Google has stated that it is working to improve the security of Android and the measures it is taking to address common threats.
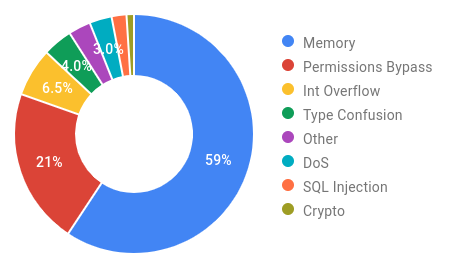
The company revealed that 59% of the critical vulnerabilities that affect the Android operating system are memory issues, such as memory corruption and overflows.
Memory security issues were by far the top category of security issues, followed by patent bypass defects, which accounted for 21% of those fixed by Google security technicians in 2019.
Memory issues are generally the top category of security vulnerabilities on large platforms such as Java, Windows 10 and Chrome. Google technicians last year said that 70% of Chrome security vulnerabilities were memory issues. Earlier, Microsoft technicians reported that 70% of all bugs fixed in its products were memory problems or software issues that allowed access to operating system memory.
Google today says it encourages developers to use memory-safe programming languages such as Java, Kotlin and Rust, but also seeks to improve the security of C and C ++. All of this is part of the company's efforts to harden Android and protect the operating system from malware and exploits.
"C and C ++ do not provide memory security like Java, Kotlin and Rust do. since majority of the security vulnerabilities mentioned in Android are memory security issues, a dual approach is applied: improving the security of C / C ++ while at the same time encouraging the use of languages that are safe in memory " a post on her blog by the Android Security and Privacy Team.
Η Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft are also pushing for Rust adoption for the same security reasons. Mozilla created Rust to address C++ memory-related security issues in Firefox's Gecko engine. Rust version 1.0 was released in 2015, but adoption of the language is still relatively low.
When it comes to Android, the majority of bugs that Google has fixed in 2020 have been in the media, Bluetooth, and NFC components. The bookcase πολυμέσων (media library) was the key element affected by critical and remote errors Stagefright on Android revealed by Google in 2015.
According to Google, its efforts to harden the media server framework on Android resulted in 2020 not receiving any reports of critical vulnerability exploits in Android media frameworks.





