Η team developers of the FonixCrypter ransomware announced on Twitter today that they have deleted the source code of the ransomware and plan to stop it from working.
As a goodwill gesture to previous victims, the FonixCrypter gang released a package containing a tool decryption files, instructions and the ransomware master decryption key.
These files can be used by infected users to decrypt and recover their files for free, without having to pay a ransom.
Fonix Ransomware Master RSA Key (Spub.key & Spriv.key) and Sample decryptor : #Phoenix #ransomware #XINOF #FonixCrypter #close_project #hack #Malware #raas #ransomware_as_a_servicehttps://t.co/JcijzvOKvf
- fnx (@ fnx67482837) January 29, 2021
Allan Liska, a security researcher, tested the decryptor and confirmed that the FonixCrypter application, instructions and master key work as the criminals report.
“The decryption key provided by the hackers behind Fonix ransomware appears to be legit, I believe it requires each file to be decrypted separately”, said Liska on ZDNet.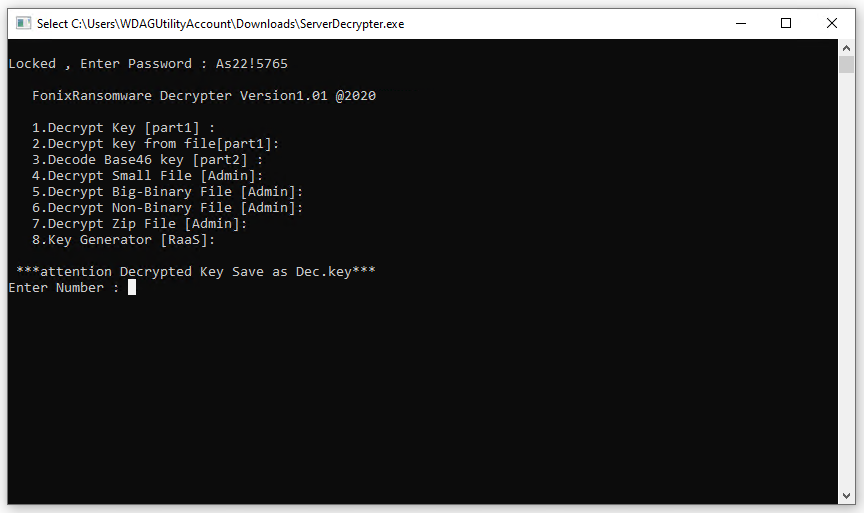
"The important thing is that they released the master key, which enables someone to create a much better decryption tool," he added.
A better cryptographer is currently in Emsisoft projects and is expected to be released next week, said Michael Gillespie, an Emsisoft security researcher.
Users are advised to wait for the Emsisoft decoder instead of using the FonixCrypter developer decryptor. No one can be sure if it contains backdoors.
The FonixCrypter ransomware gang has been active since at least June 2020, according to Andrew Ivanov, a Russian security researcher who has been following ransomware issues on his personal blog for the past four years.
Ivanov's blog post about FonixCrypter presents a history of constant updates to FonixCrypt code, with at least seven different FonixCrypt variants released last year.





