Power supplies are an essential component for computers as they provide the necessary power to keep all components running smoothly. But what will happen when he is in trouble?
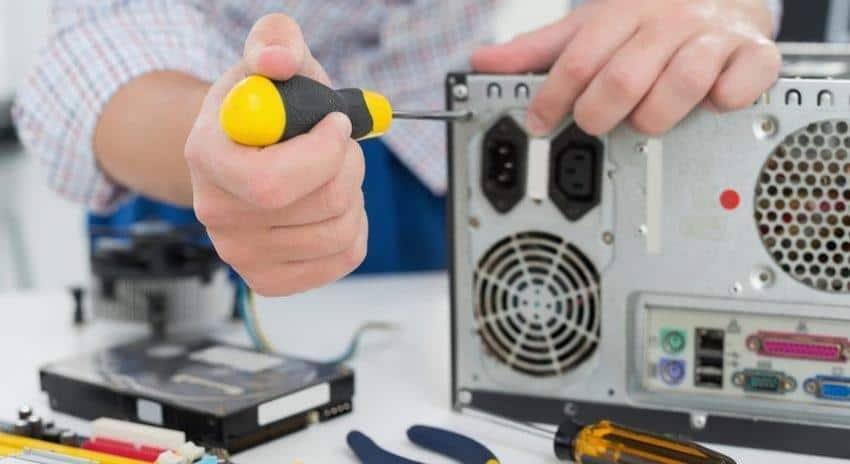

Power supplies, like all electronic components, can fail, resulting in a number of problems for the connected devices.
Understanding the symptoms of a power supply failure can help you solve the problem early, prevent it from causing further damage to your equipment, and avoid making botched replacements.
It is essential to know the symptoms of a poor diet. Let's take a look at some of the more common signs when a power supply isn't working properly, and what you can do to fix the problem.
General about PSUs
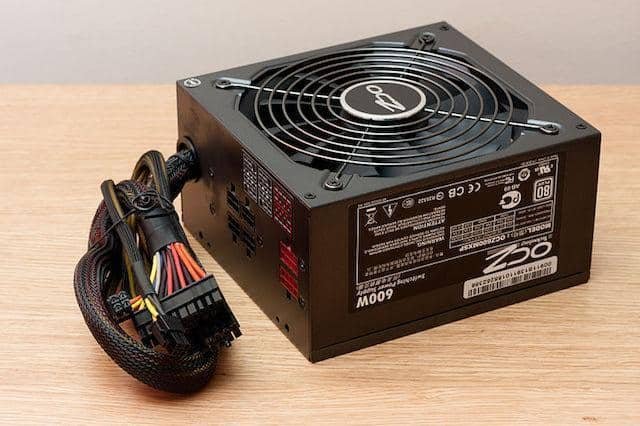

Keep in mind some basic points about PSU (Power Supply Unit). The power supply accepts your home's current and converts it from alternating to direct, steps it down from 230 Volts to various Volts such as 3.3V, 5V, 12V and supplies:
- The motherboard with the CPU,
- The fans
- The GPU (if required) and generally the PCI-e ports
- The motors of the hard disks and the dvd player
- The lighting
It is responsible for powering and charging the CMOS Battery, motherboard boot circuit, CMOS RAM, and BIOS ROM. When it starts, no matter how good the stabilization is, for a few milliseconds (under 500ms) it creates an overvoltage, but as long as it is within the manufacturing limits, there is no problem.
It has overvoltage and undervoltage protections of the DEDDIE (OVP= Over Voltage Protection), protection from overvoltage at its outputs (OCP= Over Current Protection), protection of excessive power consumption (OPP= Over Power Protection), overheating protection (OTP= Over Temperature Protection) , short circuit protection (SCP= Short Circuit Protection). However, like any electronic device, it breaks down.
A faulty PSU can damage the motherboard or components installed on a motherboard. Therefore, it is important to replace it immediately.
If it is not working properly it is better to replace it with a new one and do not attempt to repair it. The replacement value is much less than the damage it can cause.
But it's just as important to recognize the signs that may indicate a feeding problem. Signs like the following.
Note: We assume that your power supply (socket) has correct current, the external connecting cables and the socket are all fine. And the general switch of the pc is ON!.
The computer does not start

This is the most common sign of a faulty PSU. If the PSU installed in your computer has a problem, your computer will not boot.
This is because the faulty PSU is unable to supply the required voltage to the motherboard. However, there are other causes of this problem.
The computer randomly shuts down and restarts
A faulty PSU can also cause a computer to turn on and off repeatedly. If you encounter such a problem on your computer, the unit power supply may be faulty.
However, a faulty RAM can also cause the same problem.
Dust can also cause the same symptoms. Due to poor ventilation, the PSU overheats and reduces its performance or simply stops due to the overheating protection it has. In this case clean your machine from the dust.
The computer shuts down when performing heavy tasks

When performing heavy tasks, the equivalent material as the GPU draws more power. If your power supply is faulty, your computer usually shuts down while performing heavy tasks such as playing video games with heavy graphics, editing videos, etc.
There is always the possibility that the PSU may not meet the total power requirements of the system, as when you bought it it was fine but over time you have added a lot of power consuming devices and pushed it to its limits.
The computer case causes an electric shock
If you get an electric shock while touching your computer case, the power supply unit may be defective. At the same time check the leakage relay of your house.
PSU fan not spinning
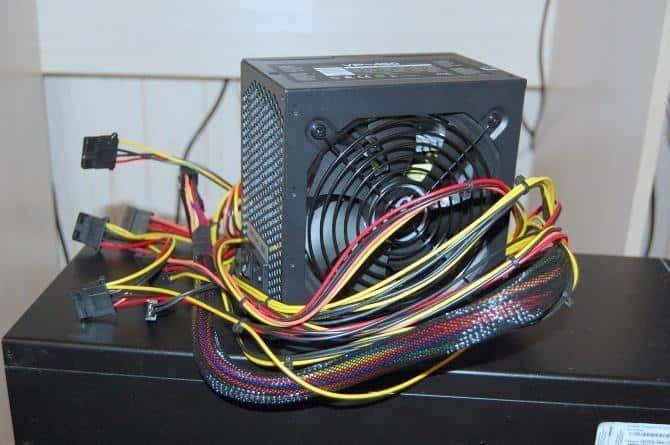

The fans of most PSUs are programmed to spin only if the PSU starts to heat up. Heat can cause physical damage to a PSU.
Therefore, when the temperature of a PSU exceeds the programmed one, the fans start spinning. But the fans of a PSU spin when the computer starts up and then stop automatically. After that, they only spin when the PSU starts to heat up.
If your PSU fan does not spin when you start the computer, the problem may be either the PSU fan or the PSU itself.
Dead motherboard

If no LEDs are lit on your motherboard, even if there is a problem with a hardware component such as RAM, CPU, etc., the problem may be with your PSU.
Smoke or burning smell
As explained earlier, the job of a PSU is to supply the DC voltage to the motherboard. A faulty PSU cannot do this job properly.
So there is a high chance that your computer motherboard is getting the wrong DC voltage. High DC voltage can burn individual motherboard components.
If you smell a burning smell, turn off your computer immediately and look for physical damage. It's time to repair your computer.
How many years does a PSU live?

There is no fixed lifetime for a PSU. It depends on the build quality (poetic brand) and how you use your computer. If the electricity is not stable in your home or you experience sudden power surges, we recommend that you install a UPS.
There is a measured characteristic of power supplies which is their expected lifetime (Life Span), which is also usually referred to as MTBF (Mean Time Between Failure). MTBF is given in hours of operation and temperature conditions of 25°C.
For example when the power supply manufacturer gives an MTBF of 100.000, then we expect the power supply to work without problems in continuous operation for about 11 years. In practice, however, only 37% of the power supplies verify this time and the main reason is their operating temperature, since it has been observed in the laboratory that an increase of 10°C cuts the life of the capacitors in half.
Efficiency of a PSU
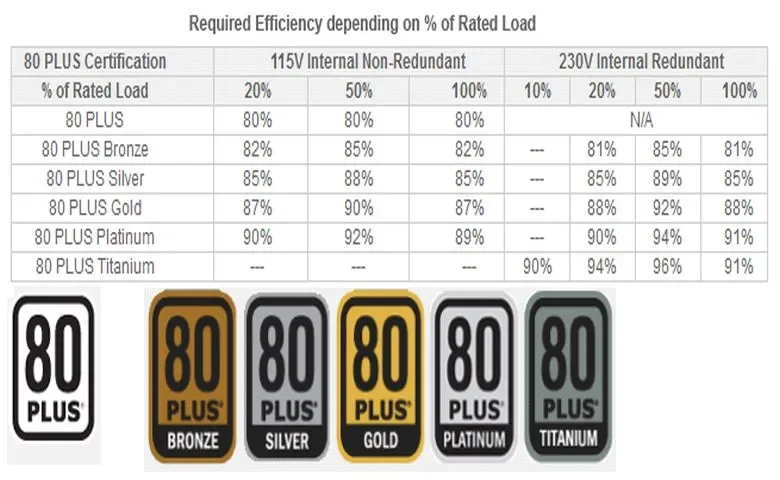
When buying a PSU make sure it is not at the energy limits of your computer as the KW it says does not all become electricity energy.
The efficiency of the power supply is the way of measuring how many Watts of what it draws from the outlet in your house, reaches your computer. The rest is converted into heat.
So a 400W PSU with an efficiency of 80% draws 400Watt from the socket and 80% of the 400W will reach the PC. That is, 320 Watts. The rest is converted into heat.
There are six efficiency ratings: 80+, 80+ Bronze, 80+ Silver, 80+ Gold, 80+ Platinum and 80+ Titanium.
Power of a PSU

A big issue is the maximum power output of the power supply. First you should know that in every DC voltage supply from the power supply there is a power limit that the manufacturer gives it in combination with a current limit.
So, for example, in a 320 Watt power supply, the manufacturer can give a current limit of 3,3 Ampere (power limit of 30 Watt) in a 99 Volt supply, while in a 5 Volt supply they give a current limit of 55 Ampere (power limit of 275 Watt). This does not mean that these amounts of power can be consumed at the same time, since they share the total power supply of 320 Watts.
If the 3,3 Volt supply has already absorbed the maximum power (99 Watts) then at the same time for the 5 Volt supply, only 221 Watts are available and not 275 Watts. The same applies to the 12 Volt supplies.
The above are marked by power supply manufacturers with the sign "compiled» where you will have to look for it on his label. If it doesn't say it, it's better to choose another PSU.





