerability is the most commonly exploited, affecting 48,3% of organizations worldwide, followed by the "Web Server Exposed Git Repository Information Disclosure" which affects 43,8% of organizations worldwide. HTTP Headers Remote Code Execution remains third on the list of most frequently exploited vulnerabilities, with a global impact of 41,5%.
Top malware groups
* The arrows refer to the change of the ranking in relation to the previous month.
This month, the Trickbot is the most widespread malware affecting 4% of organizations worldwide, followed by Emotet and Formbook, both with a global impact of 3%.
- ↔ Trickbot - Trickbot is a modular Botnet and Banking Trojan that is constantly updated with new features, characteristics and distribution channels. This allows Trickbot to be a flexible and customizable malware that can be distributed as part of multipurpose campaigns.
- ↑ Emotet Emotet is an advanced, self-replicating and modular Trojan. Emotet was once used as a banking Trojan, but has recently been used as a distributor for other malware or malware campaigns. Uses multiple methods to maintain obsession and avoidance techniques to avoid detection. Additionally, it can spread through spam phishing messages that contain malicious attachments or links.
- ↔ Formbook - Formbook is an InfoStealer that collects credentials from various web browsers, collects screenshots, monitors and records keystrokes, and can download and execute files according to C&C commands.
Leading attacks in industries worldwide:
This month, Education / Research is the industry with the most attacks worldwide, followed by the Government / Armed Forces and the ISP / MSP.
- Education / Research
- Government / Armed Forces
- ISP / MSP
The top exploiting vulnerabilities
In December, "Apache Log4j Remote Code Execution" is the most commonly exploited vulnerability, affecting 48,3% of organizations worldwide, followed by "Git Repository Web Server Exposed" which affects 43,8% of organizations worldwide. HTTP Headers Remote Code Execution remains third on the list of most frequently exploited vulnerabilities, with a global impact of 41,5%.
- ↑ Remote code execution Apache log4j (CVE-2021-44228) - There is a remote code execution vulnerability in Apache Log4j. Successfully exploiting this vulnerability could allow a remote intruder to execute arbitrary code on the affected system.
- ↔ Website Server & Hosting Exposed Go Repository Information Disclosure- A vulnerability was reported in the Git Repository. Successfully exploiting this vulnerability could allow unintentional disclosure of account information.
- ↔HTTP Headers Remote -- Execution (CVE-2020-10826,CVE-2020-10827,CVE-2020-10828,CVE-2020-13756) HTTP headers allow the user and the server to forward additional information with an HTTP request. A remote intruder can use a vulnerable HTTP header to execute arbitrary code on the victim's machine.
Top Malicious Mobile Apps
AlienBot ranks first among the most prevalent malware on mobile, followed by xHelper and FluBot.
- AlienBot -The AlienBot malware family is one Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) for Android devices that allows a remote intruder, as a first step, to enter malicious code into legitimate financial applications. The attacker gains access to the victims' accounts and eventually takes full control of their device.
- xHelper - A malicious application that has been in the forefront since March 2019 and is used to download other malicious applications and display ads. The application is capable of being hidden from the user and can even be reinstalled if it has been uninstalled.
- flubot - FluBot is an Android botnet that is distributed via SMS phishing messages, which most often impersonate delivery companies. Once the user does click on the link in the message, FluBot installs itself and gains access to all sensitive information on the phone.
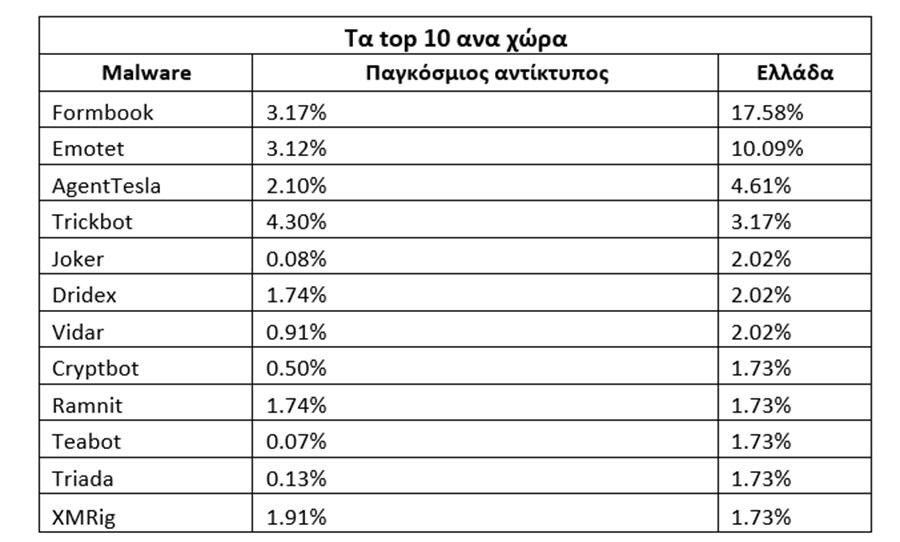
The most common malware threats in Greece for December 2021 are:
Formbook FormBook was first identified in 2016 and is an InfoStealer targeting the Windows operating system. It is marketed as MaaS in underground hacking forums for its powerful avoidance techniques and relatively low price. FormBook collects credentials from various web browsers, collects screenshots, monitors and records keystrokes, and can download and execute files as instructed by its C&C.
Emotet- The Emotet is an advanced, self-replicating and modular Trojan that was once used as a banking Trojan and now distributes other malicious programs or malicious campaigns. Emotet uses multiple methods to maintain its obsession and avoidance techniques to prevent detection and can be spread through spam emails that contain malicious attachments or links.
agent TeslaAgentTesla is an advanced RAT (Trojan Remote Access) that acts as a keylogger and password thief. Active since 2014, AgentTesla can track and collect victim input's keyboard and clipboard, and capture screenshots and extract credentials for a variety of software installed on the victim's machine (including Chrome, Mozilla Firefox and Microsoft Outlook email client). AgentTesla sells openly as a legal RAT with customers paying $ 15- $ 69 for licenses.
Trickbot- The Trickbot is a modular Botnet and Banking Trojan that targets the Windows platform, which is distributed mainly through spam campaigns or other malware families such as Emotet. Trickbot sends information about the infected system and can also download and execute arbitrary modules from a wide range of available modules: from a VNC module for remote control to an SMB module for distribution within a compromised network.
Once a machine is infected, the Trickbot gang, the menacing agents behind this malware, use this wide range of modules not only to steal bank credentials from the target computer, but also to move around and identify itself. target organization, before launching a targeted ransomware attack across the company.
Joker– An android Spyware on Google Play, designed to steal SMS messages, contact lists and device information. Additionally, the malware signs the victim silently for premium services on advertising sites.
DridexDridex is a banking platform targeted at the Windows platform, which is distributed through spam campaigns and Exploit Kits, which relies on WebInjects to spy on and redirect bank credentials to a server controlled by an attacker. Dridex communicates with a remote server, sends information about the infected system, and can also download and run additional drives for remote control.
Vidar- Vidar is an infolstealer that targets Windows operating systems. It was first detected in late 2018 and is designed to steal passwords, credit card data and other sensitive information from various internet browsers and digital wallets. Vidar has been sold on various online forums and is used as a malware dropper that downloads ransomware GandCrab as a secondary payload.
Cryptobot– Cryptbot is a Trojan that infects systems through installationof a fake VPN program and steals your saved browser credentials.
TeabotTeabot malware is an Android Trojan threat used in phishing attacks. Once Teabot is installed on the compromised device, it can stream the screen live to the perpetrator, as well as use the Accessibility Services to perform other malicious activities.
Triada- Triada is a modular backdoor for Android, which provides super-user privileges for downloading malware. Triada has also been observed to tamper with URLs loaded in the browser.
XMRigXMRig, first introduced in May 2017, is an open source CPU mining software used to extract Monero cryptocurrency.
The Global Threat Impact List and Check Point Software's ThreatCloud Map are based on the Company's ThreatCloud intelligence, the largest cybercrime collaboration network, which provides data on threats and trends in attacks, utilizing a global network threat detectors.
The ThreatCloud database includes over 3 billion websites and 600 million files daily and detects more than 250 million malware activities each day.
The full list of the top 10 malware families in December can be found at blog of Check Point





