Process Monitor is a Windows Sysinternals tool that monitors and displays in real-time all file system activity.
The Process Monitor monitors and records all actions attempted against it registerof Microsoft Windows. It can be used to detect failed read attempts and enrollmentof registry keys.
It also allows filtering on specific keys, processes, process IDs and values. In addition, it shows how applications use files and DLLs, detects some critical errors in system files, and more.
Process Monitor combines two older tools, FileMon and RegMon and usesin systems administration, computer forensics and application debugging.
It allows you to log every single incident that happens on your Windows PC. With Process Monitor, you can see which registry keys are being updated by any application. Even if a service or application spawns a new process, changes the file system in some way, or connects to a network.
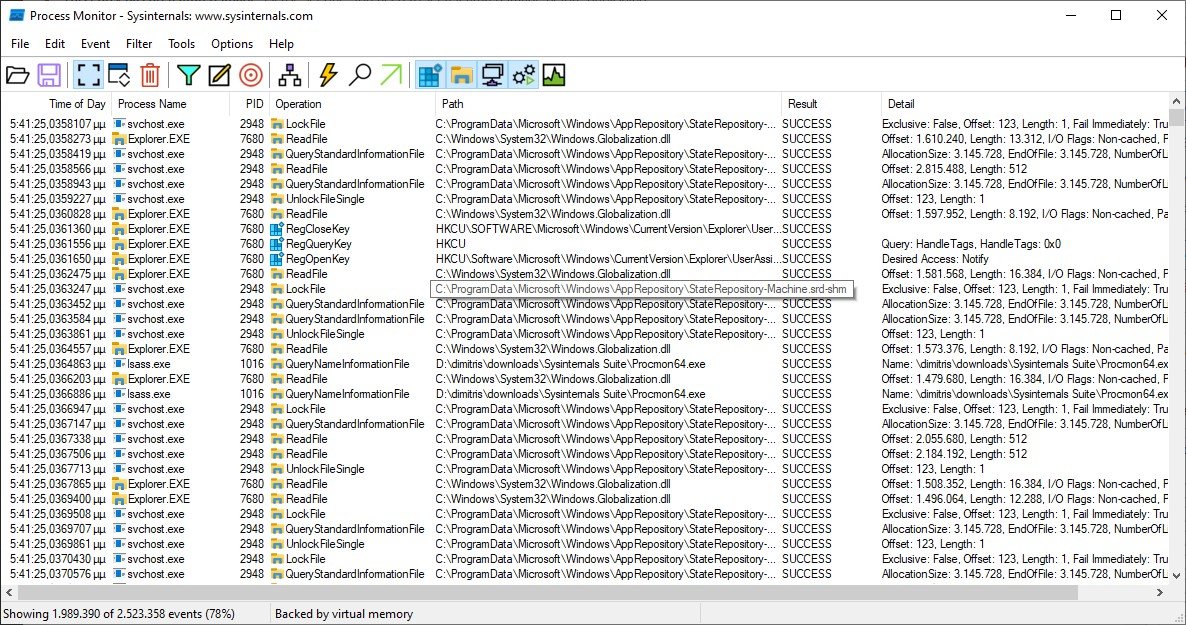
When you first open Process Monitor, it will greet you with a huge amount of rows and data. In the background, Process Monitor will continue to record any registry, file system, network, process and profile event that may occur. This means that the list of data will grow quickly even if your machine is idle as the services interact with your system.
The key to using Process Monitor effectively is to filter and focus only on the events that interest you.
For example: to quickly filter Microsoft processes, you can go to Options > Select Columns (Options > Select Columns) and include the Company Name. Then, by simply right-clicking on the column, you can use the function Include / Exclude (Include / Exclude) in the context menu to quickly filter these events.
By double- or right-clicking an event and selecting Properties (Properties) will open an additional dialog with lots of information. From this dialog, you will be able to specify the class of the event (eg File System or RegistryQueryKey), the path to the physical mode and the result.
From here you can dig even deeper by going to the tab Stack (Stack) where you can see the individual DLLs associated with the event.
By default, Process Monitor uses your computer's virtual memory to store events that are temporary. If you go to File > Backing Files (File > Backing Files), you can specify a file to write and save the data to.
It is of course free, portable and you can download from here.





