Have you ever wondered what the resolutions of a 720p, 1080p, 1440p, 2K, 4K video or camera mean? Do you know what the aspect ratio of an image is? Do you know what you have on your cell phone?

When technology was still in its infancy in the 80s, screen resolution was out of the question. Windows at the time had some preset options and, if you had a higher resolution, you would just see the censor a little clearer, flashing on a black background.
As time went on technology jumped, colors appeared, and you could choose better video cards and better screens. Today you have a variety of options regarding screens, graphics cards, their quality and supported resolutions.
In this article, we tell you the story of video resolution, explaining all the basic concepts, including common acronyms for screen resolution, such as 1080p, 2K, QHD or 4K. Let's start:
It all started with IBM and CGA
Color graphics technology was first developed by IBM. First brought the CGA (Color Graphics Adapter) followed by EGA (Enhanced Graphics Adapter) and then VGA (Video Graphics Array). Regardless of the capabilities of your monitor, you should choose one of the few options available then, through your graphics card drivers. If you feel nostalgic for your childhood, see in the photo below how things were on a once famous CGA screen, with the revolutionary 4-color resolution.

With the advent of high definition video and the growing popularity of 16: 9 aspect ratio (explained below for aspect ratio), the option of screen resolution is not the simple case it once was. This means that there are many more options to choose from, and also that there is something that almost suits the preferences of most users. But let's see what the current terminology is and what it means:
What does screen resolution mean?
The term "analysis"(resolution) is incorrect when used to indicate the number of pixels on a screen. This says nothing about how concentrated they are pixel. Essentially the pixel density is covered by another measurement, called PPI (Pixels Per Inch) or in Greek “pixels per inch".
"Resolution" is technically the number of pixels per unit area and not the total number of pixels. In this article, we use the term as it is commonly understood, instead of the absolutely technologically correct use. From the beginning, the resolution is described (accurately or not) by the number of pixels placed horizontally and vertically on a screen. For example, 640 x 480 pixels = 307200 pixels.

You can easily tell the difference between the right terminology if you have a 720p digital video which means it has a resolution of 1280x720 pixels and try to see it first on your computer screen which is 21 "and then on your TV which is 50". On the computer you will have a much better image because you just have a higher ppi, so a clearer image.
The available screen resolution options are determined by the capability of your video card and vary from manufacturer to manufacturer.

Built-in resolutions in older Windows were limited, so if you did not have the driver for your graphics card, you would be stuck on a lower resolution screen because of Windows.
If you've watched the old Windows installation process or installed a newer version of a video driver, you may have seen the low-resolution 640 x 480 screen for a moment or two. It was bad, but that was the default Windows.
As screen quality improved, Windows began to offer a few more built-in options, but the burden was still on the graphics card makers, especially if you wanted a really high resolution screen.
The latest versions of Windows can detect the default screen resolution for your monitor and graphics card and adjust accordingly. This does not mean that what Windows chooses is always the best option, but it works just fine and you can change it if you want. If you need guidance, read “How To Run PC Games At Higher Resolution From Your Screen”.
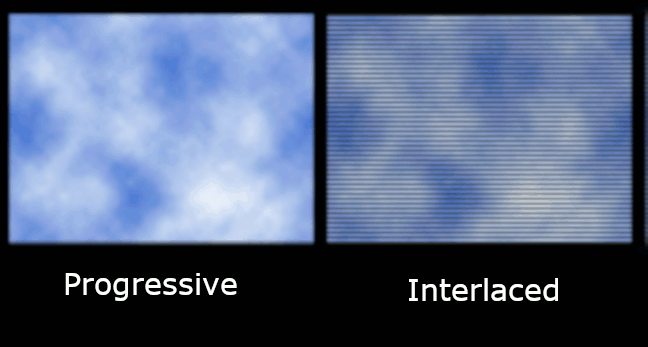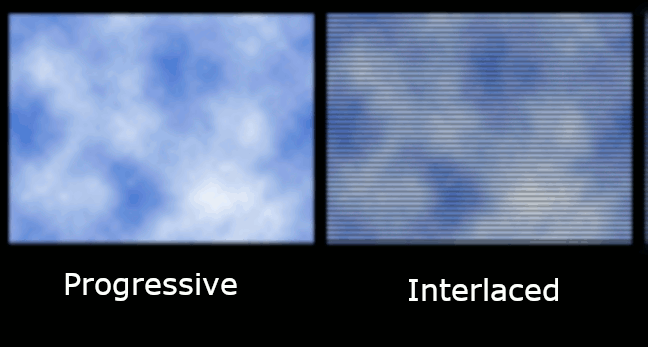
Notice the p and i in the screen resolutions
You may have seen the screen resolution described as something like 720p, 1080i or 1080p. What does this mean? Initially, the letters tell you how the image is "painted" on the screen. The "p" means progressive (progressively), and thei" means Interlaced (braided).
Our interlaced scan comes from our TV and early CRT monitors. The screen has lines of pixels arranged horizontally along it. The lines were relatively easy to see if on old screens or TVs you came too close and looked at its glass, but today the pixels on the screen are so small that it is difficult to see them even at magnification.
Screen electronics "paint" each screen, line by line, very quickly for the eye to see. A braided screen first draws all the unnecessary lines and then all the even lines.
As the screen takes shape in alternating lines, flicker has always been a problem with interlaced scans. Manufacturers have tried to overcome this problem in various ways. The most common way is to increase the number of times (frequency) that an entire screen is painted in one second, what is called the "refresh rate".
The most common refresh rate was 60 times per second, which is acceptable to most people, but could be increased slightly to get rid of the flicker that some users were still experiencing.
As people moved away from the older CRT monitors, the terminology changed from refresh rate to frame rate, due to the difference in how operation of an LED screen. Frame rate is the speed at which the monitor displays each individual image (frame) of data.
The latest versions of Windows set the frame rate to 60 Hertz or 60 cycles per second and the LED screens do not flicker. In addition, the system changed from interlaved scanning to progressive scanning, because new digital monitors are much faster.
In a progressive scan, the lines are drawn on the screen in order and not the single lines first and then the even lines. If you want to translate, the 1080p, for example, is used for screens characterized by 1080 horizontal lines and progressive scan.
What about the numbers: 720p, 1080p, 1440p, 2K, 4K and 8K?
When high-definition televisions became the norm, manufacturers developed a shorthand to explain their screen resolution. The most common numbers you see are 720p, 1080p, 1140p or 4K. As we have seen, "p" and "i" tell you if it is a screen with prograssive scan or interlaced scan.
In addition, these abbreviations are sometimes used to describe computer monitors, although in general a computer monitor may display higher definitions than a television. The unique number always refers to the number of horizontal lines on the screen.
See how the abbreviation translates:
- 720p = 1280 x 720 - commonly known as HD resolution or "HD Ready"
- 1080p = 1920 x 1080 - commonly known as FHD or "Full HD" resolution
- 1440p = 2560 x 1440 – commonly known as QHD or Quad HD resolution and commonly seen on gaming monitors and smartphone high technology. 1440p is four times the resolution of 720p HD or “HD Ready”. To make matters even more confusing, a lot premium smartphones have the so-called 2960×1440 Quad HD+ resolution, which still matches 1440p.
- 4K or 2160p = 3840 x 2160 - commonly known as 4K, UHD or Ultra HD resolution. It has a huge screen resolution and is found on premium TVs and computer screens. 2160p is called 4K because the width (vertical lines) is close to 4000 pixels. In other words, it offers four times the pixels of 1080p FHD or "Full HD".
- 8K or 4320p = 7680 x 4320 - known as 8K and offers 16 times more pixels than normal 1080p FHD or "Full HD" resolution. At the moment, you only see 8K on expensive TVs from Samsung and LG. However, you can test whether your computer can output such a large amount of data using this 8K video sample:
The problem with 2K is that it does not exist for consumer devices
In cinema there is the 2K resolution, and it refers to 2048 × 1080. However, in the consumer market it would be considered 1080p. To make matters worse, some monitor manufacturers use the term 2K for resolutions such as 2560 × 1440, because their screens have a horizontal resolution of just over 2000 pixels. Unfortunately, this is incorrect, as this resolution is 1440p or Quad HD and not 2K.

Therefore, when listening to a TV, computer monitor, smartphone or tablet with 2K resolution, this statement is incorrect. The actual resolution is likely to be something like 1440p or Quad HD.
Can you watch high resolution videos on lower resolution screens?
You may be wondering if you can watch a high resolution video on a smaller screen. For example, is it possible to use a 720p TV to watch 1080p video? The answer is yes!
Regardless of the resolution of your screen, you can watch any video on it, regardless of the video resolution (higher or lower). However, if the video you want to watch has a higher resolution than your screen, your device converts the video resolution to the one that matches your screen resolution. This is called downsampling.
For example, if you want to watch a 4K video on a 720p screen, this video is displayed in 720p resolution because that is all your screen can offer.
Pixel density
Pixel density is the number of pixels packaged in an inch of the screen and measured in pixels per inch (PPI). It is important that a large screen has a higher resolution so that the pixel density is high enough to display good quality images.
For example, a 65-inch TV with 4K resolution has about 67 ppi. Compare this to a 24-inch 1080p TV, which has a higher ppi of about 91. Although a 65-inch TV has a higher resolution, images will appear clearer. on the 24-inch TV due to the higher pixel density.

If you buy a TV, one ppi 90-110 is considered the sweet spot. For a screen, you need to aim for a higher one ppi about 200-250 or more, depending on your viewing distance. The closer you sit to a screen, the more ppi you need.
You can use an online ppi calculator for comparing screens with different sizes and resolutions.
What is the ratio of dimensions?
The term "aspect ratio" was originally used in cinema Movies, indicating how wide the image was relative to its height. Movies originally had a 4:3 aspect ratio, and this carried over to television and early computer screens.
The aspect ratio of the movie changed much faster on a wider screen, which meant that when movies were shown on the TV, they had to be cropped or the image had to be modified in other ways to fit the TV screen.

As screen technology improved, manufacturers of televisions and monitors began to move toward widescreen monitors as well. Initially, "widescreen" referred to anything wider than the standard 4: 3 screen, but it soon came to mean 16:10 and later 16: 9. Today, almost all computer monitors and TVs are only available in widescreen, and TV shows and Web sites have been customized to fit.
As of 2010, the 16:10 aspect ratio was the most popular aspect ratio for widescreen monitors. However, with the growing popularity of high-definition televisions, which used high-definition resolutions such as 720p and 1080p and made these terms synonymous with high-definition, 16: 9 became the standard ratio for high-definition dimensions.
Depending on the aspect ratio of your screen, you can only use resolutions that are specific to its width and height. Some of the most common analyzes that can be used for any aspect ratio are the following:
- 4: 3 aspect ratio resolutions: 640 × 480, 800 × 600, 960 × 720, 1024 × 768, 1280 × 960, 1400 × 1050, 1440 × 1080, 1600 × 1080, 1600 × 1200, 1600 × 1200, 1,4 × 2, 1,0 × 2, 1,0 × 2, 185 × 1, 4 × 2, 185. 1. 1536.
- 16:10 aspect ratio analyzes: 1280 × 800, 1440 × 900, 1680 × 1050, 1920 × 1200 and 2560 × 1600.
- 16: 9 aspect ratio resolutions: 1024 × 576, 1152 × 648, 1280 × 720 (HD), 1366 × 768, 1600 × 900, 1920 × 1080 (FHD), 2560 × 1440 (QHD × 2) 134, and 7680 x 4320 (8K).
Is there a relationship between aspect ratio and screen orientation?
Screen orientation refers to how you view a screen: the most commonly used screen orientations are horizontal and vertical. Horizontal orientation means that the width of the screen is greater than its height, while vertical orientation means the opposite.
Most large screens, such as those used in our computers, laptops, or televisions, use landscape orientation. Smaller screens, such as our smartphones, are usually used in portrait mode, but because their size allows you to rotate them easily, they can also be used in landscape mode.
The screen aspect ratio determines the ratio of its longest side to its smallest side. Therefore, this means that the screen aspect ratio tells you the ratio of width to height when you look at it in landscape mode. The aspect ratio is not used to describe screens (or any rectangular shapes) in portrait mode.

In other words, you could say that a 16 × 9 aspect ratio is the same as a 9 × 16 aspect ratio, but the latter is not an acceptable aspect ratio reference. However, you can refer to the screen resolution in both ways. For example, a resolution of 1920 × 1080 pixels is the same as 1080 × 1920 pixels, only the orientation is different.
How does screen size affect resolution?
Although a 4: 3 TV can be configured to display black lines at the top and bottom of the screen while viewing a widescreen movie, this does not make sense with a computer screen, so Windows does not even offer widescreen viewing. as an option. You can watch movies with black lines as if you were watching a TV screen, but this is done by your media player and not by Windows.
The most important thing in a computer is not the size of the screen, but its ability to display higher resolution images. The higher you set it resolution, the smaller the images on the screen and there comes a point where the text on the screen becomes so small that it is illegible.
On a larger screen you can push the resolution too high, but if the pixel density of this screen does not match the resolution you give it, you will not get the maximum resolution before the image becomes unreadable.
In many cases, the screen shows absolutely nothing if you tell Windows to use a resolution that the screen can not handle. In other words, do not expect miracles from a cheap screen. When it comes to high definition monitors, you definitely get what you pay for.
Do you have any other questions about screen resolution?
If you're not a technician, you're probably confused by so many technical details about screens and resolutions. Hopefully this article has helped you understand the most basic features of a screen: aspect ratio, resolution or resolution type, pixel density.
If you have any questions you can ask in the comments of the article.






What role do Mbit / sec play in a video file? What is the difference between an 8000 and 16000 or 50000 Mbit file?
You are obviously talking about the bitrate of a video or in Greek the flow rate. In a few words:
Every second of the video is filled with digital video and audio information. Other times it's a lot like a 4K video, and a few times like a live video on Facebook. These two types of videos have very different volumes of data. The amount of information per second in the video is known as a bitrate and is measured in Mbps / sec (in audio we usually measure in Kbit / sec).
The bitrate is different from other video quality metrics, such as frame rate, resolution, or video format (encoding). These factors represent specific things about the nature of the shot, such as how many frames pass through the screen per second or how big the image is, what kind of compression it has undergone. Bitrate is more fundamental.
A 4K video, with a certain number of frames and the same sound can have a different bitrate due to different compression (mp4 or avi or mov etc). The higher the bit rate, the higher the video quality, but also the larger the file size. Also, if you are talking about video streaming, that is, streaming, the bitrate should be a little smaller than your connection, otherwise the image will "hang".