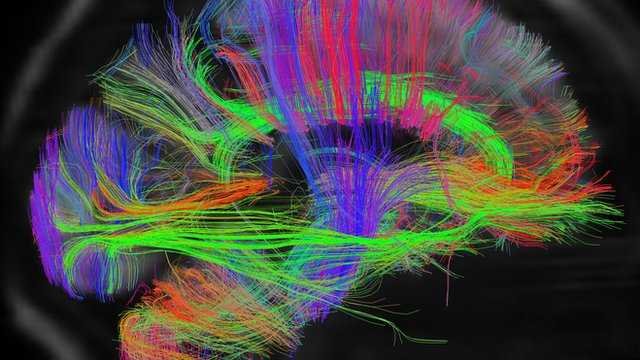
American scientists have announced that they have created the most complete 3D "map" to date of the neuronal connections inside the brain of a mammal, specifically a mouse. It is yet another major advance in the long-standing effort to understand how modeς του εγκεφάλου του ανθρώπου και των νευροεκφυλιστικών ασθενειών του. Όμως για να γίνει ένας ανάλογος «χάρτης"For the human brain, it will take several more years.
Οι ερευνητές, με επικεφαλής τον Χονγκούι Ζενγκ του Ινστιτούτου Άλεν για την Επιστήμη του Εγκεφάλου στο Σιάτλ, που έκαναν τη σχετική δημοσίευση στο περιοδικό "Nature", σύμφωνα με το πρακτορείο Ρόιτερ και το "New Scientist", χαρακτήρισαν «ορόσημο» το επίτευγμα δημιουργίας ενός αναλυτικού «χάρτη» (Allen Mouse Brain Connectivity Atlas) με όλες τις διασυνδέσεις, που σχηματίζουν τα διάφορα λειτουργικά κυκλώματα του εγκεφάλου.
Όπως είπε ο νευροεπιστήμονας Ντέηβιντ βαν Έσεν του Πανεπιστημίου Ουάσιγκτον - Σεν Λιούις, «πρόκειται για την πιο λεπτομερή ανάλυση της εγκεφαλικής "συνδεσμολογίας" που διαθέτουμε σήμερα για οποιονδήποτε εγκέφαλο θηλαστικού». Ο «χάρτης» δείχνει με ποιό τρόπο τα εκατομμύρια νευρώνες (εγκεφαλικά κύτταρα) συνδέονται και επικοινωνούν μεταξύ τους μέσω των προεκτάσεών τους (των νευραξόνων), για να παράγουν τις μνήμες, τις συμπεριφορές και τα συναισθήματα. Τα ανατομικά και λειτουργικά problems of these circuits cause brain diseases.
Before this mouse brain map, scientists had at their disposal only the complete - but much simpler - neuronal "ligature" of the C.elegans worm, which has just 302 neurons. In comparison, the mouse brain contains 75 million neurons, and the human brain has around 85 billions of neurons, each of which generates up to 10.000 connections with other neurons.
Η «χαρτογράφηση» του εγκεφάλου του ποντικιού επιτεύχθηκε με τη βοήθεια ιών, μέσω των οποίων εισήχθη μια φθορίζουσα πρωτεΐνη στον εγκέφαλο του ζώου, κάτι που "φώτισε" πράσινα τα νευρωνικά κυκλώματα κάτω από το μικροσκόπιο. Μεταξύ άλλων, διαπιστώθηκε ότι οι νευρωνικές συνδέσεις που περιορίζονται μόνο στο ένα ημισφαίριο του εγκεφάλου, είναι πάντα ισχυρότερες από εκείνες που απλώνονται και στα δύο ημισφαίρια.
Για να «χαρτογραφηθεί», ο εγκέφαλος των ποντικιών τεμαχίστηκε σε 500.000 τμήματα - κύβους, που ο καθένας είχε πλευρά 100 μικρομέτρων (εκατομμυριοστών του μέτρου. Αυτός ο «χάρτης» έχει περαιτέρω περιθώρια μεγάλης βελτίωσης από πλευράς ανάλυσης, καθώς «ιχνηλατεί» τις διασυνδέσεις μεταξύ μικροσκοπικών περιοχών εγκεφαλικού ιστού (που η κάθε μία περιέχει 100 έως 500 νευρώνες), αλλά δεν περιλαμβάνει τις ακριβείς διασυνδέσεις (συνάψεις) όλων των επιμέρους νευρώνων μεταξύ τους.
Such a sharpening "map" to the human brain (cell to cell) is the ultimate goal. It is, however, assumed that, apart from many similarities, such a "map" will be unique to each individual person, in the same way that each of us is a unique personality.
The gene's "atlas" of the human embryonic brain
Moreover, in a second study, scientists also from the Allen Institute, who made the relevant publication in the same journal, released the first detailed XNUMXD images of the stages of fetal brain development in the womb. THE research, στο πλαίσιο του προγράμματος "BrainSpan Atlas", ελπίζεται ότι θα βοηθήσει στην κατανόηση των διαταραχών που «πυροδοτούνται» πριν από τη γέννηση, όπως η σχιζιφρένεια και ο αυτισμός.
The researchers, led by Ed Lin, analyzed the brains of four human embryos, which were between 15 and 21 week of pregnancy, thus creating the first "atlas" of sequential gene changes in the developing brain, which genes are activated and they are deactivated sequentially as the brain develops.
“That was just the beginning. We want to understand the plan with base το οποίο "χτίζουμε" έναν εγκέφαλο και αυτό ήταν το πρώτο βήμα προς αυτή την κατεύθυνση, καθώς αρχίσαμε να δημιουργούμε έναν χάρτη του τρόπου που τα γονίδια καθοδηγούν την όλη διαδικασία», δήλωσε ο Εντ Λάιν. «Γνωρίζοντας πού και πότε ένα γονίδιο εκφράζεται στον εγκέφαλο, μπορεί να μας παρέχει σημαντικές ενδείξεις για τον ρόλο του».
In the future, when neuroscientific research will have gone further, scientists hope they will be able to compare the human brain with other mammals, such as monkeys and mice, to understand where human specificity is. The ultimate goal is to discover the neurobiological basis of the greatest of all mysteries: human consciousness.
Link: For original scientific papers (subscription) at the following addresses:
http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/nature13186.html and
http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/nature13185.html
News Room «Profit» with information from APE - AMPA