Improved Google is coming Translate: Google's Neural Machine Translation system "outperforms" the results of all other machine translation solutions solutions available today.
Google has announced a neural machine translation (Neural Machine Translation or NMT) system, which according to the company will reduce Mistakes in the translations of the Google Translate service from between 55 to 85%. The project's development team and scientists refer to the new technology as a "significant milestone".
The Google Translate service was announced by 10 years ago by Google Brain Quoc Le researchers and Mike Schuster.
“Ten years ago, we announced the launch of Google Translate, in combination with the use of Phrase Translation as the basic algorithm for this service. Today, we announce the Google Neural Machine Translation (GNMT), which uses state-of-the-art training techniques to achieve the greatest improvements in the quality of mechanical translation, ”the researchers said.
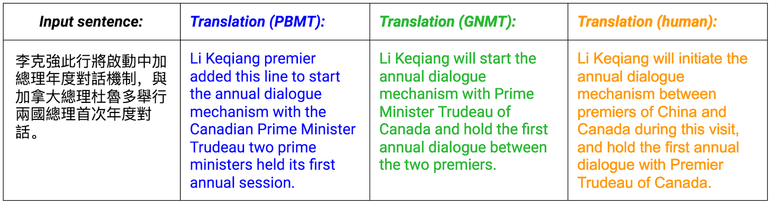
Unlike the system used to date to translate mechanical translation phrases (PBMT) (translation of words and phrases, regardless of how they exist in a sentence with known results of incorrect translations), neural automatic translation examines the entire sentence before translating it.
Researchers over the past few years have been trying to improve neural machine translation technology to work better on large ensembles. data, while maintaining better speed and accuracy.
So awaiting a new better translation service from Google that does not stop offering tools that make life easier.