In this guide we will talk about Ring3 debugging
Objectives of the guide:
- Effectively analyze a Ring3 debugger, such as Immunity Debugger
- It can control the execution of the program
- Ability to monitor / change program status (registers, μνήμη)
- Commenting on Immunity Debugger
This guide can be used as a lab module for:
- Computer architecture
- Operating Systems
- Discrete mathematics
1. Import
To reverse a malware, a quality debugger is essential.
There are two types of debuggers: user-level debuggers (e.g. OllyDbg , Immunity Debugger, and IDA Pro ), and kernel debugging (such as WinDbg , Softicce and Syser).
The difference between user / kernel-level debuggers is that kernel debuggers run with higher permissions and therefore can detect drivers and kernel devices, while user-level debuggers cannot.
It is known that modern operating system such as Windows relies on the processor (eg Intel CPU) to provide a multi-level collection areas of protection.
Για παράδειγμα, σε μια τυπική CPU της Intel, τα προγράμματα μπορούν να εκτελεστούν σε τέσσερις λειτουργίες, από ring0 (λειτουργία πυρήνα) έως ring3 (επίπεδο χρήστη). Σε αυτήν την περίπτωση, αποκαλούμε επίσης εντοπιστές σφαλμάτων επιπέδου χρήστη "ring3 debuggers"
One question you may have is: Since ring0 debugger is more powerful than ring3 debugger, why not use ring0 debuggers directly?
Ring3 debuggers usually come with a GUI that can significantly improve the productivity of a reverse engineer. Only when necessary will we use the command line detectors ring0 (such as WinDbg).
But there is one exception, IDA Pro has introduced a GUI that can be used in WinDbg to detect kernel errors. It's a nice feature but you have to pay for it.
In this guide, we assume that you would like to use open source / free software tools. The following is a combination of debuggers that we will use throughout the wizard: Immunity Debugger ( IMM for brevity) and WinDbg.
2. Short tour of IMM
A brief introduction to IMM.
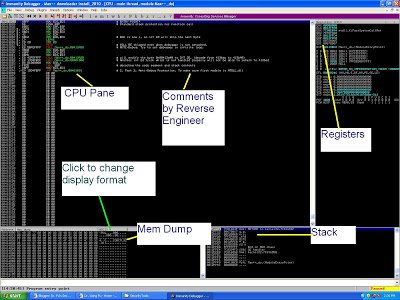 |
| Figure 1. IMM screenshot |
As shown in Figure 1, top left, we have the CPU window (which shows its sequence of instructions machineand user feedback), the Register window (in which you can monitor and modify register values), the Stack window, and the memory indicator.
Before we try to reverse the first section of Max ++, it is helpful to learn how to use the shortcut keys in the debugger effectively.
In general, to use a debugger effectively, you need to know the following:
- How to control the execution flow? ( F8 - βήμα πάνω, F7 - βήμα, F9 - συνέχεια, Shift + F9 - συνέχιση και εξαίρεση)
- How to look at the data? (In the Memroy window: right click -> binary -> edit , in the registration window: right click -> edit)
- How to set breakpoints? ( F2 for soft-breakpoint switching, F4 - τρέξτε στον κέρσορα, κάντε δεξί κλικ στην εντολή -> Breakpoint -> για hardware and memory access point )
- Comment ( ; for comment)
Most of the above are in the IMM debug menu, however, it is always helpful to remember the shortcut keys. We briefly explain some of the functions that are very useful in analysis.
2.1 Execution flow control
The difference between step over / step in is similar to all other debuggers.
The step in (F7) enters the function of a call command. Step over (F8) performs the entire operation and then stops at the next instant command. Note that the F8 may not always give you the result you want.
F9 is often used to continue from a point where you have stopped. Note that debugger automatically handles many exceptions for you. If you want to keep track of all the exceptions, you should use SHIFT+F9 . Later, we will see an example where Max ++ rewrites the SEH (structured exception) to detect the existence of debuggers. To work around this anti-debugging trick, you will use SHIFT + F9 to manually check the SEH code.
2.2 Handling data
Generally, you have three types of data to manage: (1) registers, (2) stack (Stack) and (3) all other sections (code, data and stack).
Για να αλλάξετε την τιμή ενός μητρώου, μπορείτε να κάνετε δεξί κλικ στο μητρώο και να επιλέξετε Επεξεργασία για να αλλάξετε την τιμή του. Σημειώστε ότι όταν ένα μητρώο περιέχει ένα δείκτη μνήμης (η διεύθυνση μιας υποδοχής μνήμης), είναι πολύ βολικό να κάνετε δεξί κλικ πάνω του και να επιλέξετε " Follow in Dump " the " Follow in Stack " για να δείτε την αξία του.
The IMM design does not allow you to instantly change the value of the EIP registry in the Register window. However, it is possible to change the EIP using the Python shell window.
In the Memory Dump window, select and right-click on any data, then select Binary-> Edit . You can enter data easily (as a string, or as a binary number).
Μπορείτε να επαναφέρετε τον κωδικό (ως δεδομένα). Στο παράθυρο CPU, κάντε δεξί κλικ και επιλέξτε " Assemble ", οπού μπορείτε να τροποποιήσετε άμεσα το τμήμα κώδικα.
You can even modify a program using this feature. For example, after modifying the code snippet, you can save the modified program using the following approach:
(1) Right-click on the CPU window
(2) Copy to executable
(3) Copy all
(4) Close the dialog box (list of modified instructions)
(5) Στη συνέχεια, εμφανίζεται ένα παράθυρο διαλόγου που ζητάει "αποθήκευση του αρχείου". Επιλέξτε "ναι" και αποθηκεύστε το ως νέο εκτελέσιμο αρχείο.
2.3 Breakpoints
Software breakpoints (F2). They are similar to the breakpoints available in language debuggers. You can have unlimited breakpoints (BP) and you can set conditions on a BP (eg, to specify that BP should stop the program only when the value of a registry is equal to a certain number).
BPs are applied using the directive Int 3 .
Basically, whenever you set a breakpoint at a location, the debugger replaces the FIRST byte of that instruction with INT 3 (one-byte instruction) and stores the old bytes.
Each time the program runs at this location, a pause is made and the debugger is called to handle this exception.
Thus, the debugger can then perform the condition check at the breakpoint and stop the program.
Hareware breakpoints can be configured by right-clicking in the CPU window and then selecting Breakpoints -> Hardware, at runtime .
Note that there are two other types of availalbe ( reading memory , memory access ).
As the name implies, BPs are achieved by exploiting the hardware. In an Intel processor, there are four hardware BP registers that record the location of BPs. This means that at any time, you can have up to 4 BP .
Hardware BP is very useful if you need to know which part of the code modifies a variable. Just set the BP memory access to it and you do not have to look at the whole source code to find out.
2.4 User comment
Although seemingly insignificant, user feedback and annotation is a very important function during a reverse effort.
Στο παράθυρο της CPU, πατώντας ";" σάς επιτρέπει να προσθέσετε ένα σχόλιο σε μια οδηγία και πατώντας ":" σας επιτρέπει να επισημάνετε μια τοποθεσία. Αργότερα, όταν η τοποθεσία αναφέρεται ως μεταβλητή ή συνάρτηση, θα εμφανιστεί η ετικέτα της.
This will greatly facilitate the analysis process.





