Highlights:
• The first 3 quarters of 2023 saw a 3% increase in average weekly global cyber attacks compared to the same period last year.
• The global healthcare sector experienced an average of 1613 attacks per week, showing a significant increase of 11% year-on-year.
• APAC was the most attacked region with a significant increase of 15% year-on-year
• One in 34 organizations worldwide experienced an attempted ransomware attack, a 4% increase compared to the same time last year.

Surviving the storm of cyberattacks: A global record from Check Point Research
With October being the month dedicated to global cyber awareness, it is vital to shine a light on the evolving landscape of cyber threats that affect us all. Check Point Research's latest report provides a comprehensive picture of the storm that overwhelms the digital world, especially for the period Q1-Q3 of 2023. In 2023, global cyberattacks rose 3% compared to last year's figures, with the Healthcare sector being targeted, facing an increase in attacks against 11%. Specifically, one in 34 organizations worldwide faced the chilling reality of a ransomware attempt, a 4% increase from the same period last year. Check Point shares insights to stay alert and secure in a world where the digital winds of change are blowing stronger every day.
Global attacks overall
So far, 2023 has seen a 3% increase in average weekly global cyber attacks compared to the same period last year. The average number of attacks per organization per week so far this year is 1200 attacks.
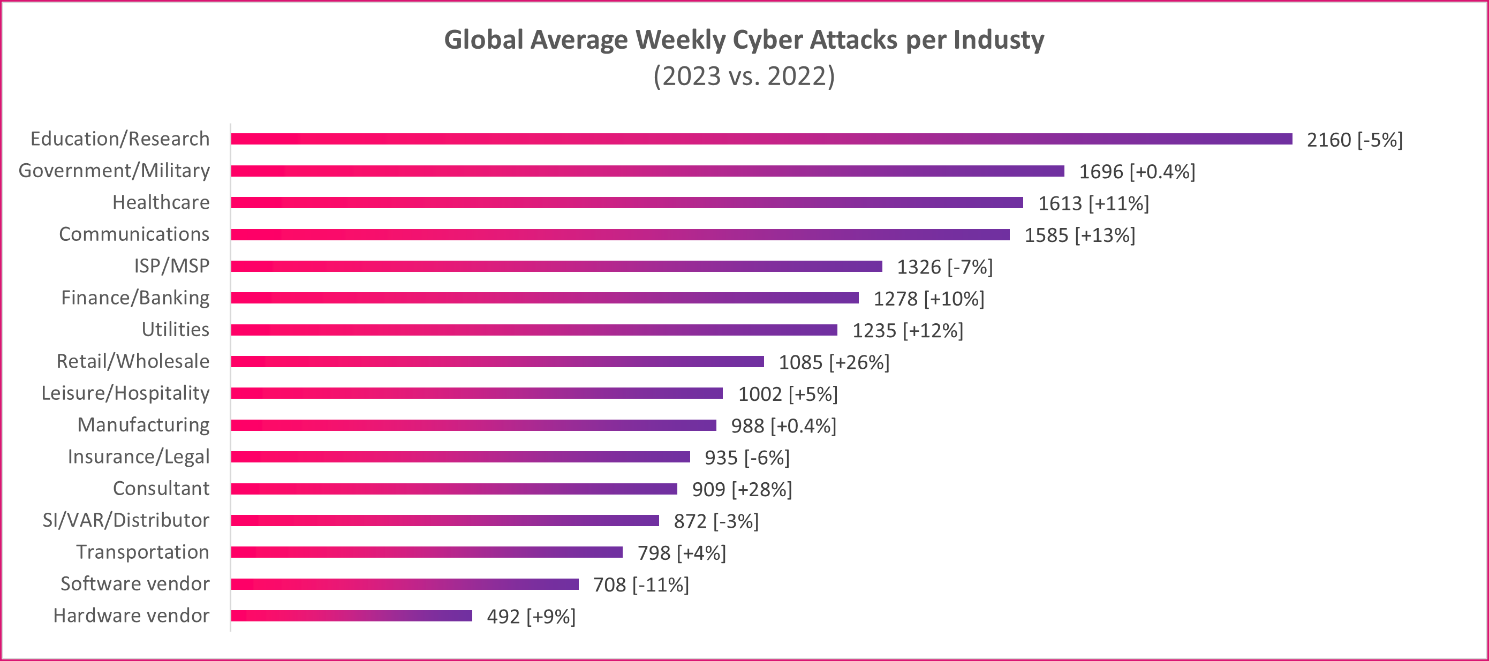
Global Attacks by Sector: 1η healthcare is under attack
The Education/Research sector faced the most attacks, on average 2160 attacks per organism per week, decreasing 5% compared to the same period in 2022. The government/military domain was second in number of attacks, with an average of 1696 attacks per week, representing an increase 0,4% from the same period of the previous year, while the sector of health care followed close behind, with an avg 1613 attacks per week, reflecting a significant annual increase Present in several = 11% .
In public statement, the MCNA (Managed Care of North America) it reported finding that someone "was able to view and obtain copies of certain information on our computer system between February 26, 2023 and March 7, 2023." MCNA, a dental insurer, has been hit by the largest health data breach of 2023, affecting more than 8,8 million Americans.
Health Scare – why are we seeing so many cyberattacks against hospitals?
Attacks on hospitals and healthcare institutions have become increasingly common for a number of reasons:
1. Rich Data Troves: Healthcare organizations store a trove of sensitive information, including personal health records, financial data and other personal information. Cybercriminals target this data for identity theft, financial gain, or even blackmail.
2. Critical infrastructure: Hospitals are part of critical infrastructure and h vacation of their operation can have serious consequences. Cyber attackers can easily exploit this to extort ransom or create chaos for political or ideological motives.
3.IoT Risk: Many healthcare organizations are using IoT, and there are a large number of unmanaged IoT devices connected to the network. Each of these IoT devices is an entry point for hackers, making almost every hospital vulnerable to cyberattacks.
4. Vulnerable points in Legacy Systems: Many healthcare systems rely on legacy technology, which may lack robust cyber security measures. These outdated systems can be more vulnerable to exploitation, making them attractive targets.
5. Limited resources IT: Healthcare institutions often have limited resources for cybersecurity, both in terms of budget and expertise. This makes them attractive targets as they may have weaker defenses compared to other industries.
6. High Expectations, Low Tolerance: The nature of healthcare means that any interruption can have immediate and life-threatening consequences. Cybercriminals can take advantage of this urgency, knowing that healthcare providers are more likely to pay ransoms quickly to restore critical services.
7. Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: The healthcare ecosystem comprises various interconnected entities including pharmaceutical companies, medical device manufacturers and insurance providers. Cyber attackers may exploit vulnerabilities in these interconnected systems to gain access to sensitive healthcare data.
8. Global health concerns: Events such as global health crises or pandemics can create a sense of urgency and distraction, providing cover for cybercriminals to carry out attacks when attention is focused elsewhere.
Total Attacks by Region: APAC saw significant growth of 15% year-on-year
During 2023 so far, the Africa experienced the highest average number of weekly cyberattacks per organization, on average 1987 attacks. This means an annual increase 6% compared to the same period in 2022. The region APAC also saw a significant increase Present in several = 15% on an annual basis to the average number of weekly attacks per organization, reaching an average of 1963 attacks.
|
Africa |
1987 |
+ 6 % |
|
APAC |
1963 |
+ 15 % |
|
Latin America |
1663 |
+ 0.4 % |
|
Europe |
966 |
-1% |
|
North America |
939 |
+ 5 % |
1 in 34 organizations worldwide experienced an attempted ransomware attack
In 2023 so far, every week on average 1 to 34 organizations worldwide faced attempted ransomware attack, representing an increase 4% compared to the same period last year.
The organizations in Africa and Latin America were most affected by attempted ransomware attacks, with 1 to 19 organizations on average face such an attack every week.
North America showed the largest increase compared to last year with Present in several = 25% compared to the same period in 2022.
|
Latin America |
1 19 out of |
+ 22 % |
|
Africa |
1 19 out of |
+ 7 % |
|
APAC |
1 20 out of |
-8% |
|
Europe |
1 47 out of |
+ 0.3 % |
|
North America |
1 69 out of |
+ 25 % |
Global ransomware attacks by industry:
In 2023 so far, the government/military domain experienced the highest number of ransomware attacks, with 1 to 24 organizations to be affected, noting 11% reduction compared to the previous year. The health care sector was the second most affected, with 1 to 25 organizations to counter such attacks by representing increase 3% on an annual basis. With a similar increase from last year, the sector of Education / Research followed far behind as o3 sector most affected globally, with 1 to 27 organizations to be affected by attempted ransomware attacks.
It is also important to note that many of the top industries affected include critical infrastructure and services, including the of public utility services, who ranks 6thposition, but has a dramatic increase Present in several = 26% on the impact of Ransomware in the past year.
|
Government/Military |
1 24 out of |
-11% |
|
Healthcare Logistics |
1 25 out of |
+ 3 % |
|
Education/Research |
1 27 out of |
+ 3 % |
|
Finance/Banking |
1 29 out of |
+ 15 % |
|
ISP / MSP |
1 33 out of |
-9% |
|
Utilities |
1 34 out of |
+ 26 % |
|
Communications |
1 35 out of |
+ 4 % |
|
Consultant |
1 38 out of |
+ 45 % |
|
SI/VAR/Distributor |
1 42 out of |
-2% |
|
Transportation |
1 46 out of |
+ 22 % |
|
Manufacturing |
1 47 out of |
-14% |
|
Retail/Wholesale |
1 48 out of |
-1% |
|
Leisure/Hospitality |
1 48 out of |
+ 16 % |
|
Insurance/Legal |
1 49 out of |
+ 22 % |
|
Software vendors |
1 62 out of |
-3% |
|
Hardware vendor |
1 65 out of |
+ 17 % |
Ransomware continues to grow for several interrelated reasons:
1. Profitable business model: Ransomware has proven to be a profitable business for cybercriminals. The ability to extort money from individuals, businesses or even governments fuels its growth. The relative anonymity provided by cryptocurrencies makes it easy for attackers to receive payments without being detected.
2. Advanced techniques: The criminals of cyberspace are constantly evolving their techniques. Using advanced tactics such as leveraging zero-day vulnerabilities and using social engineerings, allows them to bypass traditional security measures.
3. Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS): The Rise of Ransomware-as-a-Service Platforms it makes it easy for even the least skilled people to carry out ransomware attacks. This plug-and-play model provides malicious tools and infrastructure, lowering the barrier to entry for would-be cybercriminals.
4. Exploitation of weak hygiene Cyber: Many organizations, especially smaller ones, may have inadequate cyber security measures in place. Exploiting weak passwords, unpatched systems, and inadequate employee training provide avenues for ransomware attackers to gain entry.
5. Targeting infrastructure critical: Cybercriminals are increasingly targeting critical infrastructure, including healthcare, energy and transportation. These sectors are more likely to pay ransoms quickly to avoid disruptions that could have serious consequences.
6. Insufficient regulation: In some regions, cybersecurity regulations and laws are not strong enough to effectively deter attackers. This lack of consequences further encourages cybercriminals.
7. Anonymity Cryptocurrencies: Using cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin for ransom payments provides a level of anonymity that traditional banking systems lack. This facilitates the financial transactions necessary for ransomware operations without easy traceability.
Practical tips: preventing ransomware and other attacks
Cyber Awareness Training
Email messages "fishing” is one of the most popular ways to spread ransomware malware. By tricking a user into clicking a link or opening a malicious attachment, cybercriminals gain access to the employee's computer and begin the process of installing and running ransomware on it. Frequent cyber awareness training is vital to protecting the organization from ransomware, leveraging its own staff as the first line of defense to ensure a protected environment. This training should instruct employees on the classic signs and language used in phishing emails.
Updated patches
Computer update and application security patches, especially those marked as critical, can help limit an organization's vulnerability to ransomware attacks, as such patches are often overlooked or too late to provide the required protection
Use better threat prevention
Most ransomware attacks can be detected and resolved before it's too late. You must have automated threat detection and prevention in your organization to maximize your chances of protection, including email scanning and monitoring, and file activity scanning and monitoring for suspicious files.
Artificial intelligence has become an indispensable ally in the fight against cyber threats. By augmenting human expertise and strengthening defensive measures, AI-based cybersecurity solutions provide a strong shield against a vast array of attacks. As cybercriminals continually improve their tactics, the symbiotic relationship between AI and
Cyber security will undoubtedly be vital to securing our digital future.
Anti-Ransomware Solutions
The solutions Anti-ransomware monitors the programs running on a computer for suspicious behaviors commonly seen by ransomware, and if these behaviors are detected, the program can take action to stop the encryption before it goes any further damage.
Powerful data backup
His goal ransomware is to force the victim to pay a ransom to regain access to their encrypted data. However, this is only effective if the target actually loses access to its data. A robust, secure data backup solution is an effective way to mitigate the impact of a ransomware attack.





