Windows 10 has the ability to automatically empty the recycle bin, delete temporary files, and remove some other files to free up disk space.
This is possible with the Storage Sense feature. However, if you are not happy with this new operating system mode, you can disable it. This can be done either with Settings or Registry setup. You can also prevent users from changing settings either through the Policy Group or the Registry.

"Storage Sense" is a nice, modern replacement for Disk Cleanup. It allows you to prevent certain folders from becoming too large and clean complete videos. Sense Storage can be found in Settings -> System -> Storage.
Storage Sense can be used to remove Windows upgrade logs, Windows error logs, Windows Defender temporary files Antivirus, των μικρογραφιών, των προσωρινών αρχείων Internet, των πακέτων προγραμμάτων οδήγησης, της κρυφής μνήμης Shader DirectX, driver files, log files, memory dump files, system error and minidumps, temporary Windows update files, and more.
If you do not find any use in Storage Sense or you are simply not happy with its behavior, you can turn it off. To turn it off, do the following.
Set up User Saving Control
a. Through the Settings
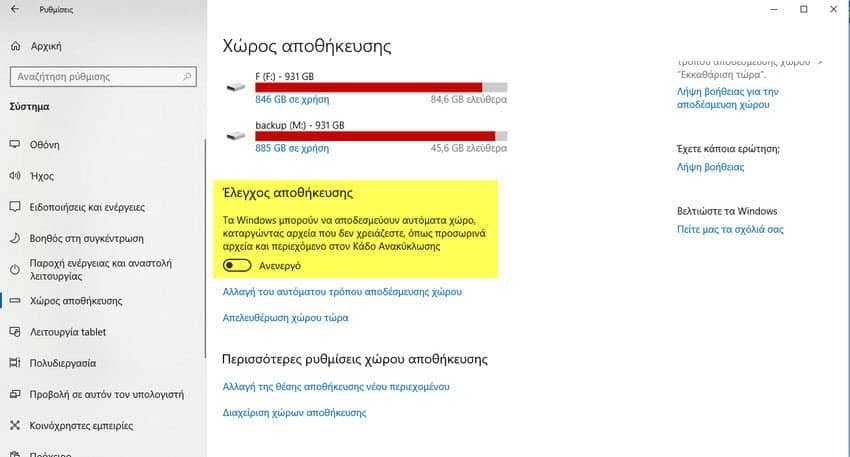
a.1 Open the settings.
a.2 Go to System - Storage.
a.3 Disable Save Storage.
β. Through the registry
First of all, make sure you are logged in as an Administrator before proceeding. Now, do the following.
b.1 Open the Registry Editor application. If you don't know how, then press the Win + R keys at the same time and in the "Run" window write regedit and press the OK button.
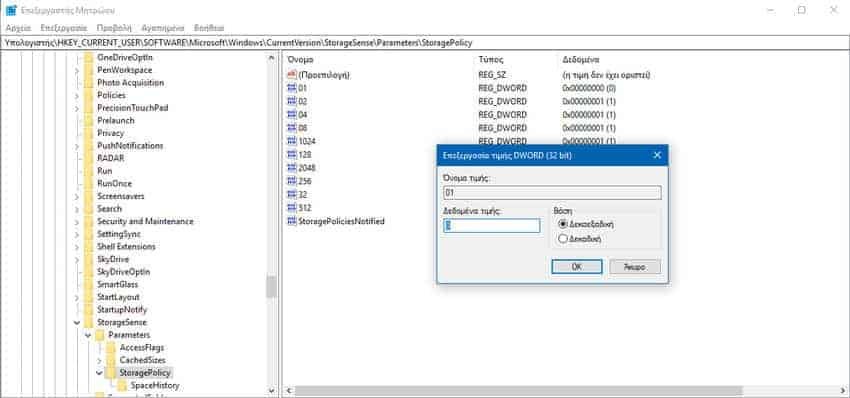
b.2 Go to the following registry key.
HKEY_CURRENT_USER \ Software \ Microsoft \ Windows \ CurrentVersion \ StorageSense \ Parameters \ StoragePolicy
b.3 On the right, modify or create a new 32 bit DWORD value called 01. Set 0 as data to turn off Storage Sense. With 1 value data, they will re-enable it.
(Note: Even if you run Windows 64-bit you have to create a 32 bit DWORD value).
To make the changes made by the registry editor simply close it and you will need to log out and log in to a user account.
Prevent user from changing the User Control
a. Through the Registry
Finally, you can disable or enable Sense Storage for all users on Windows 10, without being able to change from them, with group policy.
a.1 Open Registry Editor.
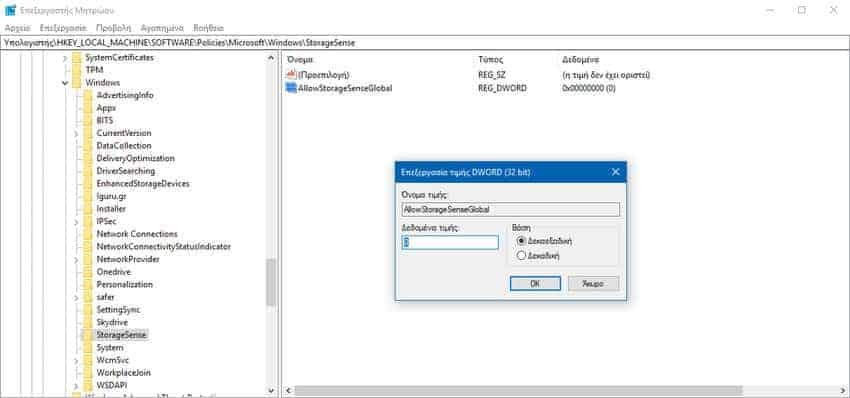
a.2 Go to the following registry key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE \ SOFTWARE \ Policies \ Microsoft \ Windows \ StorageSense
If you do not have such a key, just create it.
a.3 While in the StoregeSense key, create a new 32-bit DWORD value with name AllowStorageSenseGlobal. Note: Even if you are running 64-bit Windows, you should use a 32-bit DWORD as the value type.
a.4 Set it to 0 to disable Storage Sense.
a.5 Restart Windows 10 to apply the restriction and finish.
Later, you can delete the AllowStorageSenseGlobal value to allow the user to manually check the Storage Sense function.
b. Through the Political Group
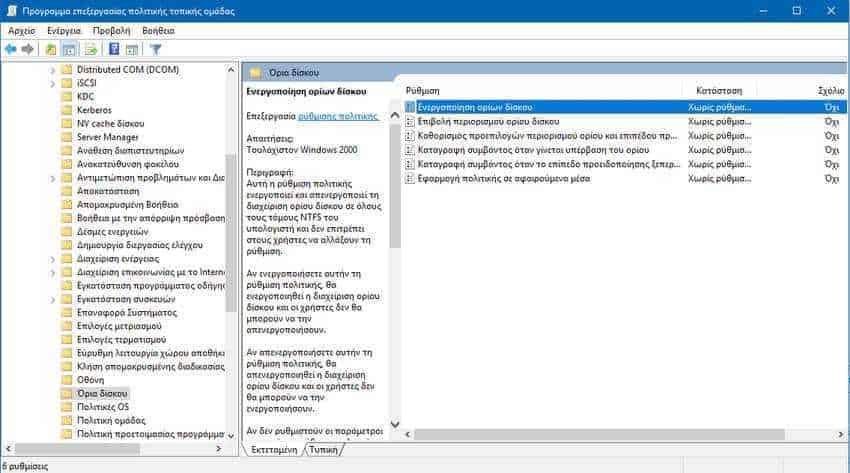
If you're running Windows 10 Pro, Enterprise, or Education, you can use the Program Editorwork Local Group Policy to configure the options listed above, with a graphical interface.
b.1 At the same time, press the Win + R keys on your keyboard and in the Running window that appears, type gpedit.msc, and then press OK.
b.2 The Local Group Policy Editor will open. Go to Computer Settings -> Management Templates -> System -> Disk Limits (Computer Configuration \ Administrative Templates \ System \ Storage Sense). Set the Allow Storage Sense policy to what you want.
If you later want to allow the user to configure it themselves, simply set "Enable Disk Limits" to "no setting". You're done.





