The World Wide Web or WWW was created in 1989. See a historical review from its birth until today.

The World Wide Web. which in English is referred to as World Wide Web (WWW) is an is an organizational system, a protocol, for information accessible over the internet.
Here perhaps we should clarify that another Internet (internet) and another o Worldwide web (www). The internet is the underlying technology that allows computers, phones, game consoles, smart home equipment, servers and other network-enabled devices to talk to each other, no matter where they are in the world.
As such, the internet includes all the physical infrastructure required for these networks to work together. Whether it's the local cables run by your ISP or the huge underwater cables that connect continents, and which are necessary to make the internet work the way it does. By its very nature, no one "owns" the internet.
The term "internet" does not include only physical materials. Also included are the protocols and standards that have been built into it so that we communicate today in thousands of ways.
Thus the World Wide Web is a collection of billions of interconnected web pages, accessible through a global network of computers known as the "internet". Wide Area Networking (WAN) predates the World Wide Web by decades.
However, it wasn't until Tim Berners Lee discovered the web in 1989 that today's internet was truly born. The World Wide Web has been evolving ever since. So, let's take a look at the history of the WWW, from its conception in 1989 to today in 2023.
1989-1993: Tim Berners-Lee invents the World Wide Web

Ο Tim Berners-Lee (Tim Berners Lee) is a scientist who worked at CERN (European Organization for Nuclear Research) in the late 1980s and early 90s.
CERN's need to share data prompted Tim Berners-Lee to submit a draft proposal for a new kind of distributed information system.
This paper described the concept of linking pages with hypertext. In 1990, Lee submitted another paper entitled “WorldWideWeb” which included an extensive plan for a new hypertext project.
By the late 1990s, Tim had laid the foundations of the modern World Wide Web. He developed the first web browser, which was called WorldWideWeb.
You can see how this browser was in this WorldWideWeb page. Tim also created in 1990 the world's first server on his computer, a NeXT machine which he then owned.
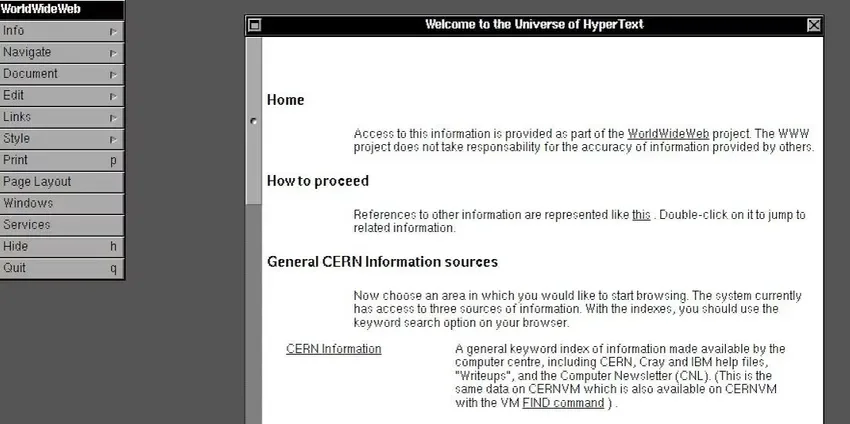
In 1991 everything was ready for the first website. Tim hosted the first website that year on his NeXT computer called “World Wide Web”. He provided a brief introduction to the World Wide Web describing it as a broad information initiative to access many documents.
The final milestone in the early development of the World Wide Web came in 1993. Tim Berners-Lee and CERN submitted a document that put the Web into public use. This document further defined the World Wide Web and confirmed that CERN did not claim any copyright to it. Therefore, no one owns the Web as CERN has adopted an open software policy for all.
1992-1995: The first browsers with graphics
The WorldWideWeb browser that Tim developed was little more than a simple text editor. It wasn't until 1992 that the first graphical browsers appeared that could handle images.
Young developers in Finland developed the first graphical browser and called it Erwise. However, its developers Erwise they didn't seek to commercialize it and so it didn't resonate.
The NCSA released in 1993 Mosaic, the first popular graphical browser. Mosaic could display images next to text. Users could now view websites that integrated text, images, video and sound for the first time. Mosaic soon became the largest browser, with one million users.
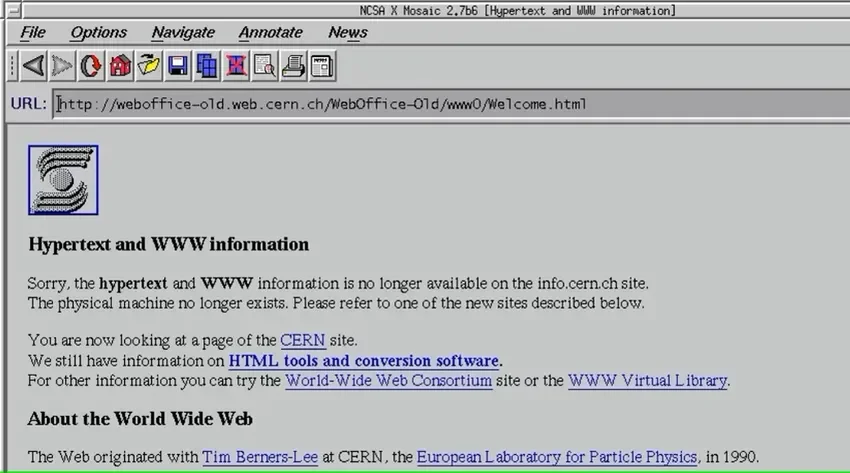
However, it would not remain the world's leading web browser for long. Microsoft launched Internet Explorer in 1995 and tied it to Windows platforms.
Internet Explorer emerged victorious in the first browser war, with a user share reaching 90 percent in its heyday.

Ο Internet Explorer it's a big story in itself.
1995: JavaScript lands and takes the web by storm
Websites during the early years of the World Wide Web were rather simple and basic. However, this began to change in 1995 when programmer Brandan Eich developed the JavaScript scripting language.
JavaScript soon became one of the main languages for website development along with HTML and CSS. It enabled website designers to add interactive elements to pages and create more dynamic websites.
1995-2000: The Dot.com boom
It didn't take long for early entrepreneurs to recognize the commercial potential of websites. Jeff Bezos founded the Amazon website in 1995. Although Bezos initially named it Cadabara (a magic spell), he later chose the name Amazon, one of the world's largest rivers.

Amazon started out as a website that sold books, but expanded to sell much, much more and has grown into the world's largest online retailer.
Computer scientists Sergey Brin and Larry Page founded the Google search engine in 1997-1998. The Google search engine was originally called BackRub, but Brin and Page soon renamed it.

It was supposed to be called Googol, but a typo established the Google domain. This search engine quickly became one of the most popular tools to find web pages.
1999-2003: The first blogging platforms were established

Blogs were online calendars and magazines and became the new big step in the World Wide Web. during the period 1999-2003.
The Blogger was one of the first notable blogging platforms founded in 1999 and allowed users to create online magazines based on template designs.
Users could now create an online presence without having to design and upload websites with software. So anyone could present themselves and their ideas publicly on the world wide web for free.
WordPress was another major blogging platform that was founded a few years after the Blogger, in 2003. It started as a blog publishing platform, much the same as Blogger. However, it expanded to become a broader web publishing platform that allowed users to create websites based on WordPress templates.
2004-2006: The beginning of Social Media

The beginning was made in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg with the founding of Facebook.
Facebook was among the first websites to popularize social media. Zuckerberg designed Facebook as a blue website because of his color blindness to red and green.
The sharing of content, opinions, and information through online communities and networks facilitated by Facebook became known as social media.
In 2006, Jack Dorsey founded Twitter and it became one of Facebook's biggest rivals in social media, experiencing explosive growth in 2009 and beyond.
Many users fell in love with Twitter's short and to-the-point tweets, which made it the most popular social media platform for journalism.
2006: Google releases Docs, Sheets, and Slides
Cloud computing became a World Wide Web must when Google released in 2006 the online productivity applications Docs, Sheets and Slides.
They are the word processing, spreadsheet and presentation applications of Google Workspace (originally Google Apps), which allow users to edit and create documents, spreadsheets and presentations through their web browsers without installing any office software.
2008-2012: The global dominance of Google Chrome

Internet Explorer was the world's leading web browser until 2008, with the more sophisticated Firefox second.
It might have remained the king of browsers if Larry Page and Sergey Brin had listened to Google's then-CEO Eric Schmidt in 2008.
Schmidt rejected the proposal for a Google web browser because he was convinced Microsoft would kill such a product and have no future.
However, Page and Brin didn't listen to him and recruited former Firefox developers to develop a trial version of Chrome. Those developers later briefed Schmidt on the new Chrome browser, leaving the Google CEO no choice but to approve it.
Google launched Chrome in 2008, which surpassed Internet Explorer's user base in 2012 to become the world's favorite web browser.
2015: Microsoft strikes again by launching Edge

Microsoft couldn't help but watch in horror as Internet Explorer's user share plummeted.
As Internet Explorer struggled to compete with Chrome, it folded and released the Edge browser in 2015. After a bit of a slow start, and some shaky steps Edge has grown since Microsoft converted to Chromium engine.
However, Chrome still has a much larger user base than Edge.
2020: HTML 5 replaces Adobe Flash

Adobe Flash was once the dominant form of multimedia content on the World Wide Web. It was used to add multimedia content such as animations and videos to almost all websites. Many games websites were also based on Adobe Flash.
However, things started to change after the introduction of HTML 5, from 2008 onwards.
HTML 5 is the most advanced version of HyperText Markup Language that has now replaced Adobe Flash. Steve Jobs snubbed Flash on Apple's iPhones in favor of HTML 5. The Flash security vulnerabilities was another major factor in its downfall. Consequently, the Adobe discontinued Flash support in 2020.
2022-2023: The explosion of Web 3.0 and the arrival of AI
The Web3.0 it's the next version of the World Wide Web, which Tim Berners-Lee has been talking about with news channels for the past few years.
This is the next stage of the web that Tim predicts will be more decentralized, with bottom-up design. Tim also talked about AI being a big part of the future evolution of the web, and we will see browsing supported by many AI assistants like ChatGPT etc.
The truth is that artificial intelligence, a technique for simulating the brain synapses and comparisons of the human mind, is predicted to dominate in the coming years, as it will provide ready-made answers without the user having to read and compare a list of answers and results in order to draw a final conclusion.
He is expected to take the role of a key assistant, who will propose actions (in the field of war, at the research level, in everyday life, in work activity, etc.) but also will present new material, regardless of whether this will be a combination of existing ideas.
The Web Changed the World

The World Wide Web is now 34 years old. It was and remains undoubtedly one of the greatest inventions of the 20th century along with cars, airplanes, computers and televisions.
The invention of the World Wide Web ushered in a new revolution in communications and information around the world. He broke the monopoly of the 4th estate (journalism) and gave a platform to all people.





