Do you have questions about what they mean and what are all these strange concepts that you often come across in computers? Let's look at a glossary of words, which will clarify the difficult points of the magic world of computers.

Do you use your computer every day, but do you know all the parts that are in it? What are the latest standards and specifications you need to know? See the following glossary of terms for a computer to understand their true meaning.
16-bit, 32-bit and 64-bit
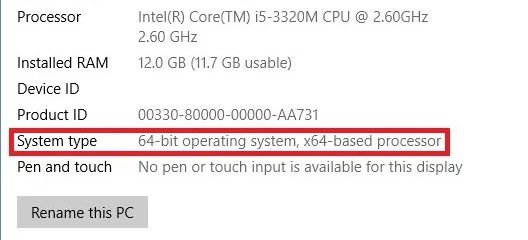
Also known as "bit number", the terms 16-bit, 32-bit and 64-bit refer to various data lengths that can be stored in a processor. A 32-bit processor still in use but on older technology computers (16-bit is rarely used nowadays) can store 232 memory addresses and is known as the x32 or x86 processor. A 64-bit processor can store 264 memory addresses and is known as an x64-based processor. On a Windows 10 device, you can find your bit number from "Device Specifications" in "About your PC" settings.
All-in-One Computer
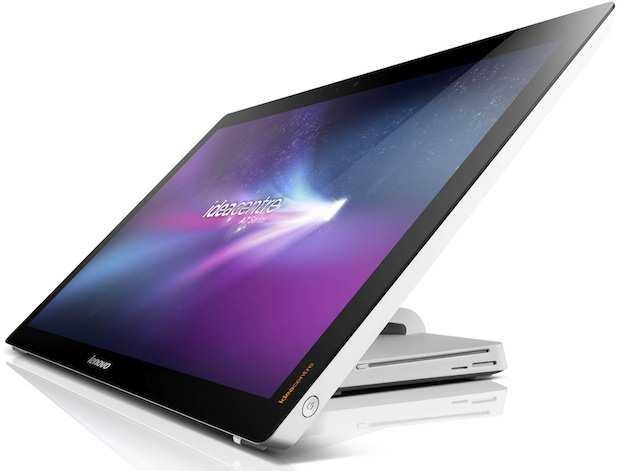

All-in-one (AIO) PCs are an advanced version of desktops that integrate the entire case and screen into a single-volume display unit. Except for the keyboard and mouse, everything else is built into the same box as the monitor, including RAM, processor, motherboard, USB ports, and disk. In other words, it is a screen with a large thickness to include the other components. AIOs are generally wide resolution (1920 x 1080) and are widely used by designers, video editors and creative professionals.
BIOS
BIOS stands for Basic Input/Output System, and is a boot firmware. The initial code is executed when the computer starts up. The primary function of the BIOS is to detect, control, and initialize system devices such as adapter monitor, hard drive, floppy drive, and other hardware. This is done to get the machine into a given state so that software stored on compatible storage media can be loaded, executed, and gain control of the computer. In modern computers, this software is the operating system, to which the BIOS passes control after its code has finished executing.
Cache Memory
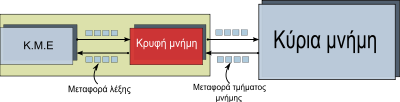
Cache memory is a high-speed memory located near the CPU and on the motherboard. It is an intermediate memory between the Central Processing Unit (CPU) and the Main Memory. It is much faster than main memory but also much more expensive.
On a computer a program is stored in main memory, but the processor when running the application tends, for a significant percentage of the total program execution time, to be limited to small subsets of program commands (something to be expected since programs contain loops repetition, otherwise they would end in a very short time). This phenomenon is called the principle of locality. The CPU cache, faster and more accurate than the main memory, but also much smaller in size (to reduce costs), takes advantage of the principle of locality to execute programs faster, since the subsets of commands and data often run in the cache, resulting in a performance similar to that of a computer that has only fast but accurate cache for a considerable amount of time.
The analogy with the use of the refrigerator in a kitchen can help in understanding the basic function of the cache. The cook has to produce some food on a daily basis. If he did not have a refrigerator he would have to go out more often to buy, e.g. meat, which would reduce its efficiency, while with the help of the refrigerator can be supplied ingredients, e.g. for a week, saving time. So the computer gets faster speed in opening programs with the cache memory.
Compact Disks (CDs)

A digital CD is a plastic computer data storage disc. It has a hole in the middle so that it can rotate like a vinyl record. It can either be ready written with the data, or it can be empty and you can register it with the data you want. A CD could contain 650 to 700 MB of stored data.
The evolution of CDs is DVDs (Digital Video Discs) that can contain up to 4,7 GB, and are used for both data and high resolution video.
CPU (Processor)
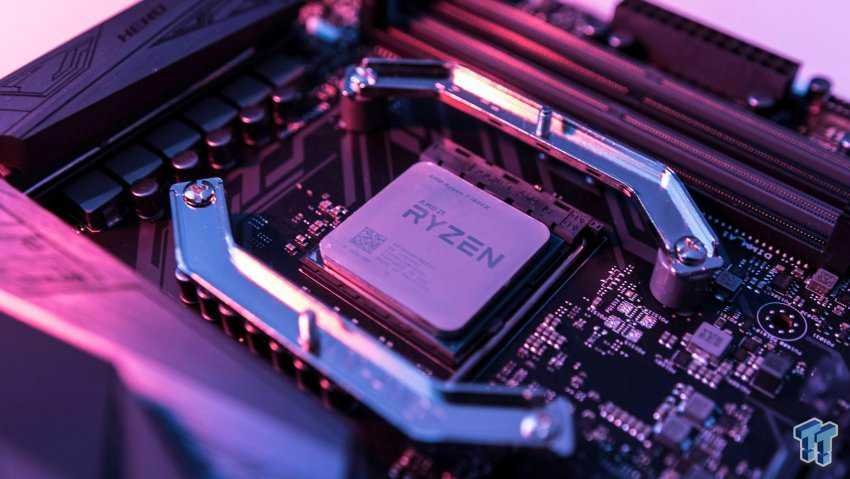

CPU stands for Central Processing Unit (CPU). It is considered the computer brain and performs most of the arithmetic, logic, and input / output (I / O) functions defined by a program. Each CPU is equipped with an internal clock that determines the "Clock Speed", ie the number of functions that the CPU can perform in one second. It looks like a black square or rectangular box with many small legs around it and a heat sink on top to absorb the heat.
If the CPU consists of a single integrated circuit, then it is called a microprocessor or microcontroller. Processors are not exclusively related to computers as they are now integrated into many electronic devices such as mobile phones, digital cameras, camcorders, video game consoles and more. To be precise, processors are integrated into any type of device that requires computing power.
Desktop
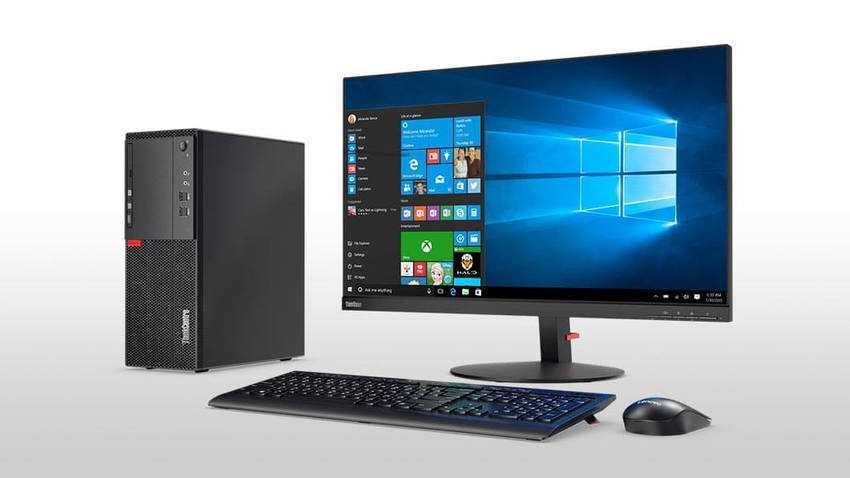

The desktop computer is the first variant of computer devices, used in homes and offices. Apple-II, Mackintosh and Commodore PET were the first desktop computers launched in the 1980s for home use. Today, a standard desktop computer includes at least one monitor, a box with the motherboard, the processor, the RAM, and in addition a keyboard and mouse.
Other types of computers, besides desktops, are laptops, tablets, aio. Desktops are superior in that they are usually upgradeable, but lag behind in that they take up relatively little space and are not portable.
Firmware
In computing, firmware refers to a specialized category of software, written in machine language that provides a low-level control of a computer hardware. It works for only one specific hardware and at a lower level than the operating system as it provides coded instructions for activating the device. An example of firmware is the BIOS installed on the motherboard of an IBM-compatible computer.
Flash Memory (Flash Memory)

Flash memory is an electronic, rewritable form of memory that can and does retain its data even if we remove the power supply or turn off our device. It differs from the RAM or ROM of a computer as these two memories need the presence of current to maintain their data.
Flash memory is used in memory cards and USB flash drives and is suitable for digital cameras, camcorders, tablet PC cards, USB sticks and more. It was invented by Dr. Fujio Masuoka in the 1980s. They have a function similar to the hard drive but are smaller in physical volume, data capacity and speed. They also withstand shocks from hard drives because they simply do not have moving parts.
Floppy Disks
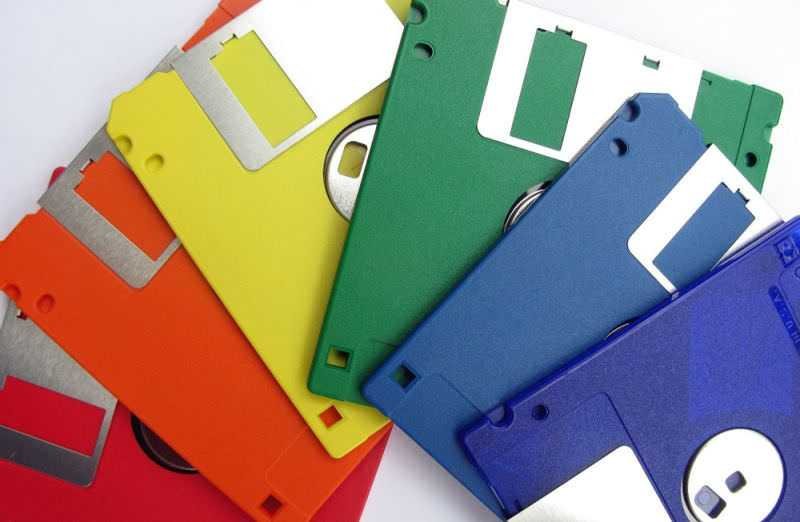

Older computers used removable disks (FDDs) to enter data. It is a portable data storage device, something like today's USB flash or DVD. They are low speed, made of a magnetic disk with a square plastic or cardboard housing and are available in 5 ¼ (133 mm) inch and 3 inch (90 mm) formats. Floppy disks are obsolete and appear only on older computers and industrial server systems.
They first appeared on IBM in 1971 and began to decline with the advent of the CD.
GPU (Graphics Card)
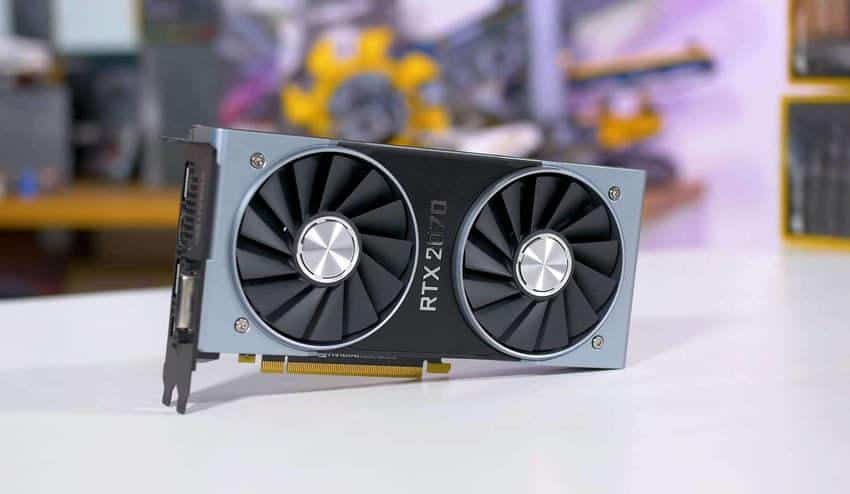

Η GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) ή κάρτα γραφικών, είναι ένα σημαντικό εξάρτημα που μας επιτρέπει την οπτική απεικόνιση όλων όσων κάνουμε σε έναν υπολογιστή. Ο όρος επινοήθηκε για πρώτη φορά από τη Nvidia που σήμερα είναι ένας από τους ηγέτες στην τεχνολογία GPU, με διάφορα μοντέλα GPU. Άλλη μάρκα είναι και η AMD.
With the development of graphics and image quality the graphics card is now a small processor, ie it has been specially designed to perform the complex mathematical and geometric calculations that are necessary for the performance of graphics. Some of the faster GPUs have more transistors than the average CPU. A GPU generates a lot of heat, so it is necessary to use a fan to cool them.
Like any hardware it has its own firmware and usually every GPU company offers additional software to optimize the performance of the computer.
Hard Drive
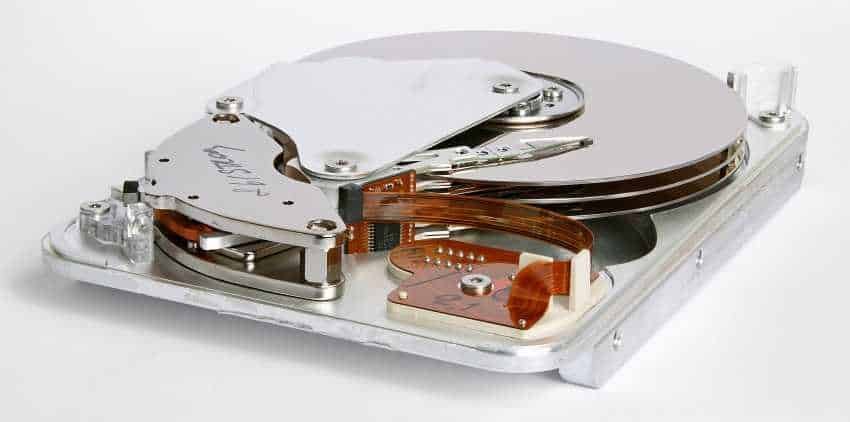

A hard disk or hard disk drive (HDD = hard drive drive) is an electromechanical data storage medium that uses a magnetic head on a flat and circular plate coated with magnetic material. Data is stored in concentric pieces on the plate called “platters”. The hard drive stores the data on your computer or installed a program. It can have a capacity of up to 1 TB or more.
Hardware
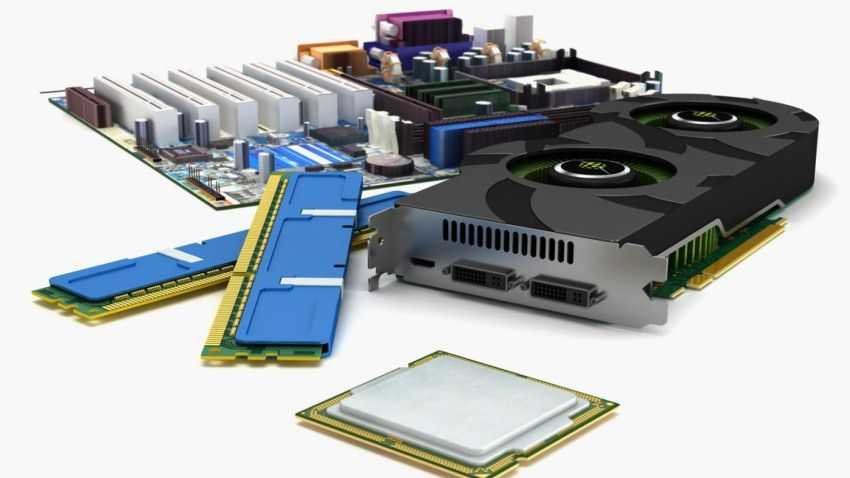

Το υλικό του υπολογιστή ή αλλιώς Hardware, αναφέρεται στα φυσικά μέρη ενός υπολογιστή, τα οποία αποτελούνται από το περίβλημα (case), την CPU, τη μητρική πλακέτα, την οθόνη, το ποντίκι, το πληκτρολόγιο, την κάρτα γραφικών, το σκληρό δίσκο, τα ηχεία, τις θύρες USB, τις κάρτες PC και πολλά άλλα. Αυτό το διαχωρίζει από το λογισμικό, το οποίο αναφέρεται σε μια συλλογή κώδικα που είναι εγκατεστημένος στον σκληρό δίσκο του υπολογιστή. Το υλικολογισμικό, από την άλλη πλευρά, είναι μια εξειδικευμένη κατηγορία λογισμικού που βοηθά την προετοιμασία του υπολογιστή για τη διασύνδεση του με τα στοιχεία του υλικού.
HDMI

HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) is an audio-visual interface (a flat plug) that transmits high-definition audio and video between a port on your computer and another device, such as a smart TV, video projector, DVD player. , a Blu-Ray player, etc., using a connection and cable. The HDMI standard was designed by a consortium of companies, including Hitachi, Philips, Sony, Toshiba and others. Most modern computers have HDMI ports that look like a thinner version of a USB port and only accept HDMI connectors.
Keyboard

The keyboard is a primary data entry material, where information is typed with its keys. It has the same shape and layout of letters as the typewriters. Modern keyboards sometimes illuminate the letters and are called "backlit keyboards". They can be wired or wireless. If the keyboard is software that simply works as a program on a screen, it is called an on-screen keyboard.
Laptop (laptop)

A laptop is a portable personal computing device, where all its basic hardware, monitor, keyboard, mouse (in the form of a trackpad), RAM, CPU, GPU, motherboard, hard disk / SSD and ports, are well integrated into one folding box. Laptops with Windows and Linux operating systems can have the same type of hardware in them, while MacBooks are designed differently to support Apple's operating system and programs.
They are generally portable, so light and concentrated. They heat up more easily than desktops, they need more care (not to fall, do not heat up, etc.) but they do not lag behind in power, as there are laptops that cost 5.000 euros and are aimed at particularly demanding gamers and designers.
MacBook

The MacBook is the latest evolution of Apple's historic Macintosh laptop. Runs the macOS operating system. Mac Mini and MacBook Air are other common Mac devices. Apple MacBooks are the largest alternative to the conventional portable devices on the market.
Monitor

A monitor is an output device that displays the interactions of a computer's programs in visual form. For AIO or laptop, the screen is integrated with the rest of the case (case), while on a standalone desktop computer, the screen is separate. As with televisions, the models stand out in dimension (diagonal in inches) and image resolution (pixels X pixels).
Motherboard

The motherboard is a central and basic printed circuit board, inside the case of a computer on which the circuits with RAM, CPU, GPU and other computer peripherals are placed. A motherboard contains expansion slots, such as PCI Express, fan plugs, heat sinks, and more.
Many motherboard models now have the built-in (on-board) graphics card (but low quality), sound and network. Rarely do they now have a parallel port and a serial port.
PCI Express
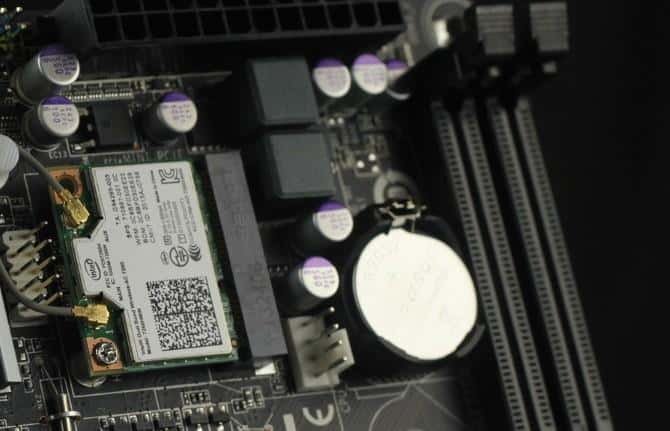

PCI Express, or PCI-e (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), is a standard, high-speed serial PC bus that can be viewed as an expansion slot on the motherboard. It is the most standard internal interface, allowing high-bandwidth communication between the motherboard and peripherals.
Printer

A printer is an external machine connected to a desktop or laptop computer or even a network port. Its purpose is to print text or images based on the commands of a printing software. Modern printers are usually combined with photocopiers and scanners. There are 3 basic types of printers depending on how you print. The dot matrix (commonly used in accounting), jets (usually home) and lasers. In addition, there are thermal printers, 3D printers and others.
RAM

Random access memory (RAM, Random access memory) is a term we use for electronic devices for temporary storage of digital data (computer memory), which allow access to stored data at the same time wherever they are, ie "random access".
In contrast are data storage devices, such as magnetic tapes and magnetic disks ("hard" or "flexible"), in which data can only be accessed in a predetermined way, usually serially, due to the way they are made.
There are two basic types of RAM: dynamic RAM (DRAM) and static RAM (SRAM). DRAM is the most common form but needs to be "refreshed" thousands of times per second, while SRAM does not need this. SRAM, as a device, is more expensive to build - and therefore market - than DRAM.
RAM is placed on the motherboard, in special ports.
Raspberry Pi
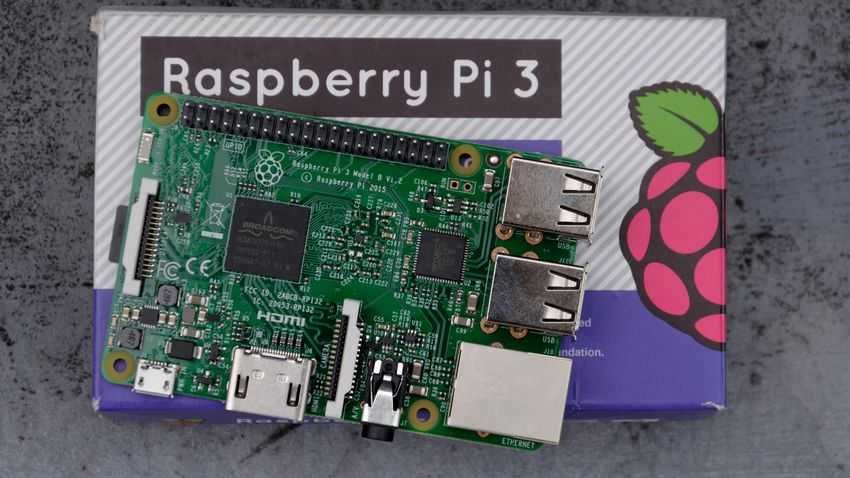

The Raspberry Pi is a low-cost, single-board, credit card-sized (SBC) computer that can be connected to a computer monitor or TV monitor and used for basic tasks. Due to its low cost it is used in many applications, such as weather monitoring, IoT devices etc. It started in England as a tool for teaching computers in schools, but eventually became much more popular than expected.
SATA
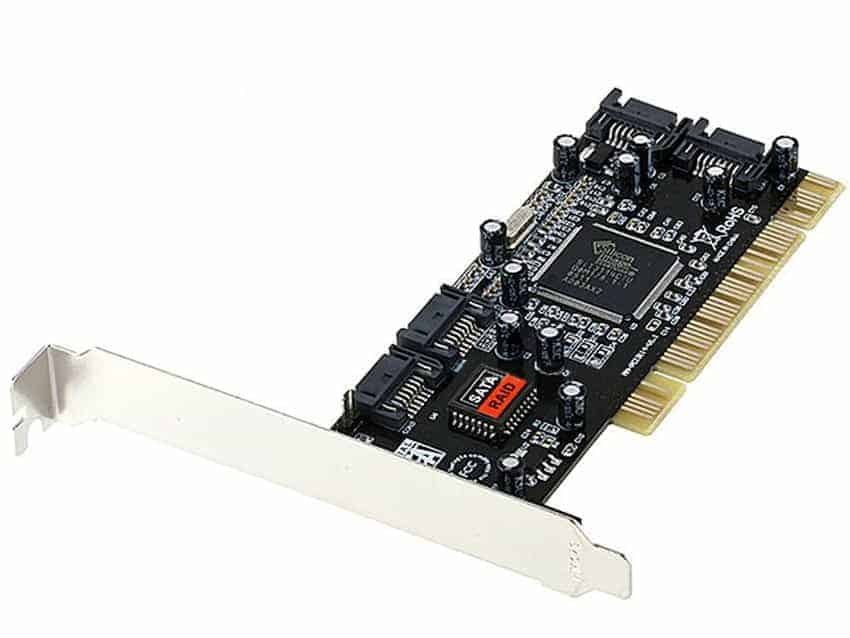

SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) is the data bus standard that is widely used in personal computers for the purpose of transferring data from hard disks or optical data storage media to the central processing unit.
The SATA bus has gradually replaced the standard IDE bus. SATA's successor is the Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe), which is characterized by higher transmission speeds.
Sound Card
A sound card, or audio adapter, is used to record and play audio by converting digital data into analog sound waves, which you can hear through the speakers. It can also be used to record audio with the microphone. Without the sound card, obviously, you can not listen to music, enjoy videos and games. It connects to the motherboard, but many motherboards also have a built-in sound card in their circuits.
SSD
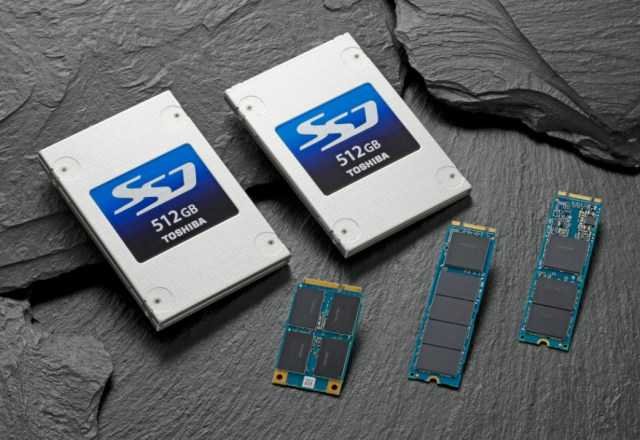

SSDs (Solid State Drives) are flash drives, similar to disks, but much faster as they use NAND memory. Although more expensive they have begun to replace hard drives (HDD). Another example is Solid State Hybrid Drives (SSHD), which use SSD cache but have the advantage of storing the hard drive.
As they do not have mechanical parts, they are not prone to shocks and that is why (and due to their small volume) they are preferred in laptops.
Trackpad and mouse

A trackpad and a mouse are hardware interfaces that allow you to do something on the computer screen. But there is an important difference: on a trackpad, your finger scrolls, while the mouse uses a surface on which it rests. You will find traclpads on a latop and a mouse on all computers without exception as they are easier to use.
Webcam

A webcam is a camcorder connected to a computer. On laptops, it is integrated into the chassis, while on desktops it is wired via a USB port. It is used for conversations but also for monitoring the computer space.
USB Flash Drive
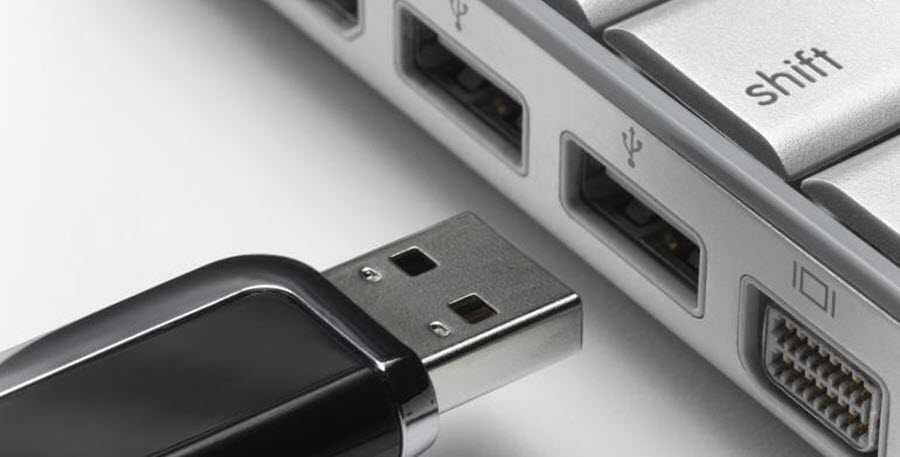

USB (Universal Serial Bus) refers to a form of flash memory (see above) that connects to a computer via a USB port. There are currently two common versions: USB 2.0 and USB 3.1, which differ in thickness. Most modern computers have USB ports for both models.
This guide will be enriched from time to time. If you have a difficult concept and want to see an explanation of it here, ask for it with a comment.





