ESET researchers completed their analysis about the counterfeit wallet wallets that appeared on Google Play along with the Bitcoin value-up.
During the current month, the bitcoin price climbed to the highest point since September of 2018. Naturally, cyber criminals quickly realized this development and started attacking users of cryptos using various scam and malicious applications.
One of these appears supposedly the popular wardrobe hardware for cryptobonds, Trezor. This illegal application is associated with a fake wallet app called "Coin Wallet - Bitcoin, Ripple, Ethereum, Tether", which has the ability to extract money from unsuspecting users through scam.

"We had never detected malware abuse of Trezor's name and we were wondering about the possibilities of such a false application. In addition, Trezor hardware wallets require physical user management and PIN verification or knowledge of recovery words for access to stored cryptosncs, "says ESET researcher Lukáš Štefanko, who is in charge of conducting the research, explain why he was particularly interested in this fake application. "
ESET found from the analysis that no damage can be done to the cryptocurrencies of the users of the original Trezor app, as the latter has multiple layers of security. However, the illegal app is linked to 'Coin Wallet', a fake cryptocurrency wallet app that is capable of extorting money from unsuspecting users via scam. "And the two αυτές εφαρμογές δημιουργήθηκαν με βάση ένα πρότυπο για creation app sold online," adds Štefanko.
The application that is "disguised" as a mobile wallet for Trezor appeared on Google Play on 1 May 2019, named developer "Trezor Inc". At first glance, the Google Play app page appeared trusted. During the ESET analysis, the fake app appeared to be the second most popular search result for Google Play Trezor, just below the official app. However, this is a false application that is used for fishing credentials.
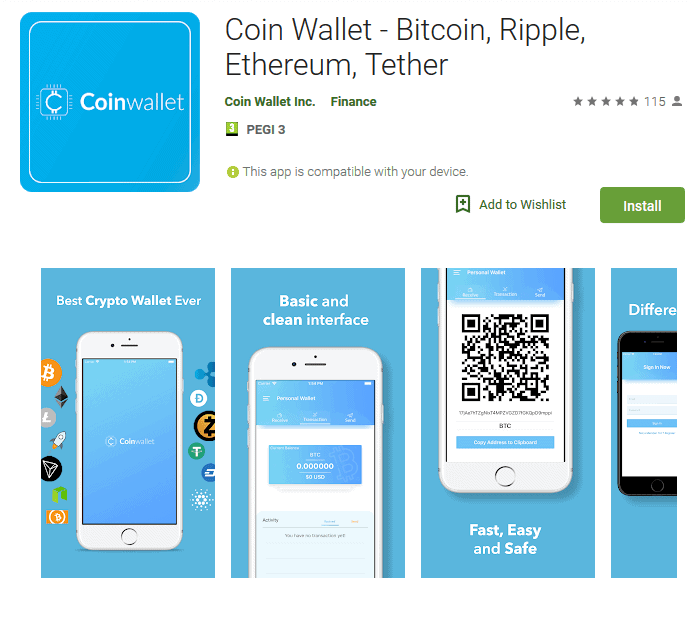
The server used to collect credentials from the fake Trezor application is hosted at coinwalletinc.com. While researching the domain, ESET researchers led to another malicious application, named "Coin Wallet" on both its website and Google Play, as well as the same code and interface. The website has a link to Google Play, where the app has been available since February at 2019.

"The application claims that it allows its users to create wallets for various cryptocurrencies. However, its real purpose is to trick users into transferring their cryptocurrencies to fraudsters' wallets - a classic case of fraud, which we called a "wallet address scam" in our previous research on crypto-targeted malware, says Luk, Ftefanko.
Finally, Štefanko gives some tips to users on how to stay safe with online cryptoscopes:
- Trust cryptic and financial services applications only if they are linked to their official website.
- Enter the sensitive ones information online only if you are sure of their security and legality.
- Keep your device up to date.
- Use a reliable security solution for cell phones to block and remove threats.
ESET has informed Google's security teams about the fake Trezor application, and has contacted the Treasurer to make this investigation public. Trezor has confirmed that the fake application is not a direct threat to its users.
However, she was concerned that e-mail addresses collected through fake applications like this could later be maliciously used in phising campaigns.
At the time of writing, both the fake Trezor app and the Coin Wallet app were not on Google Play.
______________________
- Tor Browser 8.5 for Everyone + the first stable version for Android
- openSUSE 15.1 just released the stable version
- Phishing: how it stops with mechanical learning





