The outdated thoughsafeThe very nature of FTP makes it a risky choice in today's digital world, leaving your data vulnerable to cybercriminals.
By switching to SFTP, you not only enhance data security, but also improve performance, add compatibility with modern file systems, and maintain compliance with industry standards.

In this day and age, data security and privacy are crucial. The outdated and insecure nature of FTP leaves your information vulnerable to cyber threats. It's time to embrace the more secure and encrypted alternative, SFTP, to protect yourself.
Risks of FTP: Why it's dangerous
When you use FTP, your data, including login credentials, is transmitted in plain text. If someone intercepts her transport, can easily access the information. Additionally, FTP is vulnerable to various attacks such as brute force, spoofing, and packet capture, making it a prime target for hackers looking to exploit weaknesses in your network.
File Transfer Protocol (FTP): Brief Summary
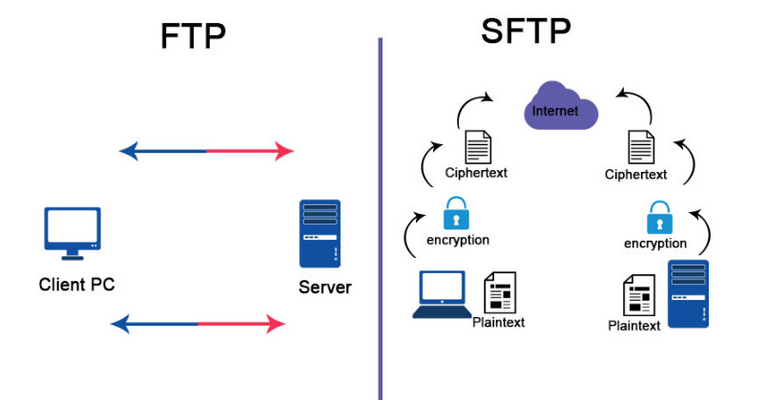
The FTP protocol allows you to transfer files between computers over a network, usually using a client-server architecture. The client initiates a connection to the server and can then download or upload files as needed.
The major problem with FTP is the lack of encryption, leaving your data open to interception and tampering. Although it is possible to add layers of security to FTP, such as FTPS (FTP Secure) or FTP-SSL, these options are not as widespread or user-friendly as they could be.
Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) a more secure alternative
The Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP), also known as SSH File Transfer Protocol, provides a more secure alternative to FTP. SFTP works over an encrypted channel, offering end-to-end protection for your data. It uses the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol for authentication and encryption, ensuring that your login details and file transfers are safe from eavesdropping and tampering.
SFTP also has advantages over FTP, such as:
- Easier setup and configuration: SFTP requires only one port, which makes it simpler to manage and configure than FTP.
- Advanced file operations: SFTP acts more like a remote file system than a file transfer protocol, making it much better for managing the contents of a remote unitof disk on a server.
Reasons to switch from FTP to SFTP
When given the choice, it seems like there's no reason not to use SFTP, but let's dig a little deeper into the specific reasons why you should switch:
- Increased security: SFTP's encryption and authentication capabilities protect your data from eavesdropping, tampering, and unauthorized access. You can even combine it with a VPN to make sure no one knows what you're transferring or even from where.
- Compliance with industry standards: Many industries, such as healthcare and finance, mandate secure file transfer methods to safeguard sensitive data. Using SFTP helps you comply with these requirements, and you could have problems using insecure technologies like FTP.
Although FTP may have been the preferred file transfer protocol for many years, the lack of security measures has made it dangerous in today's digital world. Switching to SFTP is vital to protecting your data and maintaining the integrity of your network. It's time to leave vulnerable FTP behind and adopt the more secure and efficient SFTP instead.
This is especially true if you use a service like Seedbox, where you can easily overlook thechange between FTP and SFTP when choosing the protocol you want to use!





