A performance test by Tom's Hardware showed that BitLocker slowed down SSD drives on Windows 11 Pro by 45%.

BitLocker is one technology Microsoft encryption and is available in Windows 10 Pro and Windows 11 Pro. Although it is normally disabled by default and ready to use whenever you want it, on some devices with Windows 11 Pro it was enabled by itself during the installation of the operating system.
There are ways to prevent its automatic installation, such as to use Rufus, but this is not an official solution as it allows users to bypass Microsoft's intent. Windows administrators can also enable BitLocker after installation.
BitLocker encryption can use hardware (opal) or software encryption. Hardware encryption means that the SSD chip does the heavy lifting when it comes to encryption processes. Software encryption, on the other hand, pushes the workload to the device's processor.
Tests and results
Tom's Hardware reviewed Bitlocker performance using a Samsung 990 Pro 4 TB drive on a Windows 11 Pro system. The system was powered by an Intel Core i9-12900K processor with 32 GB μνήμηs DDR4.
Hardware encryption and no encryption had similar results in PCMark 10 Storage. Tom's Hardware notes that in tests, the hardware encryption fared slightly better than the unencrypted drive. What is worrying is that the performance of the encrypted software drive dropped significantly during testing.
Tests in other benchmarking applications, Crystal Disk Mark, DiskBench, Atto Disk Benchmark and others confirmed the problem. Testers conclude that BitLocker with software encryption can significantly affect the performance of encrypted drives in Windows 11 Pro.
See if you have BitLocker enabled
The first thing Windows 11 Pro users may want to do is check if BitLocker is enabled on their devices. This can be done with a single command from a line orders:
- Open a command prompt (or Windows Terminal) with administrator rights.
- Write the command
manage-bde -statusand press key Enter.
The command will tell you status for all connected volumes.
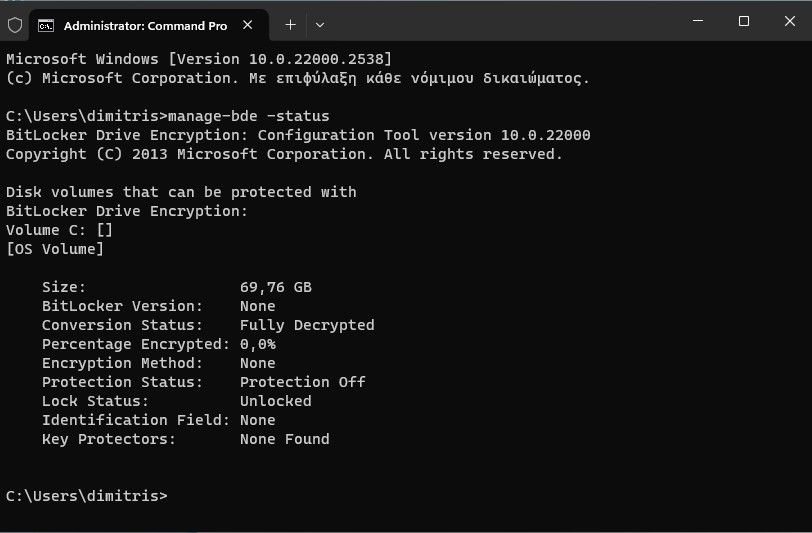
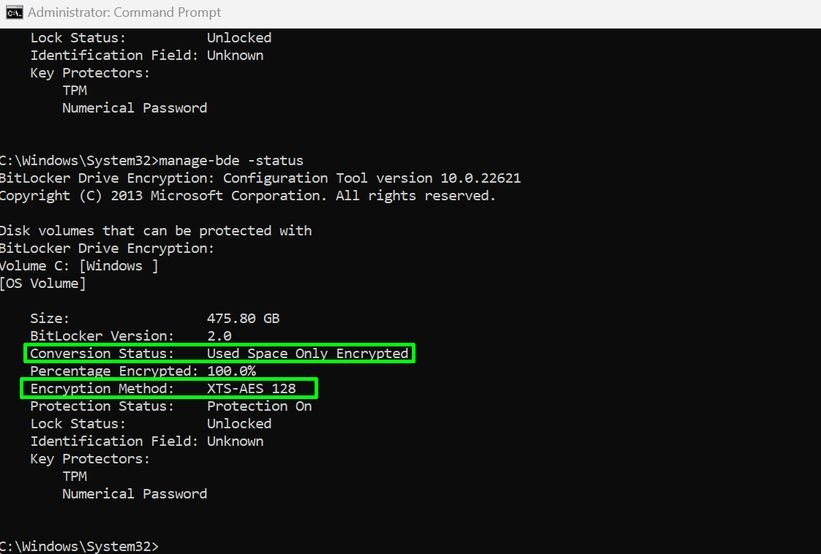
Protection Status tells you whether BitLocker encryption is enabled (On) or not (Off). If enabled, check the encryption method used. If you see “XTS-AES” there, then software encryption is used.
How to disable BitLocker encryption
Switching to hardware BitLocker encryption may be out of the question for most Windows 11 Pro users, as it requires reinstalling Windows 11 Pro.
To disable BitLocker on a drive, run the command management-bde off C: in a command prompt window with administrative privileges. Note that you may need to replace the C drive letter in the command with another drive letter, depending on the setup.
Disabling encryption leaves the data unencrypted on the drive. If you had reason for it to be encrypted, it is recommended that you use other encryption software to secure it again.
Need SSD encryption?
Encrypting the storage drive provides great protection against theft, so it's especially useful for laptops. If a thief gets hold of your computer and can't otherwise boot into Windows, they can remove your SSD, plug it into another computer, and try to read the data on it.
If the drive is encrypted and the thief does not have the encryption key, he cannot read the drive. If it's not encrypted, then they can use any SSD case to turn it into an external storage drive and gain full access to your files.
If you work with a desktop computer in your home and feel really confident that no one will have unauthorized physical access to the computer, you might want to do it without encryption.





