Learn about basic video construction terminologies and differences, i.e. Video Codecs, Containers, and Video Compression.

Those of you who have worked, even as an amateur, to edit a video you took with your friends and make it presentable, you will have come across strange terminology, such as video codecs, containers and video compression (Compression).
We are sure that then you simply click on a random selection of all of them, to proceed with the process and because you did not have the time to sit and search and find out what all the above are.
Of course it's not great science. Explaining the difference between codecs and containers is relatively simple, but the hard part is trying to understand each format.
And the lines blur worse when you realize that most common codecs are not proprietary and can use multiple compression technologies to get the job done.
So how do you know the difference between dozens of codec and container options? Just don't do it!.
You could spend weeks studying technologies that are only useful for a small number of applications, so instead we'll focus on the technologies you'll use for video encoding, understanding only the tradeoffs and playback needs.
What is a Codec?

Codec is an acronym that stands for compressor/decompressor or coder/decoder. It is an encoding tool that processes video and stores it in a byte stream.
Codecs use algorithms to efficiently reduce the size of the audio or video file and then decompress it for playback, editing or when needed.
Υπάρχουν δεκάδες διαφορετικοί κωδικοποιητές και ο καθένας χρησιμοποιεί διαφορετική τεχνολογία για την κωδικοποίηση και τη συμπίεση του αρχείου βίντεο. Βαθιά ανάσα και πάμε ...
When making a video you are asked to choose an codec to maintain a balance between: image quality, file size, processor usage and popularity.
Depending on the codec, encoding is done in one of two ways: lossy compression or lossless compression.
Loss of compression

When looking for manageable file sizes, meaning small enough to upload to Youtube, Facebook etc, lossy compression is the most viable method.
While you certainly lose quality in audio or video or both, compression is about making the best possible compromises without sacrificing quality. However, remember that quality degrades rapidly the higher the compression ratio.
For example, an average Blu-ray disc can exceed 40 GB, and this kind of storage would not only be expensive, but would make digital downloads and purchases inconvenient.
The key when using lossy compression is to set up a compression format with the highest quality for your intended use, so you tread the fine line line between quality loss and file size.
Lossless compression
Lossless compression works like a ZIP or RAR archive in that after compression and decompression, the file is essentially the same. Through the use of smart algorithms, the file does not lose much quality, but it is not an efficient way to store large files because not enough compression takes place.
In addition, streaming large video files online uses too much bandwidth and is inconvenient. Unless you work in the film industry or professional video editing, you are unlikely to share video files in lossless format.
Compression Parameters

Before we dive into the formats, you should know the parameters that will directly affect the quality of the final video. Some settings are global, i.e. similar from encoder to encoder or specific to an individual encoder.
-
bitrate (Bitrate) : The number of bits you allow the tool to describe each frame of the video. The higher the bits, the more the image quality increases, but also the file size. They are denoted by Kbps or Mbps.
-
VBR and CBR : The variable bit rate encoding (Vvariable bitrate) changes the output bits over time. For example, a higher bitrate for action-packed scenes in a movie and a lower bitrate for slow scenes. The constant bit rate (Constant bitrate) maintains a constant bit rate per segment, regardless of complexity.
-
Frame Rate (Frame Rate) : The frequency or rate at which successive images are displayed. It is expressed in frames per second (frames per second = FPS).
-
FrameType : Describes how the image data in an MPEG stream or file is structured. They play an important role in video compression and are of three types: I-frame (keyframe), P-frame and B-frame.
-
Aspect Ratio (Aspect ratio) : 4:3 and 16:9 are the two most common aspect ratios. As you scale the video resolution, you need to maintain it ratio dimensions.
Popular encoders

As you might expect, some codecs are more popular than others. Understanding where each codec is used can help you determine which codec to use for your project.
XviD/DivX
DivX is a commercially sold codec, while XviD is an open source utility that acts as an alternative to its commercial cousin. Both codecs can decode each other's output, as both are built on the MPEG-4 implementation. While still widely used, it is often used strictly for video encoding and is used with one of the more popular packages listed below.
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is the most common streaming format and consists of several parts, of which only MPEG-4 Part II is for video encoding. MPEG–4 Part II calls video codecs such as DivX or XviD to encode the video, while the audio is usually transferred in MP3 format. The modern ones updates of MPEG-4 now also use the H.264 codec.
H.264
H.264 is a swiss army knife of the codec world. It can use lossy and lossless compression depending on the settings you choose when encoding, such as frame rate, quality, and target file size. H.264 is based on x264 for encoded video (as well as others such as DivX or XviD), and audio is often encoded using AAC or MP3 audio codecs depending on the size and quality you're aiming for.
What is a Container?

A container is a bundle of audio codec, video codec and metadata (metadata) organized into a single package. It ends with file extensions like MP4, AVI, MOV, FLV and more. Metadata includes subtitles, resolution information, creation date, device type and language files.
The container file interpolates the different data types and makes them accessible to the video player. Despite their importance, a Container is useless at adequately informing you. It does not reveal how the video and audio were encoded.
Popular Container
As with codecs, there are also popular containers.
MP4
MP4 is the recommended format for online videos and services like Vimeo and YouTube, as they list it as the preferred format. The MP4 container uses MPEG-4 or H.264 encoding and AAC or AC3 for audio. It is widely supported on most consumer devices.
MKV
MKV is a fast-growing format designed to be future-proof. The container supports almost any audio or video format, making it customizable and efficient. It is considered as one of the best ways to save audio and video files.
It even allows you to play damaged video files, support multiple subtitle tracks even if encoded in different formats, DVD menus and chapters, and more. Unfortunately, although the Matroska format is a free and open standard, it is not yet universally supported.
REVIEWS
First introduced by Microsoft, AVI videos were most popular in the 90s and early 2000s. AVI files can hold different types of audio and video streams, and with the help of the DivX codec, they can display superior video quality with small file size.
However, when you compress AVI beyond a certain limit, the video loses its quality. Since screens are now capable of HD, Ultra HD and 4K, the tolerance has decreased significantly. Also, if you compress the video using a codec, you must have the same codec on your machine to play the file.
Find information about the codecs used in a video
Έχετε παρακολουθήσει ένα βίντεο στον υπολογιστή σας και ξαφνικά να αναρωτηθείτε: "Τι κωδικοποιητή βίντεο χρησιμοποιεί αυτός;". Υπάρχουν διάφοροι τρόποι με τους οποίους μπορείτε να μάθετε.
Media Info
MediaInfo is an open source codec identification tool that you can use to find out all the information about any audio or video file. The best part of the software is that it displays the extracted data in different structures like Sheet View, Tree View, HTML View and more.
Download: MediaInfo for Windows, Mac, Linux etc (Free)
VLC Media Player
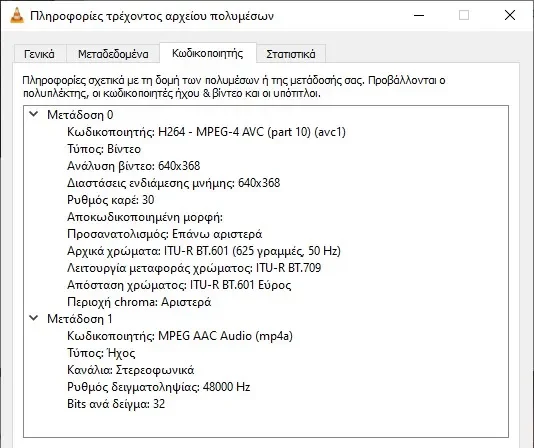
VLC gives you codec details and other related information. First, load your video file, then go to Tools > Codec Info.
You can see details like codec used, video resolution, frame rate, audio codec, sample rate, bit per sample and more.
Download: VLC for Windows, Mac, Linux etc (Free)
Which Codec and File Format Should You Choose?
If you're looking for advice on what to use, H.264 is starting to become the standard codec, while either MP4 or MKV are worthy containers.
MP4 may have the edge because it supports consumer devices and is the standard for video streaming sites. H.264 is 1,5 to 2 times more efficient than standard MPEG-4 compression, leading to smaller file sizes and seamless playback.
Also, H.264 is now included in the MPEG-4 codec (part 10, known as AVC). More analysis on the best codec to choose for each case in a subsequent article.





