Fake fingerprints can be used to unlock some Android phones, according with Yu Chen of Tencent and Yiling He of Zhejiang University.
The researchers found that two 0day vulnerabilities which are present in the fingerprint authentication framework of almost all smartphone and can be leveraged to unlock Android devices.
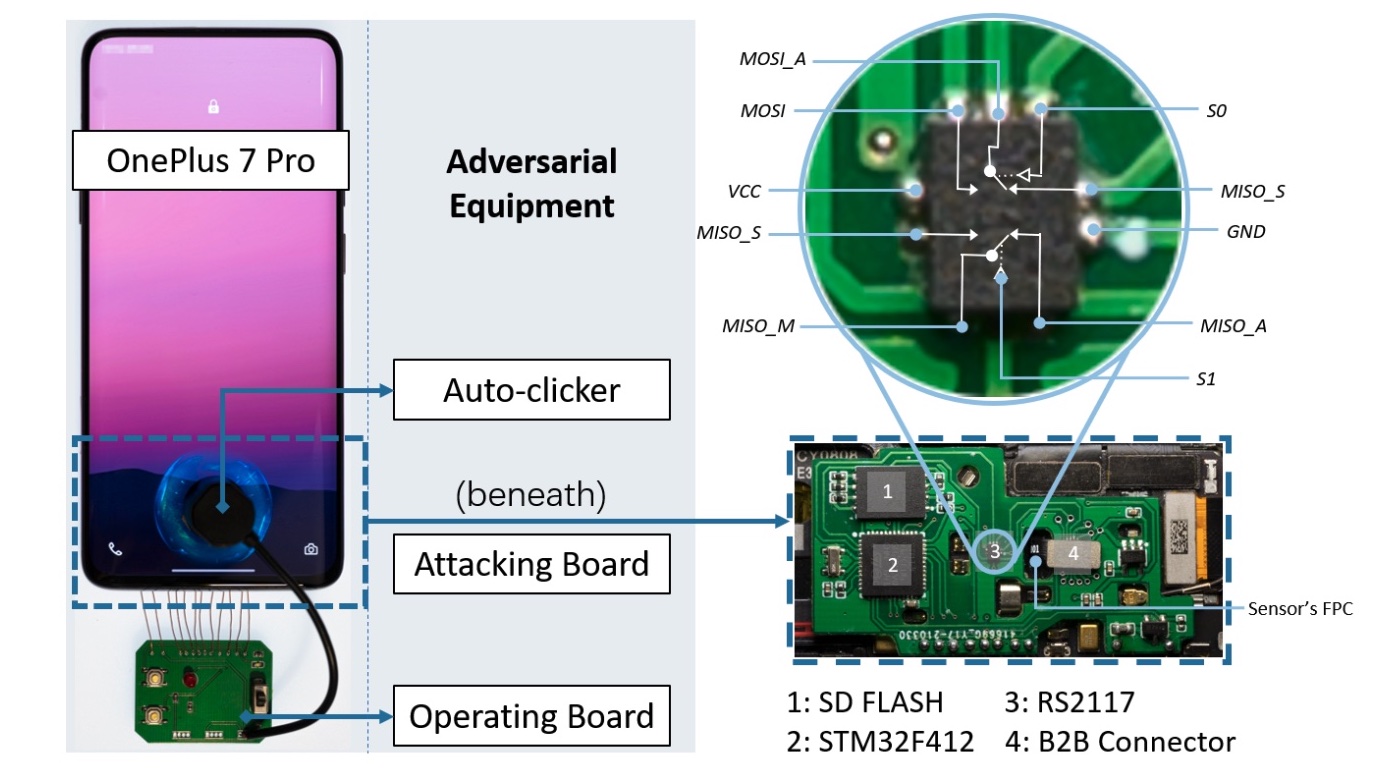
The attack was named BrutePrint. It requires a $15 board with a microcontroller, an analog switch, and an SD flash card. The attacker would also need to be in possession of the victim's smartphone for at least 45 minutes and a fingerprint database is also required.
The researchers looked at eight Android phones – Xiaomi Mi 11 Ultra, Vivo X60 Pro, OnePlus 7 Pro, OPPO Reno Ace, Samsung Galaxy S10+, OnePlus 5T, Huawei Mate30 Pro 5Gand Huawei P40 – and two iPhones – iPhone SE and iPhone 7.
Smartphones allow a limited number of fingerprint attempts, but BrutePrint can bypass this limit. The fingerprint authentication process does not need a direct match between the entered values and the database value. Uses a reference boundary to specify a match. So a malicious user can take advantage of this by trying different inputs until they use an image that closely resembles the one stored in the fingerprint database.
The attacker would need to remove the back cover of the phone to connect the $15 board and carry out the attack. The researchers were able to unlock all eight Android phones using the method. Once a phone is unlocked, it can be used to authorize payments.
This particular method does not work on iPhones because iOS encrypts the data.





