Sabayon Linux or Sabayon (formerly RR4 Linux and RR64 Linux), is an operating system based on Gentoo. It is a Linux distribution developed in Europe by Fabio ERCULIANI and the Sabayon development team. The Sabayon distribution follows the "out of the box" philosophy with the aim of giving the end user a wide range of ready-to-use applications and a self-tuning operating system.
Sabayon Linux is a rolling release, uses own repository software and a system managementof packets called Entropy. Sabayon supports two x86 and AMD64 architectures and has support for ARMv7 which is still in development.
His name was taken from the Italian zabaione dessert which is made from eggs. So the Sabayon logo is a chicken leg impression.
Let's get to the facility. We will install Sabayon Linux on a computer running Manjaro or any other distribution based on Arch or Redhat. You can download the version you are interested in from the functional repository on the ftp server of the University of Crete:
ftp://ftp.cc.uoc.gr/mirrors/linux/SabayonLinux/iso/daily/
Burn the DVD or run it with a dd command on a USB stick and we're ready to get started.
dd if = the-Sabayon.iso of = / dev / sd (x)
The distribution opposed to Gentoo uses the Anaconda graphic installer. For me, he continues to be the best installer in circulation.
Before you begin installation, make sure that you have the necessary space for the new operating system. If you do not have one, you can create space to reduce the disk you are using. Use gparted from live environment.

Live DVD impressed us as it found with all the drivers a boot something I have noticed in very few distributions. For example, in the image below you will see that Wi-Fi drivers were already found during the installation.
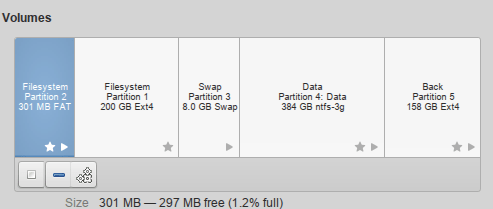
For the dual boot I chose partition 2 (boot / efi) without formatting so as not to delete Manjaro boot.
Sabayon Linux went to partition 5 (/) and as a swap you do not need to add anything as anaconda will use what already exists.
After installing, we need to tell Manjaro (or any other Arch-based or Redhat based installer) to read / boot / efi again to recognize and display the new operating system on the boot screen.
So from Manjaro now open the terminal and run the following command:
grub-mkconfig -o /boot/grub/grub.cfg
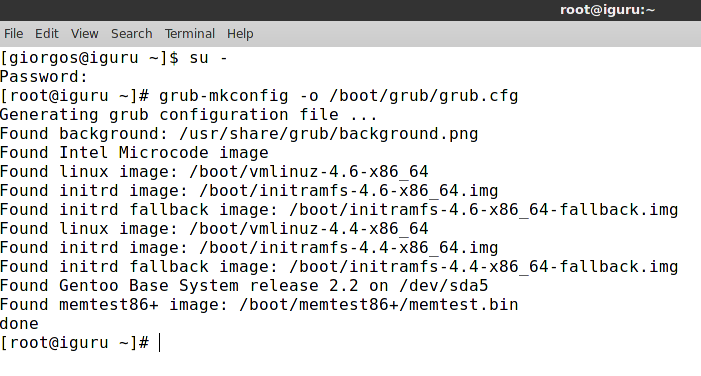 You are ready with the next reboot you will be able to see your new operating system.
You are ready with the next reboot you will be able to see your new operating system.
Information about Sabayon Linux from Wikipedia.





