Τι συμβαίνει εσωτερικά του δρομολογητή ή router σας; Ίσως γνωρίζετε ότι ο υπολογιστής σας και το τηλέφωνό σας έχουν address IP. Your IP address is used to identify you online, but the Internet is not the only network you are connected to.
Before you get to the Internet, you connect to a private network through your router. Any other device connected to the same router is part of this private network. In this network, every computer, every phone and every tablet have their own private IP.
Similarly, and your router has its own private IP within this network.
The most common default IP address for one router (router) or modem is 192.168.0.1. If you type IP into a browser, you will have access to your router's or modem's online settings page to make the changes you need.
Public and private IP
A private IP is an IP address assigned by a router to devices located within a private network.
These IPs are not accessible outside of the network.
For example, your router and each connected device are a private network. Computers that are connected to the same router can access each other, which can not be done by a computer that is out of network (connected to another router).
Within a private network, the IP address corresponding to each device is unique. But perhaps your neighbor's router on his own private network uses exactly the same private IPs for different devices.
A public IP is now the address that corresponds to devices that are connected to the internet.
This address is available from your ISP and no other internet system can have the same address.
When you connect to the internet, you become part of a much larger network that you can connect to. Your public IP is always visible unless you choose to hide it with a VPN service.
IP address templates
All IP addresses follow a template. The standard for IP addresses is defined by the Registered Internet Number Authority or the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). IANA has two standards for the public IP addresses we use.
The IP version of 4, known as IPv4, and the relatively new IPv6.
An IPv4 address consists of a series of four numbers, separated by a dot. Each number can have from 1 to 3 digits.
An IPv6 address consists of a series of eight numbers, each of which has a length of four digits. Unlike an address of the IPv4 template that is numbered, an IPv6 address uses hexadecimal numbers.
Let's say that today both models are used because there are only 4 billion unique IPv4 addresses.
If you think we live in a world where refrigerators can connect to the internet, the need for more IP addresses is obvious.
For this logic was created and there is the IPv6 standard.
Reservations for private IP addresses (routers and devices)
IANA has blocked some IP addresses to be used by private networks. We previously mentioned that a private IP address is unique on the local network, but the same IP address can be assigned to other devices in a different private network.
The number of reserved IP addresses for private networks is almost 18 million and moves to the following range.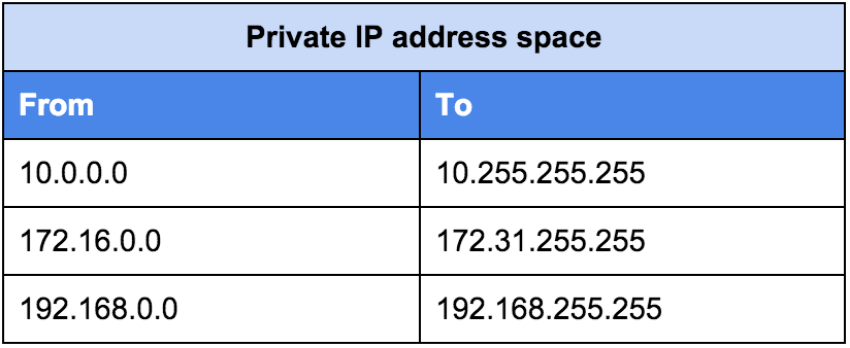
The IP 192.168.0.1 is one of these.
When you connect to the internet, you are part of a larger network. Your private network continues to be private and your private IP is not visible to anyone.
To "connect" to the Internet, you connect through the private IP address of your router, which is your router, which connects to the Internet Service Provider (ISP) you use. Your ISP will assign a public IP address to your router and your computer.
Find your public IP address
To find the public IP of your computer, visit google and search for "My IP". Google will immediately show you the public IP of your computer. You can also do it from smartphones or tablets.
Find the private IP router
To find the private IP address of your computer:
In the Windows search, search for cmd. Run the application and type
ipconfig to display the list of all the connections on your computer.
Η price of IPv4 is your private IP address.
For a wireless adapter, Wi-Fi or LAN, look for Default Gateway. This is the private IP address of your router.





