Google seems to be trying to become completely independent company, as it announced the launch of its own root certificate authority.
With this new move, Google will stop relying on intermediate certification companies, specifically GIAG2 that it used to date.
"As we look forward to the evolution of both the internet and our own products, it is clear that HTTPS will continue to be a key technology. That's why we decided to expand our current Certificate Authorities to include the operation of our own root certification authority, ”says Ryan Hurst, Google's product manager.
Thus Google was born Trust Services, a company that will issue certificates on behalf of Google and its A.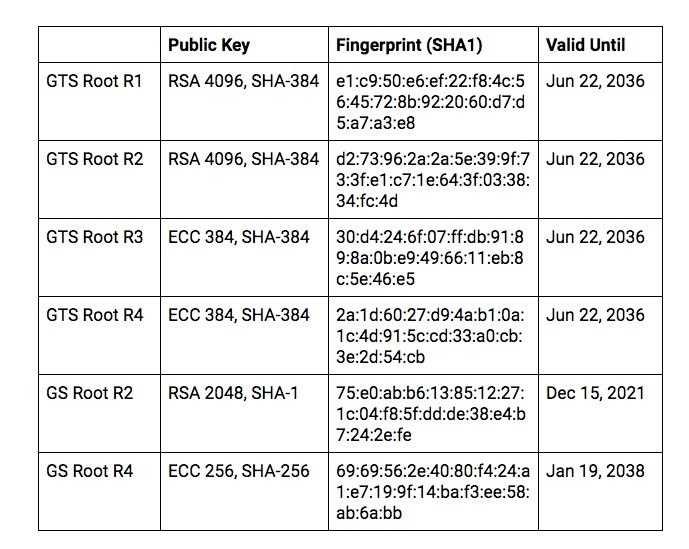
But this whole process will take time. Incorporating new root certificates into products and waiting for the relevant versions of these products to be developed takes quite some time. So Google acquired two existing Root Certificate Authorities, GlobalSign R2 and R4, which will allow the company to start issuing independent certificates much faster.
Meanwhile, Google will continue to use the existing GIAG2 certificates for the time being at least.
“If you're developing products that are intended to connect to some service of Google you should use the above root certificates. That way, even if we release our own certificates, you can still choose to work with third-party certificates.”
Google advises developers seeking to link their applications to company services to include a broad set of trusty roots in their products.





