What are the optional features of Windows, how can you install and uninstall them?
Windows has a long list of optional features that are not known to many users, as they are deep in the operating system menu. These optional features can be added or removed from your Windows installation at any time.
Although these features have some description, the information provided by Windows is either too brief or too complex for most users to understand.
So let's look at a list of these possibilities and try to explain each one of them. We'll describe what each one is or does so you can decide for yourself which Windows features you should enable and which you should disable.
NOTE: For this article, we used Windows 10 Pro version 21H2. If you have another version of Windows, you may have a different number of optional features than those listed below. Also, our version is in the Greek language and although we also mention the English terminology of each feature, the order of these will be different if you have the English language.
Optional features: List access
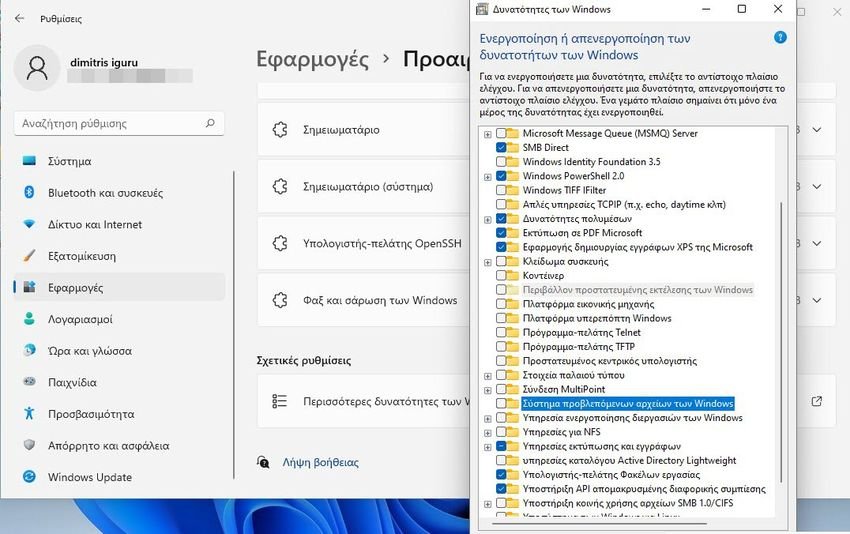
In Windows 11 and Windows 10, there is a long list of Optional features either installed by default or that you can add yourself.
In Windows 10 to see them go to Settings > Applications. Under the heading "Applications and features" press the link "Optional features".
There, on the right side of the window you will see the link "More Windows features". If you don't see it, just enlarge the settings window until it's visible. Click on this link.
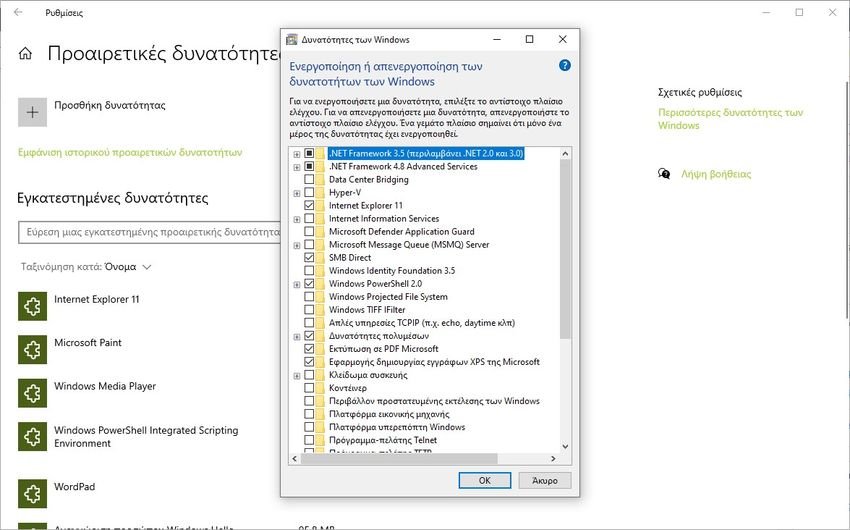
Installation and uninstallation
The process of both installing and uninstalling each of the features is really simple. Choose the one you want and check the box to the left of it to install it.
Unmark it to uninstall it.
For both actions press the OK key to confirm them and then follow the Windows instructions.
List of Windows 10 – 11 optional features
- .NET Framework 3.5 (includes .NET 2.0 and 3.0) – a software development framework created by Microsoft. Many programs and board games computer they usually use it. Windows includes, by default, the .NET Framework 4.8, which is newer. If you have older programs or games that need this version to run, you may want to install it. When you install such a program it informs you that it needs this feature to work.
- .NET Framework 4.8 Advanced Services – these advanced services include ASP.NET 4.5 (a server-side web application framework) and WCF Services – used to implement and deploy service-oriented architectures and distributed computing services. Does this all sound like gibberish to you? These services are only intended for software developers and business environments with complex infrastructures and services. Casual users will not need to install these services and should only keep the defaults that come with Windows (WCF Services, TCP Port Sharing).
- Data Center Bridging – a set of standards that were developed by the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) for data centers. They include standards for storage, data networking, interprocess communication, and traffic management that all share the same Ethernet infrastructure.
- Hyper-V – a Windows feature that allows you to create and run virtual machines. It is similar to other popular software like VirtualBox or VMware. However, Microsoft went to the next level in terms of performance: Hyper-V is faster than other similar technologies because its processes run at a lower level in the operating system. This means that virtual machines are closer to the physical layer (the real hardware) and thus run faster. If you are interested in working with virtual machines, you may want to consider installing this feature. Otherwise, you don't need it.
- Internet Explorer 11 – The old Microsoft Internet browser. You should only keep it if you still need to use it. This “feature” is only available in Windows 10, not Windows 11.
- Internet Information Services – this feature is also known as IIS. It allows your Windows PC to act as a web server. This is only useful for software developers and IT professionals. After you install these services, you can access IIS Manager from the Start menu and you can use any browser to access the websites you host. Go to http://localhost from your favorite browser to see an example.
- Microsoft Defender Application Guard – offers a safe environment for browsing the internet. In other words, allows you to isolate untrusted sites: As an administrator, you define what is trusted among sites, cloud resources, and internal networks in your company, and anything not on your list is considered untrusted.
- Microsoft Message Queue (MSMQ) Server - The MSMQ is an old service that has only one purpose: to improve communications when working with unreliable networks. This service stores messages in a cache so that whenever the connection goes down, it can resend them when the network is restored available. This feature is only useful for businesses that have applications that require this service.
- SMBDirect – Allows network adapters to use RDMA (Remote Direct Memory Access) to improve the file sharing process when using the SMB 3.x file sharing protocol.
- Windows Identity Foundation 3.5 – a software framework for building identity-aware applications. The .NET Framework 4.8 included with Windows 10 and Windows 11 includes a newer version of this framework. You should only install version 3.5 if you're using older apps that don't work without it. Most users do not need to install it.
- Windows PowerShell 2.0 – a command line tool that focuses on task automation and parameter management. it's like the Command Line but a much more powerful tool. It is intended to replace the Command Prompt as it provides more power and control to the Windows operating system. Recommended for developers and experienced users only.
- Windows Projected File System – also known as ProjFS, allows applications to create virtual file systems. If you don't work with code and develop hardware, you don't need it.
- Windows TIFF IFilter – with this feature enabled, Windows can recognize text inside TIFF image files. It is disabled by default, as OCR has a large impact on performance.
- Simple TCPIP services (eg, echo, daytime, etc.) [Simple TCP/IP services Simple TCP/IP services (ie, echo, daytime, etc.)] – a collection of "oldie but gold" command line tools including character generation, day, discard, echo and quote of the day. You don't need to use them.
- Multimedia capabilities [Media Features (Windows Media Player)] – the default media player that comes with Windows. If you're not using it to play music or video, you can remove it. Third-party media players are generally a better option. Windows Media Player is also used to stream media content over the local network.
- Print to Microsoft PDF [Microsoft Print to PDF] – Windows includes a default virtual printer available to all users, called “Microsoft Print to PDF”. Allows you to save documents as PDF files. If you don't want this feature, you can turn it off.
- Microsoft's XPS document creation application [Microsoft XPS Document Writer] – provides support for Microsoft's XPS file format, which is an alternative to Adobe's PDF format. You need this service if you want to be able to print and save XPS files.
- Κλείδωμα deviceς [Device Lockdown] – allows you to install and run services and tools that provide a specialized user interface. For example, allows you to run Windows on a machine placed in a kiosk.
- Container [Containers] – includes everything you need to create a container (an individual box) on your Windows 10 PC. These are tools that allow applications to run in their individual boxes, without knowing anything outside of that box. Regular users don't need these services and tools, but all the curious can read about them here: Windows and Containers.
- Windows Protected Execution Environment [Windows Sandbox] – allows you to run a free Windows 11 or Windows 10 virtual machine on Windows, in which you can safely run anything you want: potentially malicious email attachments you've received, running or testing applications, etc. Windows Sandbox is a great feature for anyone who needs a safe, isolated environment that doesn't affect the computer they're running on. If you're interested, check it out how to set up Windows Sandbox.
- Virtual Machine Platform [Virtual Machine Platform] – This is part of the native virtualization system offered by Microsoft.
- Windows Hypervisor Platform [Windows Hypervisor Platform] – an API (Application Programming Interface) used by other third-party virtualization software, such as VirtualBox or Android emulators.
- Telnet client [Telnet Client] – a legacy command line client that uses the Telnet network protocol to provide two-way text communication with a Telnet server. Most users will never need to use it.
- TFTP client [TFTP Client] – a simple command line tool that can be used to transfer files via the Trivial File Transfer Protocol. Most users do not need to install it.
- Protected host [Guarded Host] – allows administrators to run shielded virtual machines in Hyper-V to secure them and block access to attacks from malware or other malicious threats.
- Legacy data [Legacy Components] – DirectPlay was part of the DirectX application programming interface. It used to be a library designed for network communication. If you don't play old games developed before 2008 that you need this library, you should be fine with removing it.
- Multipoint connection [MultiPoint Connector] – allows MultiPoint Manager and Dashboard applications to monitor and manage your Windows 10 device. This is only required on certain corporate networks where such applications are used.
- Windows Process Activation Service [Windows Process Activation Service] – a service for message-based applications and Internet Information Services (IIS)-related components. It allows software developers to choose the most appropriate protocol for their needs. This feature is only useful for software developers.
- Services for NFS [Services for NFS] – Allows you to access files using the NFS (Network File System) protocol. If you have and use NAS (Network Attached Storage), you probably want this feature enabled.
- Printing and document services [Print and Document Services] – services that enable the use and management of printing, faxing and scanning devices. By default, services Internet print client [Internet Printing Client], Windows Fax and Scan are enabled in Windows. Windows Fax and Scan lets you use faxes and scanners. If you do not use such devices, you can disable this service. The Internet Printing Client enables you to connect and print to a printer connected to your local network or the Internet. Other services such as LPD Print Service and LPR Port Monitor are deprecated alternative printing technologies that are no longer widely used. Scan Management is used to monitor and manage scanners connected to the network.
- Active Directory Lightweight directory services [Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services] – a basic version of Active Directory services. The purpose of this feature is to provide directory services only. One situation in which it can be used is when you have applications that need access to a directory service but do not need access to an Active Directory database. This feature can be used even in environments where there are no Active Directory domains. As you can imagine, there is no need for casual Windows users. It is only useful for developers and businesses that use applications that require this feature.
- Workbook client computer [Work Folders Client] – allows users to synchronize a folder and its contents from the corporate network to their personal devices. Files created locally will be synced back to the file server in the corporate environment.
- Remote differential compression API support [Remote Differential Compression API Support] – is a synchronization algorithm that allows fast comparisons between synchronized files and detects the data that was removed or added from their contents. You can find more information about the RDC algorithm here. This feature is used by a small number of Windows programs and applications, so it's best to keep it enabled.
- SMB 1.0/CIFS file sharing support [SMB 1.0/CIFS File Sharing Support] – this feature allows file and printer sharing with computers running older versions of Windows, from Windows NT 4.0 to Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 R2. The Server Message Block (SMB) protocol can be used by other operating systems such as Linux or macOS to communicate with Windows devices. If this is happening on your network, it's safer not to disable it.
- Windows subsystem for Linux [Windows Subsystem for Linux] – allows you to install and use Linux distributions such as Ubuntu, OpenSUSE, Debian or Kali Linux on Windows. You can read more about it from here.
- Hosted Web core of Internet Information Services [Internet Information Services Hostable Web Core] – another web server feature that is a lighter version of IIS. It includes only the core components of the IIS web engine and requires less resources to run. You can use it to host just one website, and it's useful for enabling basic web server features for custom or debug applications. This feature is only required by software developers and IT professionals. Ordinary users do not need to install it.
This was a long guide about the additional features of Winodws 10 and Windows 11! Although the list was based on Windiws 10 21H2, Windows 11 21H2 has exactly the same capabilities with a slight difference in the title of Windows Projected File System (it says "Winodws Projected File System") and is therefore in a different order.
We hope you find it useful and that it has answered your questions about the various Windows features available.





