It is possible for a Windows machine not to want its users to be able to launch some applications or want the machine to run only specific applications. Reasons may be either a security issue, or because the computer belongs to a workspace, etc. Windows gives you this setting through a registry. Let's see how.

Before proceeding with the next steps, you should be very careful with who and for whom you are blocking them. There is a possibility to block yourself from various tools Windowssuch as processing a registry and editing a local group policy, resulting in you being without the administrator's rights. If you accidentally do so, the only way to reverse the changes is to perform System Restore. For this reason, we recommend that before you do anything you can first create a restore point for each event.
Block a user from launching specific applications by editing the registry
To block a user from certain applications by modifying the Windows registry, you must log in to your machine with the user name you want to make the changes, and then edit the registry while logged into your account. If you have multiple users for whom you want to make changes, you must repeat the process for each user.
Step 1: Log in to Windows with the user account you want to make the changes.
Step 2: Ανοίξτε τον Επεξεργαστή Μητρώου. Αν δεν ξέρετε πως τότε πατήστε ταυτόχρονα τα πλήκτρα Win + R και στο παράθυρο "Εκτέλεσης" που να εμφανιστεί γράψτε την λέξη "regedit" και πατήστε το πλήκτρο ΟΚ.
Step 3: Αν ερωτηθείτε να επιτρέψετε σε αυτήν την εφαρμογή να κάνει αλλαγές στην συσκευή σας, πείτε του "Ναι"
Step 4: In the registry editor, navigate to the following key:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER \ SOFTWARE \ Microsoft \ Windows \ CurrentVersion \ Policies
Step 5: In Policies, create a new subkey called Explorer. If you do not know how, right-click in the right pane and select Create> Key. If the key already exists simply ignore this step.
Step 6: Μέσα στο νέο κλειδί "Explorer" δημιουργήστε μια τιμή DWORD (32 bit) με το όνομα DisallowRun. Αν δεν ξέρετε πως, κάντε δεξί κλικ στο δεξί παράθυρο και πηγαίνετε στο Δημιουργία > Τιμή DWORD (32 bit). Επιλέξτε το 32 bit ακόμα και αν τρέχετε 64 bit Windows.
Step 7: Κάντε διπλό κλικ στη νέα τιμή DisallowRun για να ανοίξει ο διάλογος με τις ιδιότητές της. Αλλάξτε την τιμή στο πλαίσιο "Δεδομένα τιμής" από 0 σε 1 και στη συνέχεια, κάντε κλικ στο "OK".
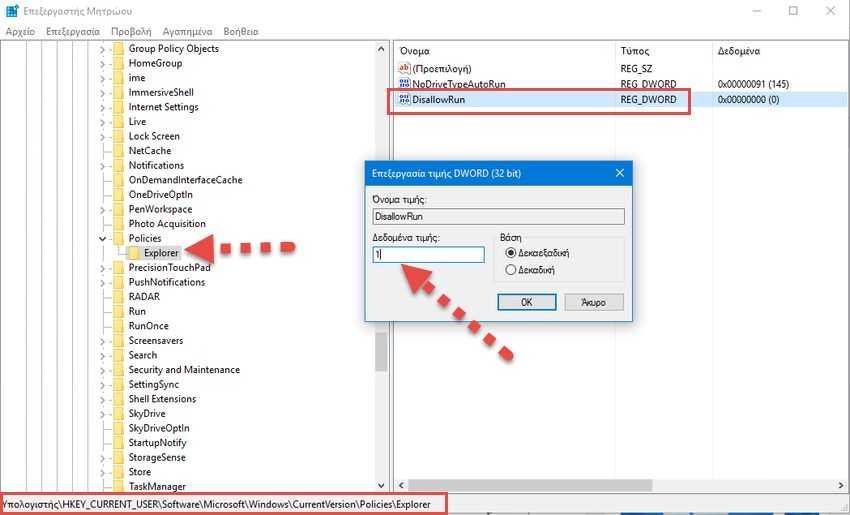
Step 8: Return back to the Explorer key and create a new key (a key rather than a DWORD value) named DisallowRun (same name as the previous DWORD value).
Step 9: Τώρα ήρθε η ώρα να αρχίσετε να προσθέτετε τις εφαρμογές που θέλετε να αποκλείσετε. Αυτό γίνεται με τη δημιουργία μιας νέας "τιμής συμβολοσειράς" μέσα στο κλειδί DisallowRun για κάθε εφαρμογή που θέλετε να αποκλείσετε. Κάντε δεξί κλικ στο κλειδί DisallowRun και στη συνέχεια επιλέξτε Δημιουργία > Τιμή Συμβολοσειράς. Ονομάστε αυτές τις τιμές με απλούς αριθμούς, έτσι ώστε το όνομα της πρώτης τιμής που δημιουργείτε να είναι το "1", μετά το "2" και ούτω κάθε εξής.
Step 10: Double-click the new value (the one named 1) to open its edit window and type in the value data the name of the executable archiveυ που θέλετε να αποκλείσετε (π.χ., calc.exe ), και στη συνέχεια κάντε κλικ στο κουμπί "OK".
Step 11: Επαναλάβετε αυτή τη διαδικασία των βημάτων 9 και 10, ονομάζοντας την δεύτερη τιμή συμβολοσειράς "2", την τρίτη "3" και ούτω καθεξής, και στη συνέχεια προσθέτοντας τα ονόματα των εκτελέσιμων αρχείων που θέλετε να αποκλείσετε στα δεδομένα τιμής κάθε συμβολοσειράς.
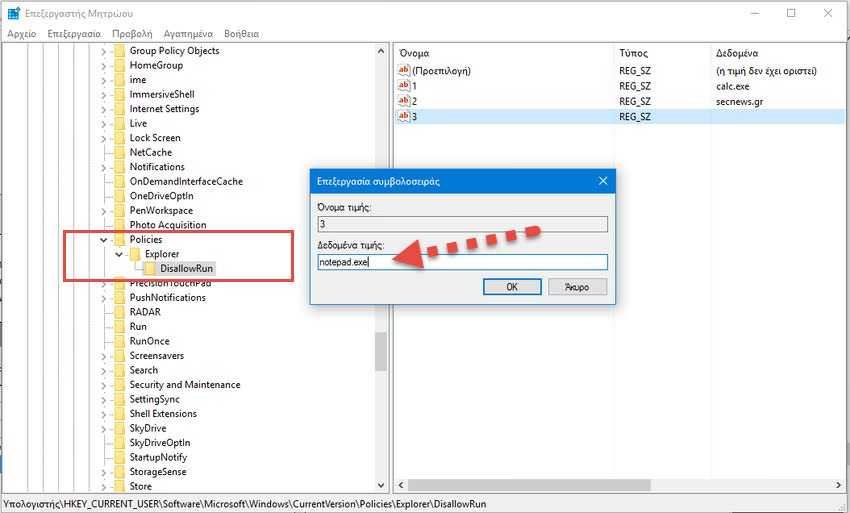
Step 12: When finished, quit the registry editor (the changes will be automatically saved) and restart Windows. Sign in to that user account and try to run each of these applications. You should see a pop-up restriction window that will let you know that you can not run the application.
Repeat all the above steps for each user account for which you should block apps. However, if you block out the same applications for multiple user accounts, you could export the DisallowRun key that you created and configured the first user account, and then import it into each subsequent account.
If you want to restore access to all applications, you can either delete the entire Explorer key that you created, along with a DisallowRun subkey as well as all values. Or you could just go back and change the value of the DisallowRun value you created from 1 to 0, leaving the list of apps in the registry in case you want to activate it again in the future.
Allow a user to only start some applications by editing the registry
In relation to the first section of this article, the second section will show you how to block ALL applications from a particular user and allow it to access only certain applications that you set them by editing the registry.
Access to specific applications follows almost exactly the same procedure as module one.
Step 1: Log in to Windows using the user account you want to change.
Step 2: Ανοίξτε τον Επεξεργαστή Μητρώου. Αν δεν ξέρετε πως, τότε πατήστε ταυτόχρονα τα πλήκτρα Win + R και στο παράθυρο "Εκτέλεσης" που να εμφανιστεί γράψτε την λέξη "regedit" και πατήστε το πλήκτρο ΟΚ.
Step 3: Αν ερωτηθείτε να επιτρέψετε σε αυτήν την εφαρμογή να κάνει αλλαγές στην συσκευή σας πείτε του "Ναι"
Step 4: In the registry editor, navigate to the following key:
HKEY_CURRENT_USER \ SOFTWARE \ Microsoft \ Windows \ CurrentVersion \ Policies
Step 5: In Policies, create a new subkey called Explorer. If you do not know how, right-click in the right pane and select Create> Key. If the key already exists simply ignore this step.
Step 6: Μέσα στο νέο κλειδί "Explorer" δημιουργήστε μια τιμή DWORD (32 bit) με το όνομα RestrictRun. Αν δεν ξέρετε πως, κάντε δεξί κλικ στο δεξί παράθυρο και πηγαίνετε στο Δημιουργία > Τιμή DWORD (32 bit). Επιλέξτε το 32 bit ακόμα και αν τρέχετε 64 bit Windows.
Step 7: Κάντε διπλό κλικ στη νέα τιμή RestrictRun για να ανοίξει ο διάλογος με τις ιδιότητές της. Αλλάξτε την τιμή στο πλαίσιο "Δεδομένα τιμής" από 0 σε 1 και στη συνέχεια, κάντε κλικ στο "OK".
Step 8: Return back to the Explorer key and create a new key (a key rather than a DWORD value) named RestrictRun (same name as the previous DWORD value).
Step 9: Now it's time to start adding the apps that the user will be able to access. Αυτό γίνεται με τη δημιουργία μιας νέας "τιμής συμβολοσειράς" μέσα στο κλειδί RestrictRun για κάθε εφαρμογή που θέλετε να δώσετε πρόσβαση. Κάντε δεξί κλικ στο κλειδί RestrictRun και στη συνέχεια επιλέξτε Δημιουργία > Τιμή Συμβολοσειράς. Ονομάστε αυτές τις τιμές με απλούς αριθμούς, έτσι ώστε το όνομα της πρώτης τιμής που δημιουργείτε να είναι το "1", μετά το "2" και ούτω κάθε εξής.
Step 10: Κάντε διπλό κλικ στη νέα τιμή (αυτή με την ονομασία 1) για να ανοίξει το παράθυρο επεξεργασία της και πληκτρολογήστε στα δεδομένα τιμής το όνομα του εκτελέσιμου αρχείου που θέλετε να δώσετε πρόσβαση (π.χ., notepad.exe ), και στη συνέχεια κάντε κλικ στο κουμπί "OK".
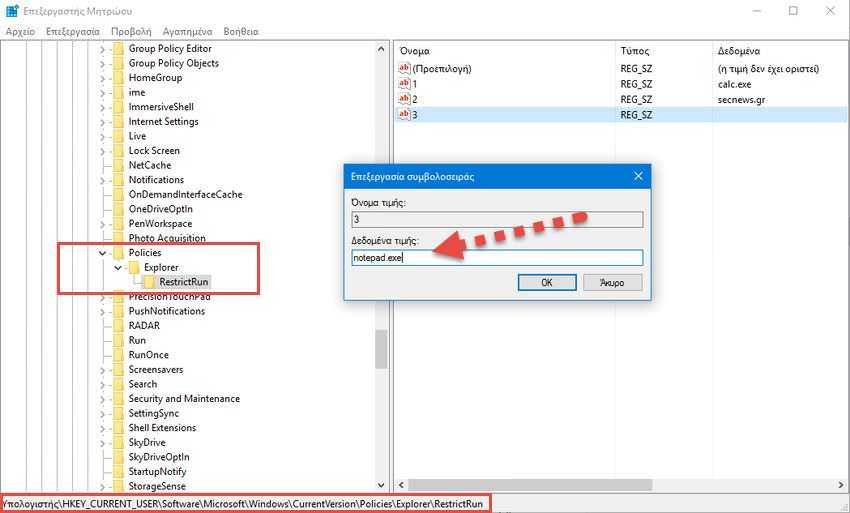
Step 11: Επαναλάβετε αυτή τη διαδικασία των βημάτων 9 και 10, ονομάζοντας την δεύτερη τιμή συμβολοσειράς "2", την τρίτη "3" και ούτω καθεξής, και στη συνέχεια προσθέτοντας τα ονόματα των εκτελέσιμων αρχείων που θέλετε ο χρήστης να έχει πρόσβαση, στα δεδομένα τιμής κάθε συμβολοσειράς.
Step 12: When finished, quit the registry editor (the changes will be automatically saved) and restart Windows. Log in to this specific user account and test if you can run each of these apps as well as another one you did not specify in step 11. It should be able to execute ONLY the applications you have assigned to it and in the others to see a pop-up restriction window that will let you know that you can not run the application.
You will need to repeat the process with each user account that you only want to access to certain applications. But if you have to do the same work on multiple user accounts, you could export the RestrictRun key that you created and configured the first user account and then import it into each subsequent account.
If you want to restore access to all applications, you can either delete the entire Explorer key that you created, along with a RestrictRun subkey and all values. Or you could just go back and change the value of the RestrictRun value you created from 1 to 0, leaving the list of applications in the registry in case you want to re-enable it in the future.
Windows Pro and Enterprise: Block applications with the local group policy editor
If you use the Windows Pro or Enterprise versions, you can block access to specific applications to a user in a much easier way by using the Local Group Policy Editor. A big advantage is that you can apply the policy settings to other users, or even user groups, without having to log in as each user individually to make changes for that user.
The caveat here is that you'll need to do a little extra setup first by creating a policy object for the users. You can read all about that in our guide to applying local group policy tweaks to specific users. You should also know that the political group is a very powerful one tool, so it's worth spending some time learning what it can do.
Also, if you are on a network for example your company, check the changes you want to make with your administrator first. If your work computer is part of a domain, then it is most likely that it is part of a domain group policy that has replaced the local group policy anyway.
The process to allow or restrict some applications through the local group policy editor is almost identical, so we'll show you how to restrict users from running only some apps by pointing out the differences for the second case.
Step 1: Sign in to Windows with any user account you want.
Step 2: Ανοίξτε τον Επεξεργαστή πολιτικής τοπικής ομάδος. Αν δεν ξέρετε πως, τότε πατήστε ταυτόχρονα τα πλήκτρα Win + R και στο παράθυρο "Εκτέλεσης" που να εμφανιστεί ράψτε την λέξη "gpedit.msc" και πατήστε το πλήκτρο ΟΚ.
Step 3: Αν ερωτηθείτε να επιτρέψετε σε αυτήν την εφαρμογή να κάνει αλλαγές στην συσκευή σας πείτε του "Ναι"
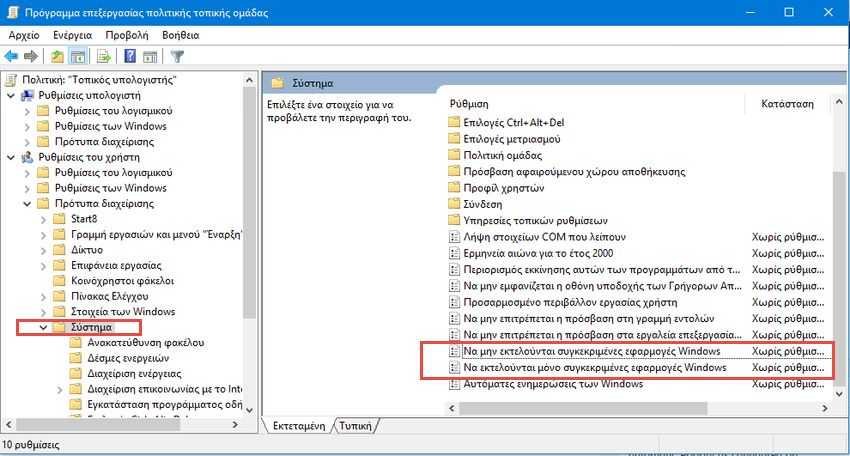
Step 4: Για λόγους ασφαλείας στο παράδειγμά μας θα αλλάξουμε την πολιτική περιορισμούς εφαρμογών σε όλους τους μη administrator λογαριασμούς χρηστών. Στο αριστερό παράθυρο Πολιτική¨"Τοπικός υπολογιστής", πλοηγηθείτε στο Ρυθμίσεις του χρήστη > Πρότυπα managements > System.
Step 5: Στο δεξί παράθυρο βρείτε τη ρύθμιση "Να μην εκτελούνται μόνο συγκεκριμένες εφαρμογές των Windows" και κάντε διπλό κλικ επάνω του για να ανοίξει το παράθυρο των ιδιοτήτων του. Αν θέλετε να αποκλείσετε ΟΛΕΣ τις εφαρμογές και να επιτρέψετε μόνο συγκεκριμένες να εκτελούνται ανοίξτε το "Να εκτελούνται μόνο συγκεκριμένες εφαρμογές των Windows" αντ 'αυτού.
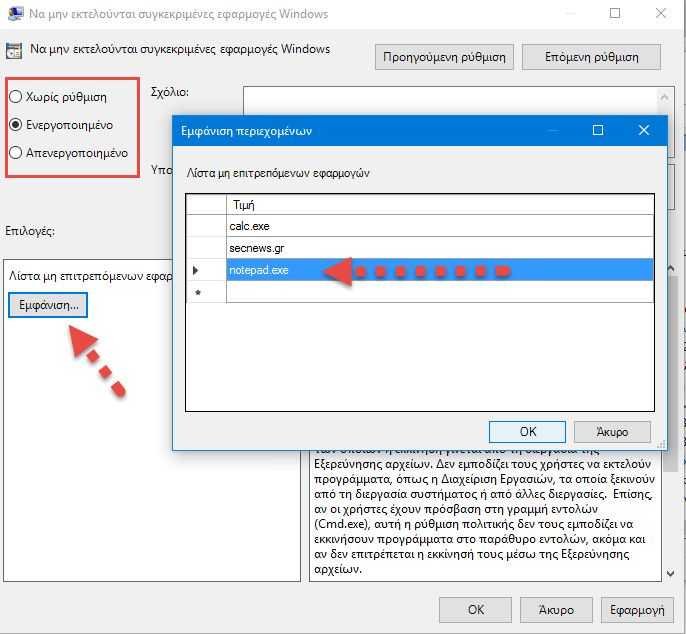
Step 6: Στο παράθυρο ιδιοτήτων που μόλις άνοιξε, κάντε κλικ στην επιλογή "Ενεργοποιημένο" και στη συνέχεια κάντε κλικ στο κουμπί "Εμφάνιση".
Step 7: Στο νέο παράθυρο "Εμφάνιση Περιεχομένων", κάντε κλικ σε κάθε γραμμή στη λίστα και πληκτρολογήστε το όνομα του excecutable αρχείου που δεν θέλετε οι χρήστες να είναι σε θέση να τρέξουν (ή το όνομα των εφαρμογών που θέλετε να τρέξουν αν ρυθμίζετε την δεύτερη επιλογή). Όταν τελειώσετε την συμπλήρωση της λίστας σας, κάντε κλικ στο "OK".
Step 8: Exit the Local Group Policy window. To check your changes, sign in with one of the affected user accounts and try to start an application that the user will not be able to access. Instead of starting the application, you should see an error message.
Αν θέλετε να απενεργοποιήσετε τις αλλαγές σας, απλά ανοίξτε ξανά τον επεξεργαστή πολιτικής τοπικής ομάδος, πηγαίνετε στην ρύθμιση που "πειράξατε" προηγουμένως και επιλέξτε την επιλογή "Απενεργοποιημένο" ή την "Χωρίς ρύθμιση". Κάντε κλικ στο πλήκτρο ΟΚ και τα Windows θα επανέλθουν στη πρωτύτερη κατάσταση. Ο κατάλογος με τις εφαρμογές έχει παραμείνει στο υπομενού και έτσι μπορείτε να απαγορεύσετε εκ νέου την πρόσβαση όποτε το θελήσετε.





