getos.c is an OS fingerprinting tool which detects and captures the type of operating system, using the default TTL response of the ping. It is an open source program written in C by the Greek Developer Athanasios Emmanouilidis.
Use of OS fingerprinting
OS Fingerprinting is the process of analyzing the data packets coming from a network in an attempt to gather information to be used in later attacks.
By identifying the operating system a network is running on, hackers target known vulnerabilities.
OS Fingerprinting can also collect configuration attributes from remote devices. This type of attack recognitions is usually the first step in a larger effort.
The networks running old, outdated or out-of-date Operating Systems become easy targets when attackers discover their weakness.
Installation
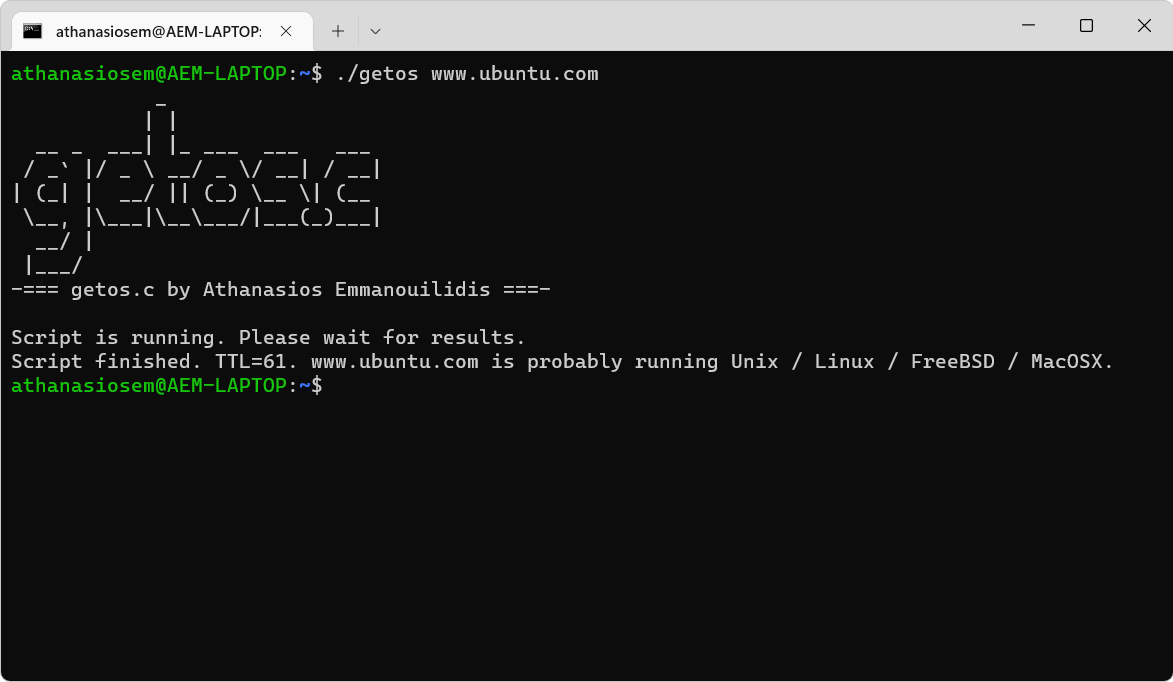
You can compile getos.c using GCC by running the following command:
gcc getos.c -o getos
Use
You can run getos.c with the following command:
./getos www.example.com
How to recognize this threat: To detect OS Fingerprinting, it is important to understand exactly what is going on.
There are two types of OS Fingerprinting: Active and liabilities.
In active OS Fingerprinting, attackers send a packet to a victim and then wait for a response to analyze the contents of the TCP packet.
In a passive effort attackers do not make intentional changes or actions against the network.
Passive OS Fingerprinting is a more secretive, but much slower process. NMAP is probably the most popular and widely used tool for OS Fingerprinting.
How to prevent this threat: The best way to prevent fingerprinting is to limit the types of traffic your network accepts and responds to, and to strictly control the information that your network returns.
By blocking timestamps, echo responses, and address masks, administrators can greatly reduce the usefulness of information that attackers can extract.
You can download the program from here.





