See how you can check the read and write speed of your SSD drive with the Winsat command in Windows.

An SSD disk offers better performance and speeds compared to a conventional hard disk drive (HDD). So an SSD boosts a computer's performance, especially if the operating system is placed on top of it, but its speed can also vary in different scenarios.
If you have a Windows PC we will show you how to run a performance test of your SSD with the Winsat Command Line command. Alternatively we will talk to you about the portable program CrystalDiskMark.
Winsat command
Windows computers have a built-in disk speed test tool under the Command Prompt. It's the Winsat utility which you can run from a command prompt window with administrative privileges.
step 1 : Open a command prompt window with administrative privileges. If you don't know how, press the Win + X keys at the same time and select “Command Prompt (Admin)”.
step 2 : Type the following command for specific disk you want to measure its speed and then press Enter:
winsat disk -drive c
The above command will take some time to execute completely. After its completion implementations, you will see them Results of C drive speed test like this:
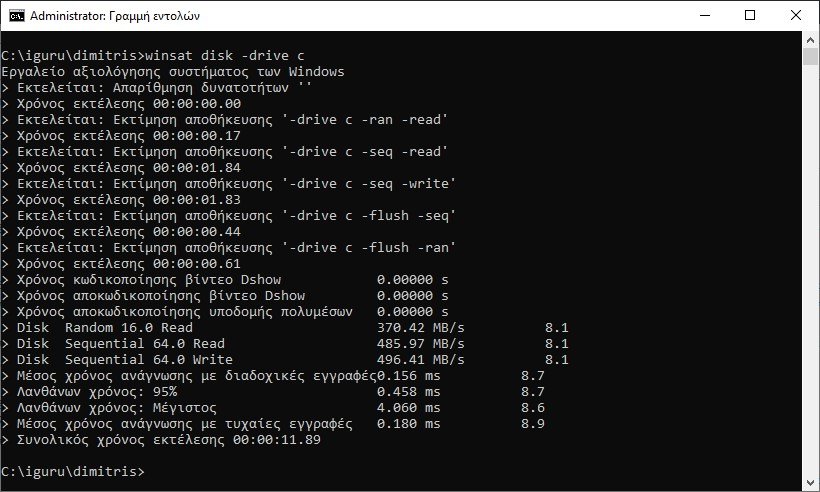
The command measures the performance of the ssd disk using one of three types of evaluation:
- Evaluation of sequential or random reading speed.
- Evaluation of sequential or random write speed.
- Disk performance evaluation with flush write mode.
Other parameters of Winsat
The Winsat command essentially evaluates the individual components of your machine. In addition to your disks, it can also inform you about other parts, such as memory, CPU, etc. See a list of the parameters it can accept:
- winsat dwm = Evaluates a system's ability to display Aero desktop effects.
- winsat d3d = Evaluates a system's ability to run Direct 3D applications such as games.
- winsat meme = Evaluates system memory bandwidth by simulating large memory in memory buffer copies.
- winsat disc = Evaluates the performance of disk drives.
- winsat cpu = Evaluates the performance of the CPU(s).
- winsat media = Evaluates the performance of video encoding and decoding (playback) using Direct Show.
- winsat mfmedia = Evaluates video decoding (playback) performance using Media Foundation.
- winsat features = Lists related information of the system.
- winsat formal = Runs a set of predefined evaluations and stores the data in an XML file in %systemroot%\performance\winsat\datastore .
CrystalDiskMark
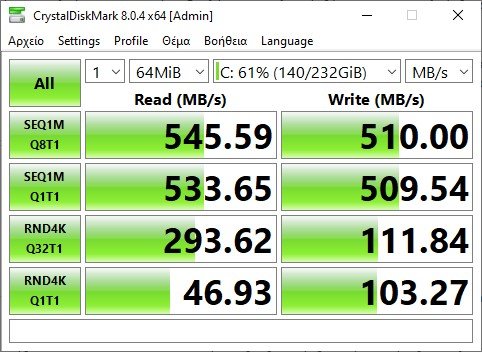
Alternatively you can use the CrystalDiskMark program. It is a hard drive benchmarking tool that runs different tests on your hard drive to check its performance and speed.
Could you download from its official website. It has a simple user interface and is easy to use. This tool requires administrator rights to check SSD speed. Hence, start it as Admin.
For an SSD, it offers the following four types of test parameters:
- SEQ1M Q8T1
- SEQ1M Q32T1
- RND4K Q32T1
- RND4K Q1T1
CrystalDiskMark runs two types of disk tests, sequential and random. In the above parameters, SEQ indicates Sequential testing and RND indicates Random testing.
All test parameters are different. For example, SEQ1M Q8T1 means a sequential test with a block size of 1 MiB, a Queue depth of 8, and 1 Thread. RND4K Q32T1 stands for Random Test with 4 KiB block size, 32 queue depth and 1 thread.
Evaluation and further actions

You can compare your test results with the exact speed of the SSD as stated by the manufacturer. If there is a noticeable difference between the speeds, it may not be the drive's fault, but your SSD may need to be optimized.
First above all, the disk should not be full. If you keep a lot of data on your SSD, it will slow down its performance. Free up space on your SSD by deleting unnecessary files.
Secondly check whether the TRIM command is enabled or not. If the TRIM command is enabled, Windows sends an instruction to your SSD every time you delete a file which tells the SSD to perform a background cleanup called “reclaim” that helps them prepare for the next writes. Enable the TRIM command if it is not enabled.
Third keep your SSD firmware up to date.