NoSQL databases (also known as non-relational) do not use SQL for queries. There are a variety of different types of NoSQL databases, such as:
- Key-Value
- Key-Document
- Column-Family
- Graph
NoSQL was designed in response to flexible design methodologies. Relational databases (SQL) require pre-defined schemas and do not allow updates when the data is already in the database. Adding new fields requires moving the database to a new format, which can be time consuming.
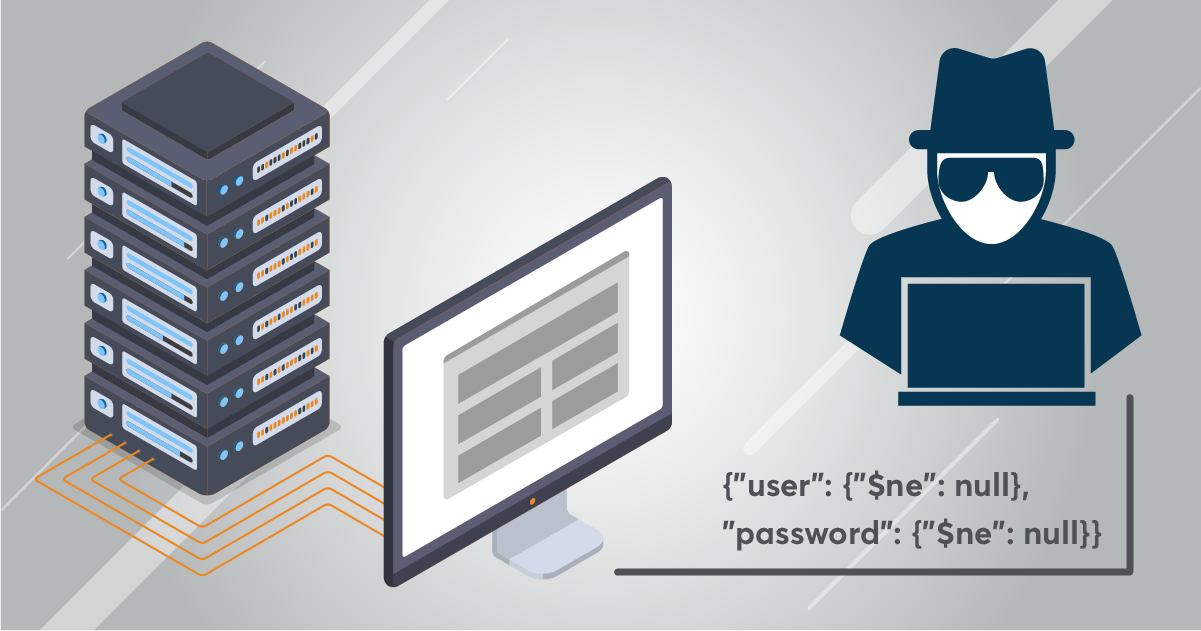
NoSQL attack
While NoSQL databases, such as MongoDB, do not use SQL for queries, they still query based on user input.
The main difference between SQL and NoSQL injection is the grammar and syntax of the query. NoSQL databases do not have a standard language. However, the syntax of their languages is similar (since they are designed to do the same thing).
A NoSQL injection application is an attack on web applications created in the MEAN stack (MongoDB, Express, Angular and Node). When transmitting data, MEAN applications use JSON, which is the same thing used by MongoDB. Penetration of JSON code into a MEAN application can enable injection attacks on a MongoDB database.
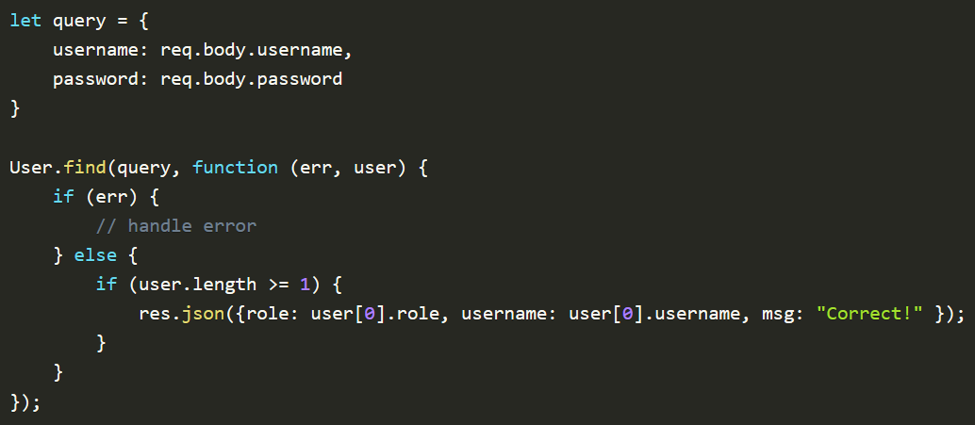
For example, the above screenshot (from NullSweep ) shows an application that is vulnerable to NoSQL. From a request, the code pulls one name user and a password and puts it into a MongoDB query. By passing the JSON {“username”: “myaccount”, “password”: {“$ne”: 1}} , an attacker could authenticate to the service without a password.
MongoDB and other NoSQL databases are commonly used in web applications. For example, a web page may request user account credentials on a web form, save information authenticate against a MongoDB database and perform credential checks using JavaScript.
Strict integration of MongoDB in JavaScript and other programming languages means that NoSQL attacks can be used to execute attacks at other levels. A NoSQL injection attack that includes JavaScript code will allow this code to be executed within the web application.
NoSQL injection protection against attacks
NoSQL injection attacks are very similar to SQL injection attacks: they exploit the poor sanitization of user input during creation database queries. This means that the same tools to protect against SQL injection attacks also work for NoSQL, such as:
NoSQL databases are still databases, which means that it's often important to run queries using user-supplied data. As with SQL databases, it is important to ensure that information is properly sanitized before using it in a query to minimize vulnerability of an application to injection attacks.
Πηγές
- Foreword, OWASP
- 2019 CWE Top 25 Most Dangerous Software Errors, Common Weakness Enumeration
- NoSQL Databases Explained, MongoDB
- NoSQL Injection, RangeForce (Medium)
- A NoSQL Injection Primer (with Mongo), NullSweep