Two hackers gained access to thousands of Google Chromecasts by sending their owners a prenotice for the security hole.

In their warning message they state that Chromecast devices can be hijacked by hackers and remotely force them to play any video of YouTube they wish
Google's Chromecast is an internet device that connects to your TV and makes it smart. That is, it brings the internet to your TV. The error CastHack, which hackers used to breach thousands of Chromecasts, exploits a weakness in the Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) networking standard.
The two hackers, who use the nicknames HackerGiraffe and J3ws3r, in addition to warning about error on Chromecast devices, encouraged device owners to sign up for YouTuber PewDiePie.
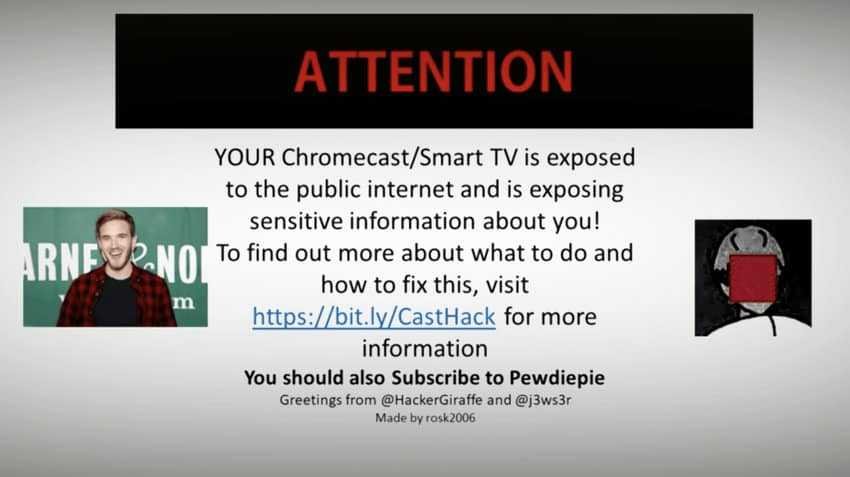
If any of the above names remind you of something it's because HackerGiraffe is the one who last month violated about 50.000 printers worldwide, making them print a message that encouraged owners to sign up for the channel of PewDiePie, so as to maintain its position on the platform as the channel with the largest audience.
Google has announced that the issue is not actually a Chromecast flaw, but rather a flaw that affects routers in general. In addition, the problem can be addressed with the apactivation of UPnP on your router. Still, it's worrying to know that an attacker could be messing around with your Netflix at any time.
Of course, this is not the first time there has been an issue with the Chromecast. There were bugs that allowed hacking in both 2014 and 2016. Since these devices are used by both adults and children, Google has not been able to secure them and prevent unauthorized access by malicious hackers.





