As we mentioned in morning publishing Google has added a new log in mechanism to Chrome 69 for all company services (YouTube, Drive, Gmail or Docs).
We do not know what Google intends to do, but we do know from some of the company's developers that the sync service is enabled to allow program browsing to send data on Google servers.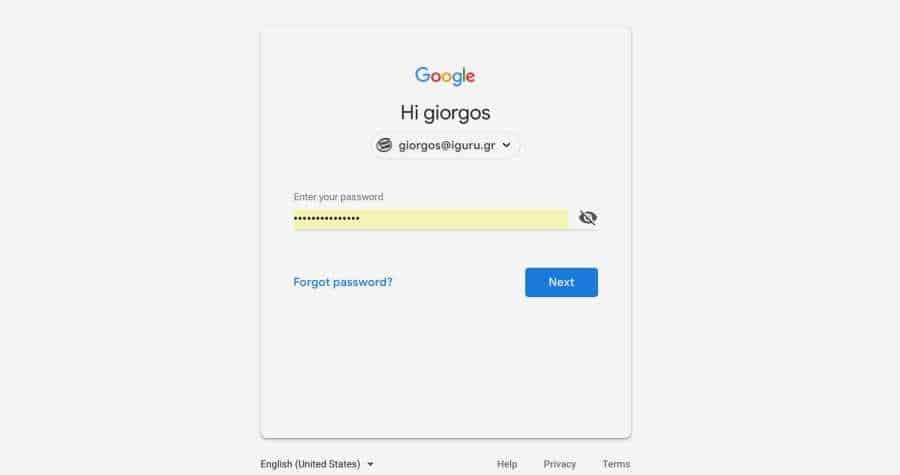
Automatic change of login in Chrome was released as a means of distinguishing between many users who use it installation of the Chrome browser to prevent data leakage between accounts according to Google technicians.
Whatever the motive for Google's decision, there are many users who have expressed dissatisfaction with this feature.
If you are one of these and you do not want to connect to Chrome below, we'll see a simple solution to your problem.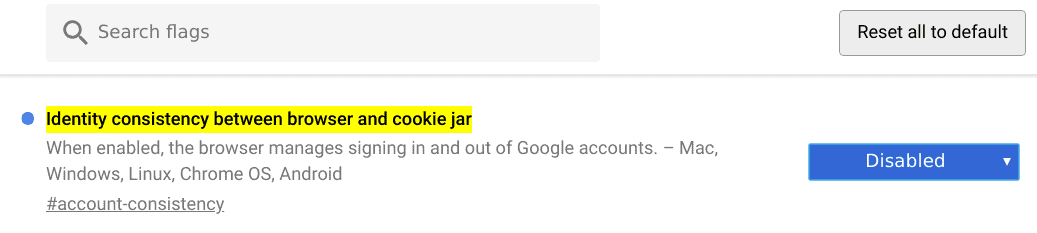
We will see how you can disable the automatic connection from the Chrome flags.
Open the internal address:
chrome: // flags / # account-consistency
and disable the flag "Identity consistency between browser and cookie jar"
According to the flag description "When enabled, your browser manages to sign in and sign out of your Google Accounts - Mac, Windows, Linux, Chrome OS, Android".
As soon as the flag is disabled, you will be prompted to restart Chrome to apply the changes, Chrome will return to its previous mode, and will not log in to your account unless you select it.
Caution: The more tweak will not be true forever as Google tries countless flags from time to time. So you need to be prepared because the company can remove this flag at any time.
Of course another much more secure solution is to leave Chróme and use the Mozilla Foundation browser. Firefox won't disappoint you ...





