The upcoming Google Chrome version 63 will include a new security feature that will detect attacks Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) in your browser.
The attack MitM happens when an application installed on your computer or on a local network monitors web traffic.
For malicious users who carry out MitM attacks, the hard part is if there is HTTPS encrypted traffic. Most tools attacks MitM fail to rewrite user encrypted connections correctly, causing errorthe SSLs that Chrome will detect in an upcoming version.
The new feature of Chrome 63 will be displayed when there is a reason in the form of a new alert screen. The error you see below will appear every time Chrome detects a lot of SSL connection errors in a very short time, which is a sign that someone is trying - and failing - to steal your internet traffic. 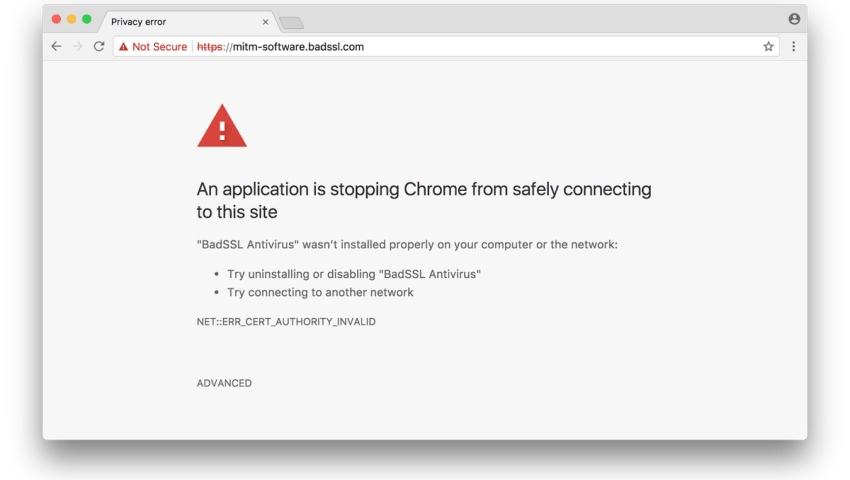
The new Google Chrome warning screen will not appear for your antivirus and firewall software, but only for applications that do not correctly rebuild SSL connections, resulting in errors in your browser's SSL connections.
According to the Chromium Development Calendar, Google will release the new Chrome 63 on December 5, except of the unexpected of course.
Meanwhile, if you're in a hurry, you can try the developer preview version known as Google Canary.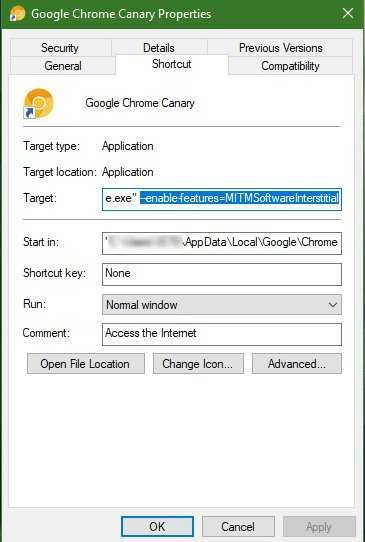
This option is not available by default in Chrome Canary. To enable it, follow these steps:
Find the Google Chrome Canary (shortcut) icon and right-click on it. (See picture above)
Select “Properties” from the menu in the window that will open.
In the "Target" or "Target" field without deleting what already exists, add the following text "-enable-features = MITMSoftwareInterstitial" and click "Save" or "Apply" and "OK".





