Ildar Rakhmatulin, a research fellow at Heriot-Watt University works on machine learning. In a study – conducted last year but published in Oriental Insects on last week – Rakhmatulin and colleagues used a laser insect control device automated with machine vision to perform a series of experiments on cockroaches.

So they managed not only to detect the cockroaches with high accuracy, but also to keep them at a distance of 1,2 meters.
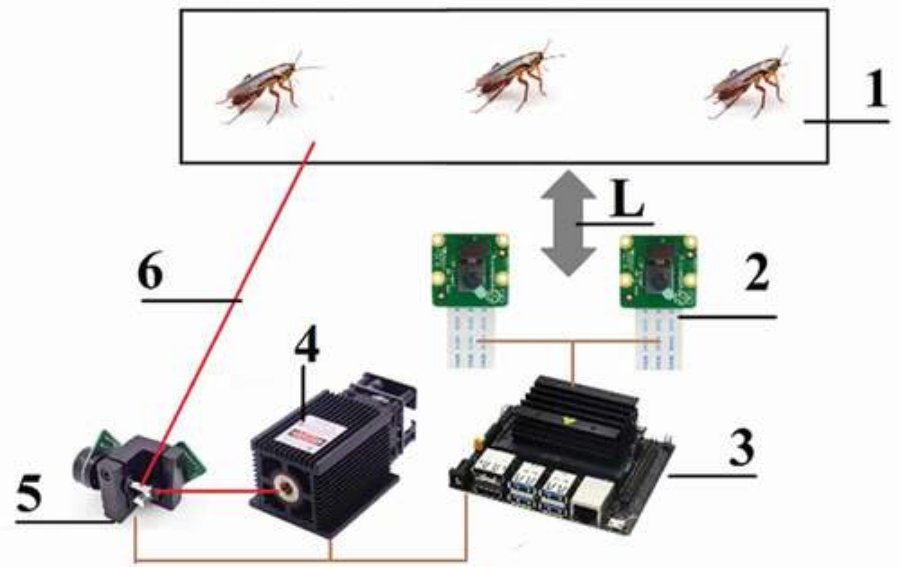
“I started using a Jetson Nano that allowed me to use technologies deep learning more accurately to detect an object,” says Rakhmatulin. Jetson Nano is a small computers that can run algorithms machine learning. The computer processes a digital signal from two cameras to determine the location of the cockroach.
It transmits this information to a galvanometer (a machine that measures electric current), which changes the direction of the laser to "shoot" the target. According to the publication, Rakhmatulin tested the above at different power levels for the laser.
At a lower power level, he found that he could influence the behavior of cockroaches. Thus, they could possibly be trained not to resort to a certain dark region. At a higher potency level, the cockroaches were effectively "neutralized", in other words, killed.
“I use very cheap material and cheap technology and everything is open source," Rakhmatulin said. "All sources are rising on my GitHub and you can use them. If it can harm cockroaches, it can also harm other pests in agriculture.”
However, it is not ready for home use. "It's not recommended because it's a bit dangerous," Rakhmatulin said. "Lasers can not only harm cockroaches but also your eyes."
Watch a video of the device in action
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VwZunUqHbiU





