End of 2013, h Symantec discovered an Internet of Things worm ( Worm IoT ) with the name Linux.Darlloz. The virus targets computers running Intel x86 architectures. Beyond that, the virus also focuses on ARM, MIPS, and PowerPC ARMs, typically found in routers and set-top devices. After the initial discovery of Linux.Darlloz, the company discovered a new variant of the virus early this year. According to the analysis, the creator Worm IoT constantly upgrades the code and adds new features, focusing in particular on making money through the virus.

Investigating the entire Internet IP field in February, Symantec discovered that there were more than 31.000 devices infected by Linux.Darlloz (Worm IoT).
Coin mining
Additionally, the company discovered that the current target of the virus is cryptocurrency mining. Just one computer που λειτουργεί με Intel αρχιτεκτονική μολυνθεί από μία νέα παραλλαγή, ο ιός εγκαθιστά ένα cpuminer, ένα ανοιχτό λογισμικό που λειτουργεί ως πηγή mining νομισμάτων. Ο ιός έπειτα αρχίζει την εξόρυξη Minocoins ή Dogecoing από τους μολυσμένους υπολογιστές. Στο τέλος του Φεβρουαρίου του 2014, ο εισβολέας απέσπασε 42.438 Dogecoins (about US$46) and 282 Mincoins (about 42.438 Dogecoins). These amounts are relatively low for average cybercrime activity, so we expect the attacker to continue to evolve their threat to increase revenue.
The new currency coin mining feature only affects computers running Intel x86 architectures and Symantec has not yet identified its impact on IOT devices. These devices require more memory and a powerful CPU for mining coins.
Why Mincoin and Dogecoin?
Worm IoT seems to be targeting Mincoins and Dogecoins, instead of focusing on the famous and more widespread means of Bitcoin transactions. The reason for this is that Mincoins and Dogecoins use the scrypt algorithm, which can be successfully mined from home PCs while Bitcoins require ASIC chips to make a profit.
New goals
The original version of Darlloz has nine combinations of user names and codes for routers and set-top devices. The most recent version now has 13 from these input authentication combinations, which also work for IP cameras, commonly used for remote building surveillance.
Why devices IoT;
The Internet of Things ( Worm IoT ) is associated with connected devices of all kinds. While many users can assure that their computers are safe against attacks, they may not have realized that their IoT devices also need protection. Unlike ordinary computers, many IoT devices send information with a default username and password and many users may not have changed them. As a result, the use of preselected user names and passwords is one of the leading agents for attacks against IOT devices. Many of these devices also contain vulnerabilities associated with incomplete updates that the user does not know.
While this particular threat focuses on computers, routers and IP cameras, the virus could be upgraded to target other IoT devices in the future, such as home automation devices and technology devices that can be worn.
By preventing other intruders
The virus prevents other intruders or viruses, like viruses Linux.Aidra, from targeting devices already infringed by Linux.Darlloz. The malware developer attached this feature to the virus when it was released last November.
At the beginning of the year there were reports about a backdoor in a router. Using the backdoor, attackers could access the routers remotely, allowing them to break the user's network. For Darlloz's creator, this was a threat, so they added a feature that prevents access to the backdoor slot by creating a new rule for the firewall on infected devices to ensure that no other attacker can access the same rear door.
Contamination of systems
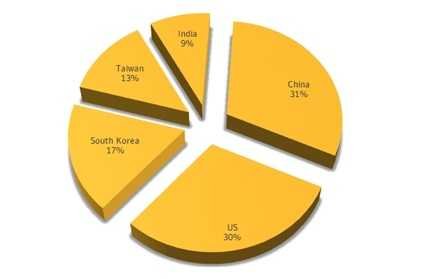
Some statistics on virus infection:
- 31.716 IP addresses that were infected with Darlloz were detected.
- Darlloz infestations affected 139 sites.
- 449 were identified fingerprints OS fingerprints from infected IP addresses.
- 43% of Darlloz infections violated computers that contained Intel or servers using Linux.
- 38% of Darlloz infections appear to have affected a variety of IOT devices including routers, set-boxes, IP cameras and printers.
The five regions that accounted for 50% of all Darlloz infections were China, the US, South Korea, Taiwan and India. The reason for the high rate of infections in these countries is more likely due to the large amounts of Internet users or the penetration of IoT devices.
Infected devices IoT
Consumers may not realize that their Ip devices can be infected with malicious software. As a result, this virus has infected 31.000 computers and IOT devices in four months and is still spreading. We expect the creator to continue to upgrade this virus with new features as the technology landscape is constantly changing. Symantec will continue to closely monitor this threat.
Meters
- Apply security patches for all software you install on computers or IoT devices
- Upgrade your firmware to all devices
- Change the default codes on all devices
- To prevent her connection on port 23 or 80 from outside if not required





